Cyberattacks powered by artificial intelligence (AI) have moved beyond a niche threat; they represent a systemic risk for organizations worldwide. From automated phishing emails to AI-driven credential theft, the scope and sophistication of these attacks are growing fast. Industries ranging from healthcare to finance now face mounting losses and reputational damage. In real-world scenarios, organizations that failed to adopt AI-aware security saw average breach costs rise sharply, while firms using AI-powered defenses gained in speed and resilience. This article unpacks the latest statistics, lays out current trends, and points to how defenders can respond.
Editor’s Choice
- 87% of organizations report being targeted by at least one AI-based cyberattack in the past year.
- The global cybercrime cost is estimated at $10.5 trillion by 2025.
- The average global cost of a data breach in 2025 stands at $4.45 million.
- In the U.S., average breach costs hit a record $10.22 million.
- Ransomware accounted for 44% of all breaches in 2024, up from 32% the year before.
- Credential-based phishing attacks surged by 703% in the second half of 2024.
- Over 80% of phishing emails now involve some form of AI.
Recent Developments
- The value of global cybercrime is projected to reach $10.5 trillion by 2025, reflecting escalating volume and sophistication of attacks.
- Organizations are responding, and global cybersecurity spend rose 15% in 2025.
- Talent shortages remain acute, with 4.8 million unfilled cybersecurity roles globally.
- Roughly 60–68% of breaches still involve a human element.
- Automated attacks and scanning have accelerated dramatically as AI-driven scanning increases the attack surface.
- Malware families such as stealer-as-a-service are gaining more users because of low entry cost and high profitability.
- Regulatory pressure and compliance demands are rising, pushing organizations to rethink AI governance.
- Many companies now face tighter detection and containment windows, with faster breach response essential to manage risks.
Overview of AI Cyber Attacks
- In 2025, 87% of organizations worldwide said they faced at least one AI-related cyberattack within the previous year.
- Global cybercrime burden is forecast at $10.5 trillion this year.
