Cybersecurity has shifted from a technical concern to a global economic and security priority. Threat actors now exploit digital transformation, remote work, and AI tools to launch more frequent, costly, and sophisticated attacks. Organizations across industries face escalating risks, from breaches that erode customer trust to ransomware attacks that halt operations. For example, global cybercrime is projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually, surpassing the GDP of many nations, while businesses face multiple attacks every single day.
These trends influence boardroom agendas in sectors such as healthcare and finance, where data breaches can translate into millions in losses and regulatory scrutiny. Later sections of this article break down the latest figures, threat types, and what they mean for organizations worldwide, inviting readers to explore the full analysis.
Editor’s Choice
- $10.5 trillion is the estimated global cost of cybercrime in 2025, up sharply from previous years.
- 600 million attacks per day were recorded in 2024 across malware, phishing, and identity attacks.
- Ransomware accounted for about 24% of breaches worldwide in 2025, remaining one of the most damaging attack types.
- A cyberattack occurs every 39 seconds, based on U.S. cybercrime complaint data.
- 75% of SaaS incidents involved compromised credentials in 2025.
- The global average data breach cost reached $4.44 million in 2025.
- 68% of breaches stemmed from human error or human-related factors.
Recent Developments
- In December 2025, over 200 million user records were exposed in a high-profile data breach targeting a major entertainment platform.
- Denmark attributed two major disruptive cyberattacks to a pro-Russian hacking group, emphasizing state-linked threats.
- Iranian-linked cyberoperations intensified, targeting political figures and institutional data leaks.
- Global cyber threats continued rising through 2025, with new records in attack sophistication and stealth techniques.
- Supply chain and third-party systems remain a vector for cascading compromise in multinational operations.
- AI adoption in cyberattacks, including automated phishing and deepfake infiltration, has increased threat complexity.
- Shifts in geopolitical tensions were mirrored in cyber campaigns targeting critical national infrastructure and utilities.
- Organizations accelerated cyber defense investments, yet gaps in governance and skilled talent persist.
Global Cyber Threat Overview
- 72% of organizations report that cyber risk increased over the past year.
- By 2025, global cybercrime costs are expected to exceed $10.5 trillion annually.
- Threat actors increasingly adopt AI-enhanced techniques for malware-free attacks and social engineering.
- Major firms face malware-free detections in nearly 80% of monitored threats.
- Nation-state activity and hybrid warfare tactics contribute to elevated global cyber tensions.
- Interconnected digital ecosystems expand attack surfaces across multiple industries.
- Organizations struggle to scale defenses against zero-day exploits and credential abuse.
- Limited cross-border cybercrime cooperation complicates global mitigation efforts.
Worldwide Breakdown of Cybersecurity Threat Sources by Nation
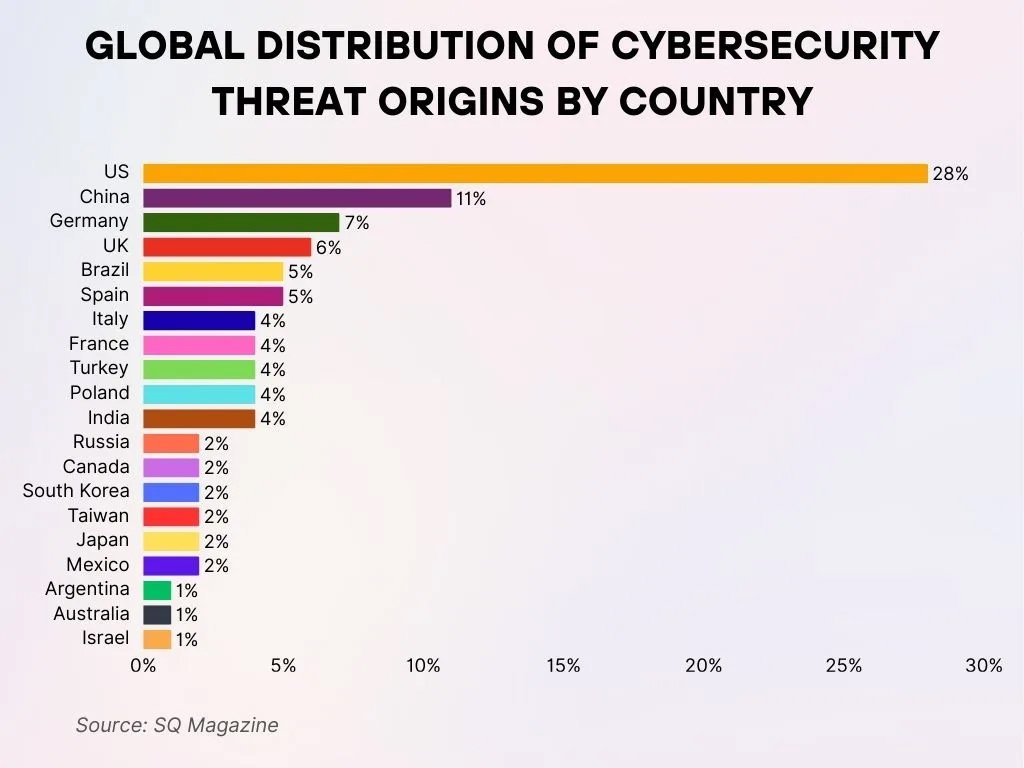
- The United States dominates by a wide margin, contributing 28% of global cybersecurity threats worldwide.
- China holds the second position with 11%, underscoring its significant role in the global cyber threat environment.
- Germany accounts for 7%, making it the largest contributor in Europe to overall cyberattack origins.
- The United Kingdom comes next with 6%, continuing to stand out as a major source of cyber threats.
- Brazil and Spain each contribute 5%, signaling increasing cyber activity across Latin America and Europe.
- Italy, France, Turkey, Poland, and India are evenly matched at 4% each, reflecting a shared level of cyber threat contribution.
- Russia, Canada, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, and Mexico each report 2%, indicating moderate but notable involvement in cyber incidents.
- Argentina, Australia, and Israel each account for 1%, representing a smaller yet measurable share of global cyber threats.
Cost of Cyber Attacks Worldwide
- The average global data breach cost was $4.44 million in 2025, slightly lower than in 2024.
- U.S. breach costs remained significantly higher, averaging over $10 million per incident.
- Ransomware and extortion breaches cost organizations $5.08 million on average in 2025.
- Data breaches added roughly $1.3 million in lost business costs.
- Breach identification and containment lifecycles averaged 241 days.
- Security AI implementation reduced average breach costs by 34%.
- Small companies faced an average breach cost of $3.31 million in 2024.
- Global cybercrime damages include direct losses, recovery expenses, and reputational harm totaling trillions.
Most Common Types of Cyber Threats
- Phishing accounts for 36% of all data breaches as the leading cyber threat.
- 3.4 billion phishing emails flood inboxes daily worldwide.
- Ransomware strikes 44% of data breaches in 2025.
- 43% of organizations faced ransomware attacks in 2025.
- Business Email Compromise fuels 12% of global cyber incidents.
- Credential theft incidents skyrocketed by 160% in 2025.
- Malware dominates with ransomware at 34% of all infections.
- Supply chain attacks enable 22% banking trojan prevalence.
Cyber Threats Are Escalating at an Alarming Rate
- Cybersecurity threats are increasing rapidly, with both ransomware and crypto-based attacks posing significant risks to organizations worldwide.
- An estimated 30,000 websites are compromised every day globally, highlighting the scale and persistence of modern cyberattacks.
- Cryptojacking incidents have surged by 659%, making unauthorized cryptocurrency mining one of the fastest-growing attack vectors.
- Ransomware attacks targeting Industrial Control Systems (ICS) have increased by 20%, raising serious concerns for critical infrastructure and operational technology environments.
- These trends indicate a broader shift toward more automated, financially motivated attacks, impacting businesses across all industries.
- Data cited from Astra Security, SonicWall, and Kaspersky underscores the credibility and severity of these findings.