- Attackers increasingly leverage AI to create non-human identities, expanding attack surfaces.
- AI-powered attacks now span reconnaissance, phishing, malware deployment, and credential theft.
- AI reduces the barrier to entry, making complex attacks accessible to low-skilled attackers.
- Attack vectors frequently include credential theft, phishing, and exploitation of vulnerabilities.
- Digital transformation increases exposure and system complexity, creating more opportunities for AI-powered attacks.
- Defenders are increasingly using AI-based tools for detection, although governance still lags.
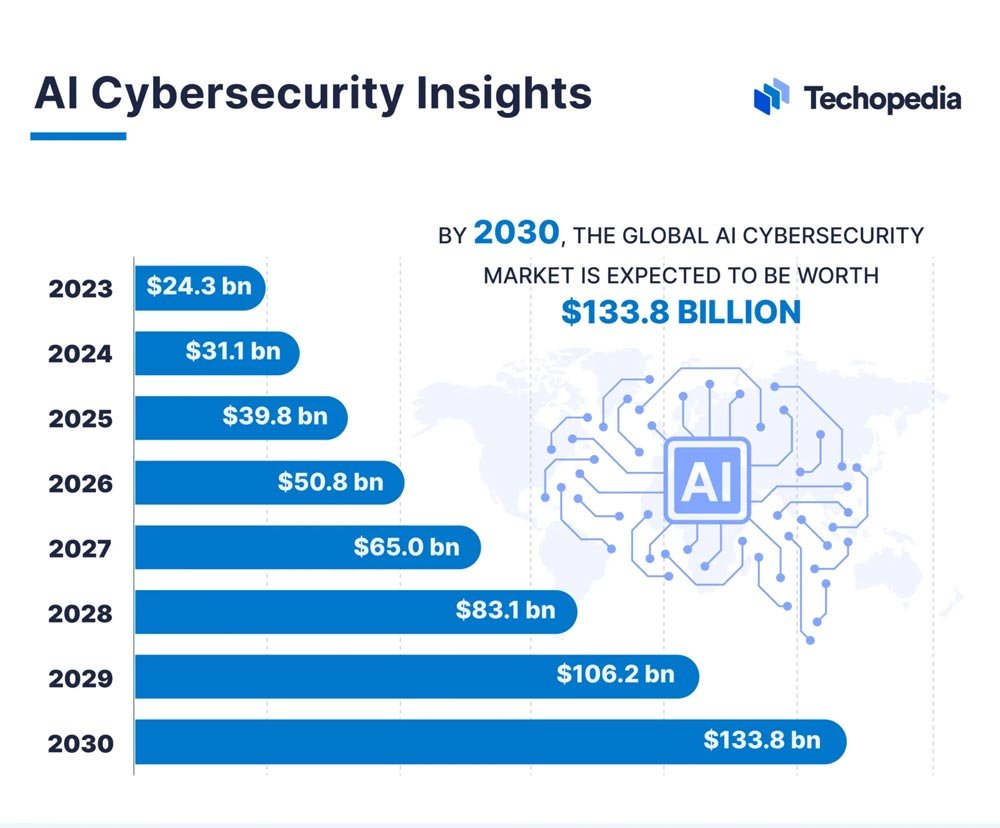
AI Cybersecurity Market Growth Forecast
- In 2023, the global AI cybersecurity market was valued at $24.3 billion, reflecting the early scale of AI-driven security adoption.
- By 2024, the market is projected to rise to $31.1 billion, indicating an expanding reliance on AI cybersecurity solutions.
- In 2025, it’s expected to reach $39.8 billion, showcasing rapidly increasing adoption of AI security tools.
- The value increases to $50.8 billion by 2026, highlighting continued industry investment in advanced AI-based protection.
- By 2027, the market is set to further grow to $65.0 billion, emphasizing escalating global focus on AI-powered defense systems.
- In 2028, it will climb to $83.1 billion, demonstrating accelerated demand for intelligent cybersecurity technologies.
- The market is projected to reach $106.2 billion in 2029, marking a significant expansion in the AI security ecosystem.
- By 2030, the global AI cybersecurity market is forecasted to hit $133.8 billion, marking more than a 5x increase from 2023 and underscoring massive long-term growth.
Frequency and Cost of AI Cyber Attacks
- Global cybercrime cost is projected at $10.5 trillion by 2025.
- The average global cost of a breach stands at $4.45 million.
- U.S. breach costs reached $10.22 million.
- Healthcare breach costs average between $7 million and $10 million.
- AI-based detection tools can save $1–2 million per breach.
- 44% of breaches involved ransomware in 2024–25.
- 60–68% of breaches involved human error.
- Infostealer malware contributed to 2.1 billion stolen credentials globally.