Ransomware Attack Statistics
- Ransomware victims averaged 520 to 540 per month by mid-2025.
- Global projections estimate 11,000 ransomware attempts per day by late 2025.
- 43–47% of organizations experienced a ransomware incident.
- Phishing remains a leading ransomware delivery method.
- Ransomware was linked to 75% of system intrusion cases.
- Double and triple extortion tactics increased in prevalence.
- Supply chain and zero-day vulnerabilities amplify ransomware reach.
- Healthcare, education, and mid-sized firms remain prime targets.
Phishing and Social Engineering Statistics
- Phishing accounted for 36% of all breaches.
- 3.4 billion phishing emails circulate daily.
- Advanced spear phishing continues to rise in sophistication.
- Infostealers delivered via phishing increased 84% year over year.
- Human error keeps social engineering effective.
- Younger workers show higher susceptibility to social engineering.
- Google blocks 100 million phishing emails daily.
- Encrypted phishing threats rose 92% in 2024.
Business Email Compromise (BEC) Statistics
- Many organizations report frequent BEC attempts.
- BEC attacks caused over $2.4 billion in losses in 2024.
- The average loss per BEC incident reached $120,000.
- Financial-loss BEC cases accounted for 15% of reported incidents.
- Identity fraud comprised 11% of self-reported cybercrime threats.
- AI-generated impersonation tools fuel BEC success.
- Cloud collaboration platforms are common BEC targets.
- Employee awareness programs reduce BEC success rates.
Major Cybersecurity Risks Confronting APAC Enterprises
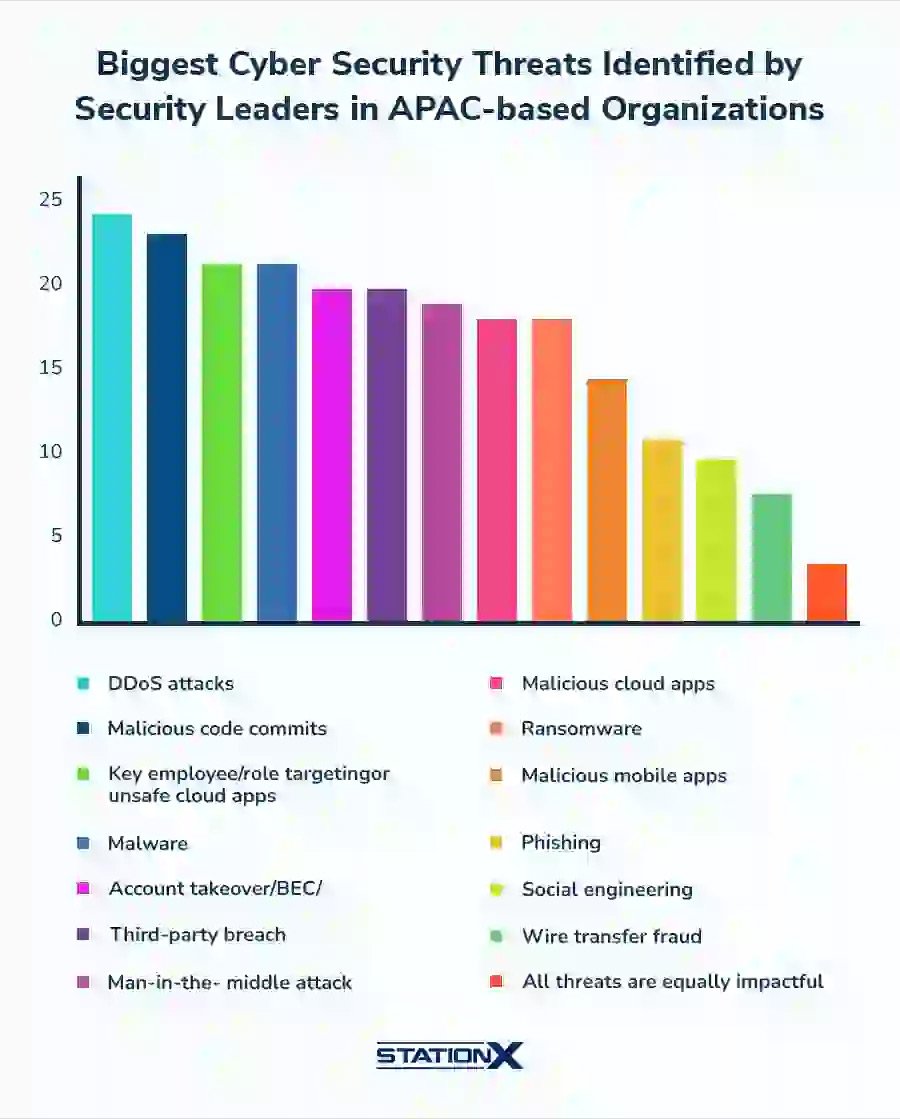
- DDoS attacks emerged as the most frequently cited threat, with over 24% of security leaders across the APAC region identifying them as a primary concern.
- Malicious code commits closely followed as a major risk, having been flagged by around 23% of surveyed respondents.
- Key employee or role targeting and unsafe cloud applications each represented significant concerns, reported by 21% of security professionals.
- Malware continues to be a persistent cybersecurity challenge, impacting 21% of organizations across the region.
- Account takeovers and Business Email Compromise (BEC) threats affected nearly 20% of companies, underscoring ongoing identity risks.
- Third-party breaches and man-in-the-middle attacks were each recognized by 19% of industry leaders as notable threats.
- Malicious cloud applications and ransomware threats were cited by 18% of respondents, reflecting growing cloud-related risks.
- Malicious mobile applications concerned 14%, clearly highlighting gaps in mobile security readiness.
- Phishing attacks were identified by 11% of organizations as a top cybersecurity concern.
- Social engineering and wire transfer fraud were flagged by 9% and 8%, respectively, indicating continued human-centric attack vectors.
- Only 4% believed that all threats are equally impactful, reinforcing the importance of prioritized and risk-based security strategies.
Data Breach and Data Leak Statistics
- The global average breach cost was $4.44 million in 2025, down 9% from 2024.
- U.S. breaches often exceed $10 million per incident.
- Ransomware featured in 44% of breaches.
- Third-party breaches doubled as a share of total incidents.
- Governments and universities faced high-profile breaches in 2025.
- Breach detection and containment often take several months.
- Stolen credentials are a leading initial access vector.
- Regulatory fines add significantly to breach costs.
DDoS Attack Statistics
- DDoS attacks doubled in 2024 from the prior year, with early 2025 volumes surging 350% to over six terabits.
- Cloudflare mitigated 20.5 million DDoS attacks in Q1 2025 alone, a 358% year-over-year increase.
- The US presidential election 2024 saw a 316% surge in DDoS attacks on US targets like banks and government sites.
- Iran faced over 15,000 DDoS attacks during the Iran-Israel conflict, compared to just 279 on Israel.
- Public administration is hit by DDoS in 60% of cyber incidents, with central governments facing 69% of attacks.
- The average botnet grew to 150,000 devices by Q2 2025, capable of 100–500 Gbps floods.
- Only 48% of SMBs feel ready for DDoS attacks, lacking staff and training.
- Cloudflare blocked 8.3 million DDoS attacks in Q3 2025, with network-layer attacks making up 71%.
- The government sector absorbed 28% of all DDoS traffic in H1 2025.
Vulnerability and Zero-Day Exploit Statistics
- Over 25,000 CVEs were disclosed annually as of June 2025.
- Average 115 vulnerabilities disclosed daily, up 30% year-over-year.
- 98 zero-day exploits were identified in 2025.
- 75 zero-days were exploited in the wild during 2024.
- Unpatched vulnerabilities caused 32% of ransomware attacks.
- 925 known exploited vulnerabilities in CISA’s KEV catalog.
- 55,525 vulnerabilities scored 7-8 on the CVSS scale.
- Average 130+ new CVEs requires daily triage in 2025.
- 49% of MSPs rate automated patching as very important.