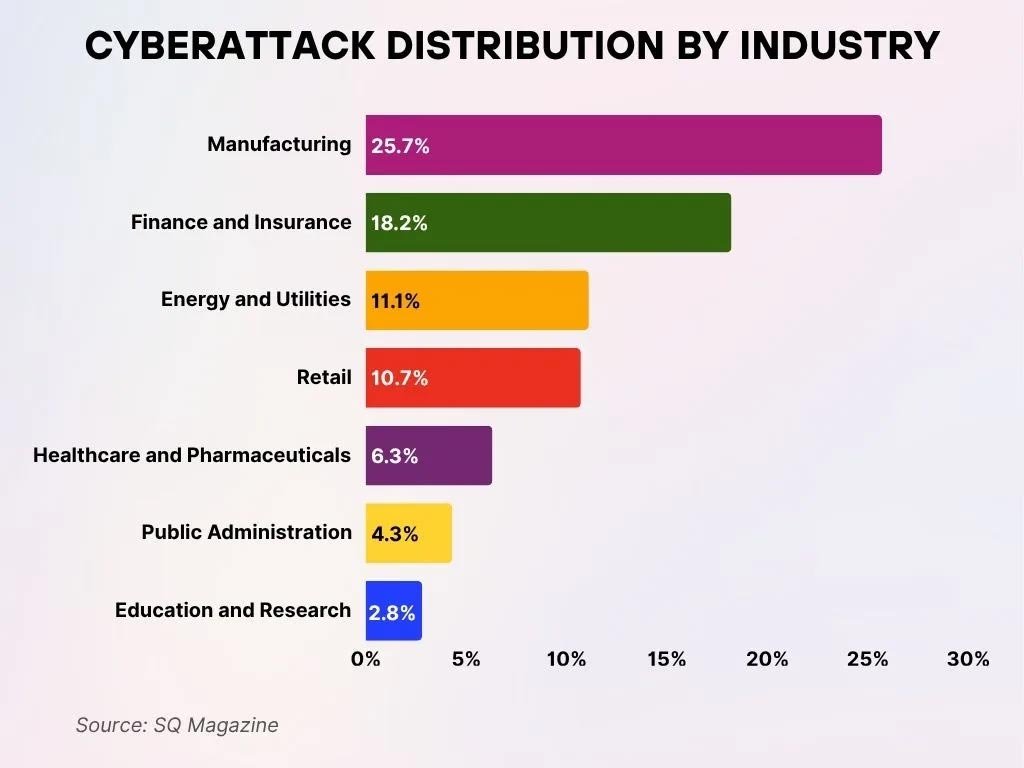
Cyberattack Distribution by Industry
- The Manufacturing sector emerges as the most heavily targeted, making up 25.7% of all cyberattacks and representing more than a quarter of overall incidents.
- The Finance and Insurance industry follows closely behind, sustaining 18.2% of the attack share and highlighting the sector’s heightened vulnerability tied to sensitive data and assets.
- The Energy and Utilities fields confront 11.1% of attacks, illustrating the rising threat level against critical infrastructure.
- The Retail sector is significantly affected as well, receiving 10.7% of cyberattacks, likely driven by high transaction activity and exposure of customer data.
- The Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals domain accounts for 6.3% of attacks, with cybercriminals exploiting patient information and essential medical systems.
- The Public Administration segment holds 4.3% of incidents, reinforcing that government services remain vulnerable to targeted cyber threats.
- The Education and Research institutions encounter 2.8% of all cyberattacks, reflecting the increasing danger associated with academic data and open network structures.
AI Phishing Attack Statistics
- Over 80% of phishing emails in 2025 use AI.
- Credential phishing attacks rose 703% in late 2024.
- Phishing volume increased by 202%.
- Generative AI reduces phishing email creation time to 5 minutes.
- Phishing remains the leading initial-access vector in major breaches.
- Phishing-related breaches can cost up to $4.88 million per incident.
- In 2025, 42% of organizations reported phishing or social engineering attacks.
- Advanced phishing simulations show high click-through rates despite filters.
- AI-powered phishing widens risk for both enterprises and individuals.
Deepfake and AI-Generated Impersonation Stats
- Deepfake files increased from 500,000 in 2023 to 8 million in 2025.
- Deepfake fraud attempts rose 3,000% in 2023 and continued rising.
- 53% of financial professionals reported a deepfake scam attempt.
- Deepfake fraud now makes up 6.5% of total fraud attacks.
- Deepfake incidents rose 19% in Q1 2025 alone.
- Human detection accuracy for deepfake videos is only 24.5%.
- 72% of enterprises cite deepfake risk as a major concern.
- 43% of enterprises plan to invest in deepfake protection technologies.
AI-Based Password and Credential Attacks
- AI credential-stuffing bots bypass CAPTCHA and MFA in 48% of tests.
- 16% of all breaches involve attackers using AI.
- Of AI-related breaches, 37% used phishing and 35% involved deepfakes or synthetic identity methods.
- 2.1 billion credentials were compromised globally via infostealer malware.
- Infostealer malware costs as little as $200 per month.
- Remote and hybrid work expanded attack surfaces for credential theft.
- AI-powered identity intrusions make up 30% of intrusions.
- Few organizations report readiness to mitigate AI-driven identity threats.
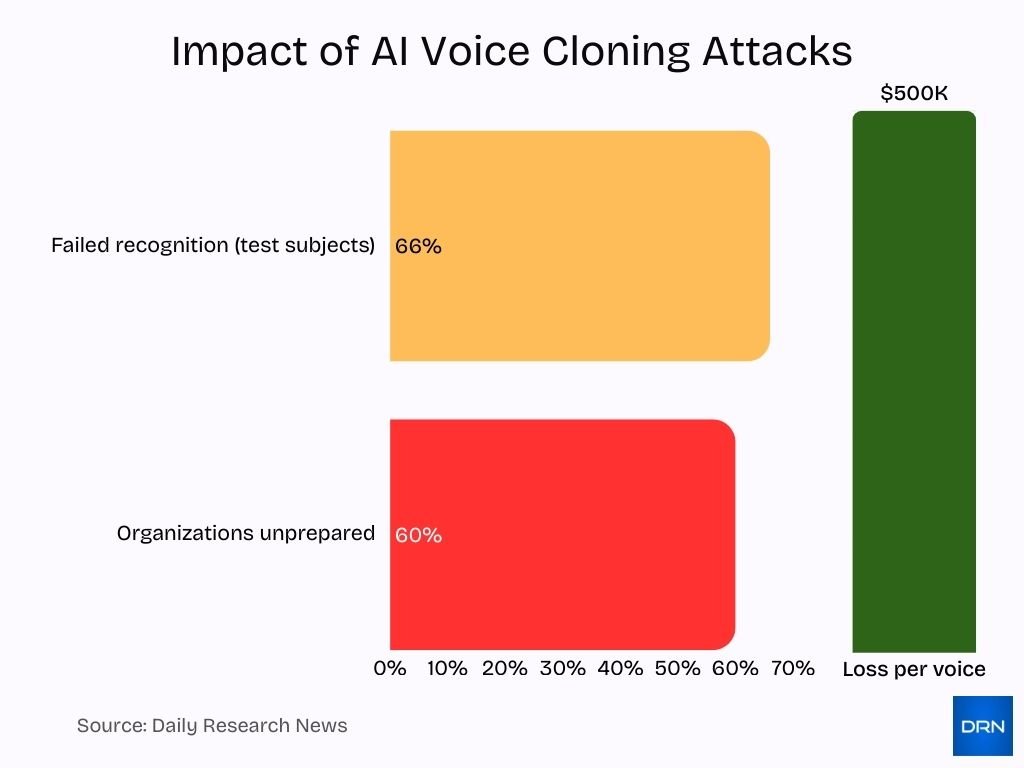
AI Voice Cloning Attack Statistics
- 66% of people fail to recognize an AI-generated voice in tests.
- Audio deepfakes and voice cloning are key impersonation vectors.
- Voice and video deepfake scams average $500,000 in losses per incident.
- 60% of organizations feel unprepared for voice-cloning threats.
- Voice-cloning attacks increasingly target financial verification systems.
- Voice cloning kits on dark-web marketplaces have increased sharply.
- Experts recommend combining AI-based detection with procedural verification.
Types of AI-Powered Cyberattacks
- Polymorphic malware using AI made up 22% of APTs in 2025.
- Identity-based intrusions made up 30% of intrusions.
- AI-enhanced social engineering appeared in 29% of breach cases.
- AI-ready tools allow low-skill attackers to launch multi-vector attacks.
- Global malware infections reached 6.5 billion in 2025.
- Ransomware attacks surged 40% year-over-year.