Most Important Security Steps According to Experts
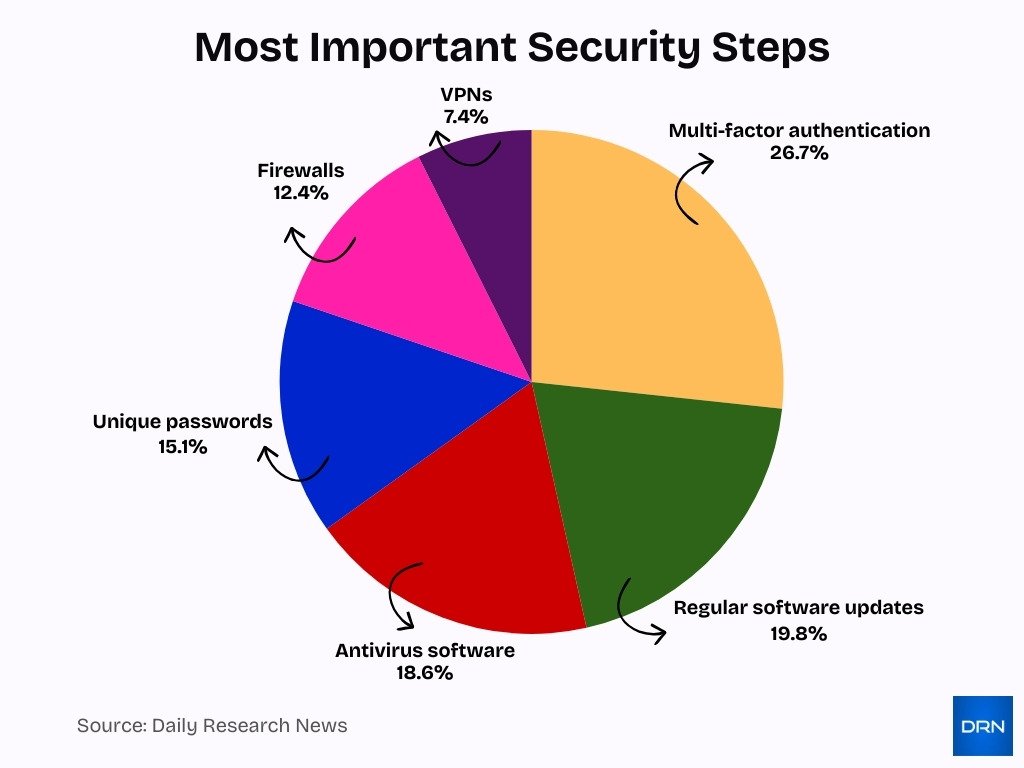
- Multi-factor authentication (26.7%) is identified as the single most important security measure, reflecting strong expert consensus on the value of layered identity verification to prevent unauthorized access.
- Regular software updates (19.8%) rank second, underscoring the importance of patching vulnerabilities and keeping systems protected against newly discovered threats.
- Antivirus software (18.6%) remains a core defensive tool, highlighting that malware protection is still a critical component of modern cybersecurity strategies.
- Unique passwords (15.1%) are emphasized as a key best practice, reinforcing the need to avoid password reuse and reduce the risk of credential-based attacks.
- Firewalls (12.4%) continue to play a meaningful role by monitoring and controlling network traffic, particularly in organizational and enterprise environments.
- VPNs (7.4%), while still relevant, are considered less critical than other controls, suggesting they are most effective when used as part of a broader, layered security approach.
Cloud Security Threat Statistics
- 80% of companies experienced at least one cloud security incident.
- 27% of organizations reported public cloud security breaches.
- 23% of cloud incidents stemmed from misconfigurations.
- 82% of misconfiguration breaches resulted from human error.
- 80% of data breaches involved cloud-stored data.
- Over 50% of organizations reported increased cloud-targeted attacks.
- Credential theft affected 68% of cloud environments.
- Multicloud complexity increases security visibility challenges.
Mobile and IoT Cyber Threat Statistics
- Malicious mobile apps were downloaded over 42 million times in 2025.