- 41% of active ransomware variants used AI modules.
- AI-driven malware bypasses endpoint detectors 18% more successfully.
Social Engineering Attacks Leveraged by AI
- In 2024, 42% of organizations reported phishing or social engineering attacks.
- Malware-laden emails rose 131%, phishing rose 21%, and scams rose 35% in 2025.
- 77% of CISOs cite AI-generated phishing as a major concern.
- Phishing now spans email, chat, SMS, and social platforms.
- AI tailors emotional triggers and tone in real-time.
- AI-powered phishing kits increased 50% in 2025.
- Finance and HR departments remain top targets.
- SMBs are especially vulnerable to AI-driven social engineering.
Malware and Ransomware Driven by AI
- Malware infections rose from 6.2 billion to 6.5 billion between 2024 and 2025.
- Early 2024 saw 236.7 million ransomware attacks globally.
- Ransomware makes up 28% of malware cases.
- 41% of ransomware families incorporate AI modules.
- AI-crafted malware bypasses detection at rates 18% higher.
- AI polymorphic malware contributes significantly to APT activity.
- Over 6 billion emails per month are analyzed, showing rising AI-enabled malware delivery.
- AI ransomware causes longer downtime and higher ransom amounts.
Adversarial AI and ML Attacks
- 30% of intrusions in 2025 involve AI-assisted identity attacks.
- Adversarial AI is now commonly combined with polymorphic malware in advanced persistent threats (APTs).
- Adversarial ML tools are widely available and actively sold on dark-web marketplaces.
- AI-driven identity verification systems face vulnerabilities exploited in 72% of deepfake-related fraud cases.
- The finance sector experienced over 3,300 incidents and 927 breaches linked to ML-targeted attacks in 2025.
- Healthcare reported 1,542 breaches out of 1,710 incidents, largely due to ML exploitation in 2025.
- Over 90% of organizations lack robust governance frameworks for AI systems as of 2025.
- AI-powered polymorphic malware increased by 76% in 2025, enhancing adversarial AI attack capabilities.
- Synthetic identity fraud, often AI-assisted, surged by 62% in 2025, impacting multiple sectors.
- Nearly 47% of surveyed organizations recognized AI governance as a top-five strategic priority in 2025.
Greatest Inhibitors to Defending AI-Powered Threats and Attacks
- Insufficient personnel to manage tools and alerts emerges as the top-rated inhibitor, holding a score of 3.10, emphasizing the continued strain on teams tasked with countering AI-powered threats and attacks.
- This score of 3.10 further indicates a significant shortage of skilled security staff required to continuously monitor, analyze, and respond to escalating AI-driven threats.
- Insufficient knowledge or limited use of AI-driven countermeasures ranks closely behind with a score of 3.07, reflecting the ongoing challenge of integrating and mastering AI-powered defensive tools.
- The score of 3.07 also highlights a critical gap in expertise and adoption surrounding modern AI-enabled defense mechanisms.
- Insufficient cybersecurity budget, receiving a score of 2.90, signifies how financial limitations hinder the ability of organizations to acquire essential technologies and resources to counter AI-based attacks.
- This 2.90 rating clearly suggests that budgetary constraints remain a substantial barrier preventing adequate investment in advanced cybersecurity capabilities.
- Lack of management recognition regarding the rising impact of AI-powered threats ranks lowest yet still notable at 2.61, revealing leadership-underestimation issues.
- The 2.61 score further points to persistent organizational awareness challenges and a pressing need for improved executive buy-in on AI-related risks.

AI-Generated Cryptocrimes
- Up to 50% of new malware strains in 2025 are AI-built.
- AI-assisted cryptocrime has caused $30 billion in damages so far.
- 82.6% of phishing emails use AI, enabling crypto theft at scale.
- AI-powered supply chain attacks surged by 156% in 2025, embedding crypto-stealing modules.
- AI-driven cryptominers increasingly target cloud and edge environments.
- AI lowers technical barriers, expanding crypto-fraud participation widely.
- Hybrid attacks now combine phishing, identity theft, and financial fraud tactics.
- DeFi and anonymization tools contribute to easier and attractive laundering.
- AI-generated phishing emails have a click-through rate of approximately 54%.
- AI-enabled cryptocrimes cost is predicted to reach $146.52 billion by 2034 with a CAGR of 19.34%.
Sector-Wise Impact of AI Cyber Attacks
- The average breach cost in 2025 is $4.45 million, with higher costs in critical sectors.
- Healthcare breach costs averaged $9.77 million in 2024.
- Financial services remain top targets for fraud and ransomware.
- 70% of secondary schools reported cyberattacks in 2024–25.
- Retail remains vulnerable to AI-driven credential stuffing.
- Public sector and critical infrastructure face rising supply-chain and cloud attacks.
- One-third of SME breaches stem from third-party vulnerabilities.
- Sectors with fast digital transformation face the highest risks.
Enterprise vs Individual Targeting Trends
- 87% of organizations experienced at least one AI-driven attack in 2025.
- Enterprises face complex multi-vector AI-assisted attacks.
- Individuals face rising AI-generated impersonation and fraud scams.
- Remote work expands exposure for individual users tied to corporate systems.
- Third-party breaches rose 6.5% since 2023.
- AI-enabled financial scams heavily impact consumers.
- AI defense tools save enterprises $1.9 million per breach on average.
- Many individuals and SMEs lack the governance and resources to defend against AI threats.
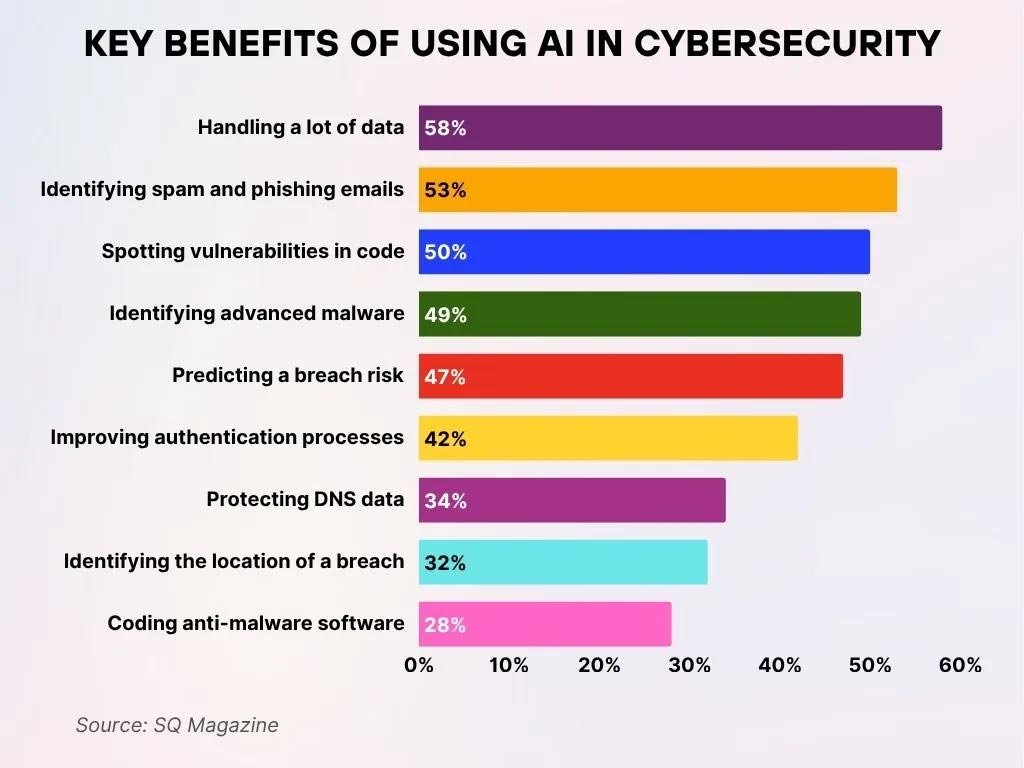
Key Advantages of Implementing AI in Cybersecurity
- 58% of professionals report that AI significantly assists in managing a large volume of data, thereby streamlining detailed analysis and accelerating threat detection processes.