- Mobile malware activity rose 67% year over year.
- Global IoT devices reached 27.1 billion by 2025.
- Over 50% of IoT devices are vulnerable due to critical weaknesses like default credentials.
- 5G cyberattacks are projected to surge 300% in the next five years.
- Mobile phishing attacks hit 1 million in Q1 2025 alone.
- Data breaches from enterprise mobile threats averaged $4.9 million globally in 2024.
- IoT botnets in DDoS attacks grew from 200K to 1 million devices in 12 months.
- Session hijacking token replay attacks rose 111% year over year in 2023.
Critical Infrastructure and OT Attack Statistics
- Ransomware complaints targeting U.S. infrastructure rose 9% year over year in 2024.
- Nearly half (50%) of 2025 ransomware incidents affected critical sectors like manufacturing and energy.
- 91% of critical infrastructure firms faced OT breaches in the last 18 months.
- OT attacks surged 146% in 2024, hitting 1,015 facilities with physical disruptions.
- Cyberattacks on U.S. utilities jumped 70% in 2024 over 2023.
- 43% of organizations suffered cyber incidents on legacy OT systems last year.
- 18.2% of all cyber threats now target OT in industrial systems.
- 28% of ransomware attacks hit critical infrastructure sectors.
- Over 22% of organizations reported OT cybersecurity incidents in 2025.
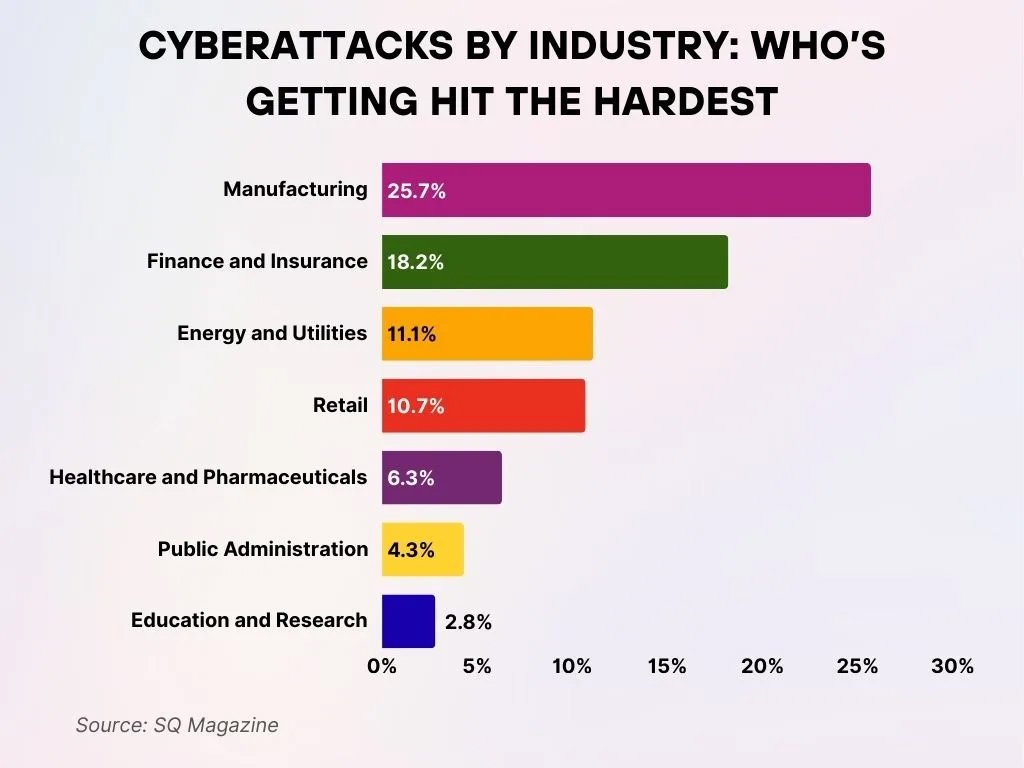
Cyberattacks by Industry: Sectors Facing the Greatest Impact
- Manufacturing remains the most targeted industry, accounting for 25.7% of all cyberattacks, highlighting the sector’s expanding digital exposure and vulnerabilities.