- 53% of experts state that AI is highly effective in recognizing spam and phishing emails, which helps reduce exposure to social engineering attacks.
- 50% indicate that AI is instrumental in uncovering vulnerabilities in code, which enhances software security throughout the development cycle.
- 49% rely on AI to pinpoint advanced malware, enabling faster detection of highly sophisticated threats.
- 47% believe that AI provides strong value in forecasting breach risks, supporting more proactive defense strategies.
- 42% highlight AI’s importance in strengthening authentication processes, thereby improving overall identity verification.
- 34% of respondents use AI to safeguard DNS data, contributing to stronger protection against DNS-based attacks.
- 32% benefit from AI’s capability to determine the location of a breach, which helps speed up effective incident response.
- 28% mention that AI aids in developing anti-malware software, boosting the efficiency of automated security development.
AI Governance, Policy, and Compliance Gaps
- 97% of organizations with AI incidents lacked proper access controls.
- 63% of firms have no formal AI-use policies.
- 16% of data breaches in 2025 involved AI-driven attacks.
- Machine identities outnumber humans, with 72% of identity pros citing management challenges.
- Only 14% of companies audit more than half of third-party AI vendors.
- 77% of Ethics & Compliance teams actively play roles in AI governance.
- Regulatory frameworks lag; just 58% adoption in regulated sectors versus 92% in tech.
- Over 60% of AI systems raise concerns about explainability, bias, and privacy.
- Governance teams spend 37% more time managing AI risks than before.
- Humans risk over-reliance as tests show many fail to detect AI mistakes properly.
Future Trends and Predictions for AI Cybersecurity
- By 2027, 17% of all cyberattacks will involve generative AI.
- AI-driven supply-chain attacks are projected to increase by 45% annually.
- Cloud-related AI attacks are expected to grow by 38% by 2026.
- Over 60% of identity models will need reengineering to handle blurred human-machine identities by 2028.
- Hybrid AI defense strategies are forecasted to reduce breach impact by 35% compared to legacy methods.
- By 2027, 74% of organizations will face stricter AI regulatory compliance demands.
- Cryptocrime involving AI-driven ransomware is expected to evolve with a 50% increase in sophistication by 2026.
- AI-related synthetic identity fraud cases will rise by 30% annually over the next five years.
- Demand for AI cybersecurity skills is projected to grow by 80% from 2025 to 2027.
- Effective AI defense will require an integration of technology, policy, and human expertise in over 85% of enterprises.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
87% of organizations say they’ve been targeted by at least one AI-related cyberattack in the past 12 months.
The global average data breach cost is $4.45 million in 2025.
44% of all breaches in 2025 involved ransomware, up significantly compared with prior years.
The global AI-cybersecurity market is valued at around $30 billion in 2025.
Conclusion
The data makes clear that AI-powered cyberattacks no longer belong to a fringe threat category; they have become a central challenge across industries and geographies. From cryptocrime and ransomware to deepfake fraud and AI-enhanced supply-chain attacks, threat actors are leveraging automation and scale to achieve greater volume and impact.
Meanwhile, organizations that adopt AI-driven cybersecurity, combined with strong governance and human oversight, often see lower breach costs and improved response times. The divide is growing between those prepared for the AI era and those relying on legacy defenses. As attacks evolve, so too must defense strategies, blending technology, policy, and people. The time to act is now.