- The Finance and Insurance sector follows closely, experiencing 18.2% of attacks, reflecting its concentration of high-value financial data and critical assets.
- Energy and Utilities infrastructure endured 11.1% of total attacks, underscoring the significant cybersecurity risks to essential national infrastructure.
- The Retail industry recorded 10.7% of cyberattacks, largely driven by consumer data theft and reliance on online payment systems.
- Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals were affected in 6.3% of cases, emphasizing the high sensitivity and value of patient and medical data.
- Public Administration accounted for 4.3% of cyberattacks, indicating that government systems remain a prominent target for threat actors.
- Education and Research institutions faced 2.8% of cyberattacks, as digital learning platforms and valuable research data continue to be exposed to risks.
Identity Theft and Credential Theft Statistics
- 75% of SaaS incidents involved compromised credentials in 2024.
- Identity theft affects 1 in 22 Americans annually, with 6.47 million reports filed.
- Deepfake fraud attempts surged 2137% over the last three years.
- Credential phishing for SaaS access increased by over 700% in late 2024.
- 63% of confirmed data breaches stem from weak, stolen, or default credentials.
- Consumers suffered $27.2 billion in identity fraud losses in 2024.
- Biometric data theft via AI deepfakes rose 1100% in Q1 2025.
- 47% of enterprises lost over $300,000 to identity fraud incidents.
- 22% of all breaches originated from stolen credentials in 2025.
Supply Chain and Third-Party Risk Statistics
- 45% of organizations worldwide will experience software supply chain attacks by 2025, a threefold increase from prior years.
- 35.5% of all data breaches in 2024 originated from third-party compromises, up 6.5% year-over-year.
- Supply chain attacks doubled in 2025, averaging 26 incidents monthly since April versus prior rates.
- 98% of organizations have at least one third-party vendor that suffered a data breach.
- 431% surge in supply chain cyber attacks from 2021-2023, projected to rise further into 2025.
- 52.4% of retail & hospitality breaches stem from third-party vendors.
- 30% of 2025 data breaches involved third-party suppliers, per Verizon reports.
- Supply chain attacks hit 41 incidents in October 2025, a 30% record high over prior peaks.
Emerging AI-Driven Threat Statistics
- Automated attacker scanning reached 36,000 probes per second in high-volume campaigns.
- AI-powered phishing attacks surged by a 1,265% increase driven by generative AI tools.
- 16% of breaches in 2025 involved an AI component, per IBM data.
- 83% of organizations lack automated AI security controls, exposing sensitive data.
- AI-powered phishing boasts a 42% higher success rate than traditional scams.
- Organizations using AI-driven defenses cut incident response times by 70%.
- 60% of companies faced AI-enabled attacks in the past year, BCG survey finds.
- Software supply chain attacks hit 41 incidents in October 2025, a record high.
- Only 7% of organizations have fully embedded AI governance despite widespread use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
India experienced over 265 million cyberattacks in 2025, according to recent national threat reporting, showing a sharp rise in targeted digital threats.
Global cybercrime damage is projected to reach around $10.5 trillion annually by 2025, making it one of the largest economic risks worldwide.
Approximately 36% of all cybersecurity breaches in 2025 were linked to phishing attacks, highlighting its continued prominence as an attack vector.
Credential theft surged 160% in 2025, significantly contributing to unauthorized access and breach incidents globally.
Conclusion
Cyber threats span every layer of the digital ecosystem, from cloud misconfigurations and identity exploitation to AI-powered attacks and supply chain compromise. The rising volume and sophistication of these incidents highlight the need for continuous vigilance, advanced defenses, and cross-sector collaboration. As attackers leverage automation and AI, defenders must adopt proactive strategies that integrate identity, cloud, and infrastructure security.
Understanding the data helps organizations prioritize investments and strengthen resilience, but the evolving landscape demands ongoing adaptation and informed decision-making across every industry.