AI is shifting from promise to practice in healthcare. Hospitals and health systems increasingly use AI to support diagnostics, workflows, and predictions, transforming how care gets delivered. From image analysis that spots early signs of disease to predictive tools that flag patient risk, the impact spans clinical outcomes and operational efficiency. The examples below trail real shifts in adoption, showing AI’s growing reach in both everyday care and long-term health planning. Dive into the full article to explore detailed stats across adoption, diagnostics, economics, and emerging trends.
Editor’s Choice
- 71% of U.S. non-federal acute-care hospitals reported using predictive AI in 2024, up from 66% in 2023.
- 66% of U.S. physicians used health AI tools by 2024, rising sharply from 38% in 2023.
- The global AI in healthcare market was valued at approximately $29.01 billion in 2024.
- Projections estimate the global market could jump to $39.25 billion in 2025, with further growth toward $504.17 billion by 2032.
- The segment of AI used for diagnostics is expected to grow from $1.94 billion in 2025 to $10.28 billion by 2034.
- In a 2024 survey, over 70% of healthcare organisations reported pursuing or already implementing generative AI capabilities.
- Among digital health workloads in 2025, data analytics (58 %), generative AI (54 %), and large language models (53 %) rank as the top uses across the sector.
Recent Developments
- Adoption of predictive AI in U.S. hospitals rose from 66% in 2023 to 71% in 2024.
- Use cases gaining traction include automating billing (jumping from 36% to 61%) and scheduling (from 51% to 67%) between 2023 and 2024.
- More than 70% of respondents from providers, payers, and health tech firms are exploring or already using generative AI.
- By early 2025, 22% of healthcare organisations had deployed domain-specific AI tools, a sevenfold increase over 2024.
- Use is rising across sectors: health systems (27%), outpatient providers (18%), payers (14%).
- Among digital health professionals in 2025, 81% reported increased revenue and 73% reported reduced operational costs after AI adoption.
- In a 2025 survey, 86% of respondents called AI “critical to their future,” and 83% expect it to reshape healthcare in the next 3 to 5 years.
AI Adoption in Healthcare
- 71% of U.S. non-federal acute-care hospitals used predictive AI in 2024, up from 66% in 2023.
- Among individual providers, 66% of U.S. physicians used AI tools by 2024, a substantial increase from 38% in 2023.
- In a broad healthcare industry survey, 94% of organisations called AI core to their operations, and 86% reported active use.
- Generative AI, machine learning, and data analytics capture the leading share of AI workloads: 54% use generative AI, 58% use analytics, 53% use LLM-based systems.
- Smaller, rural, or independently owned hospitals lag in adoption compared with larger, urban and network-affiliated hospitals.
- Use of predictive models built into major EHR platforms dominates adoption, while third-party and self-developed tools are growing.
- AI adoption is expanding beyond hospitals into outpatient clinics, payers, and biotech companies.
Market Size and Growth Projections
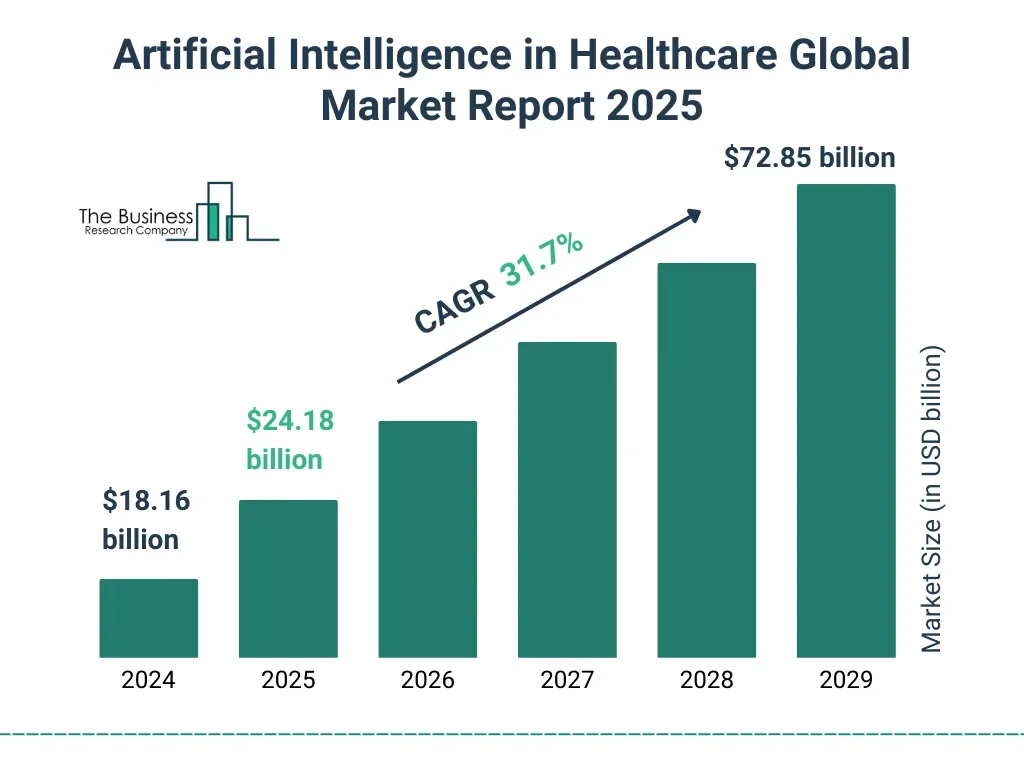
- The global AI in healthcare market is anticipated to rise from $18.16 billion in 2024 to $72.85 billion by 2029, reflecting substantial sectoral momentum.
- This surge represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 31.7%, highlighting the rapid adoption of intelligent technologies across the healthcare landscape.
- In 2025, the market is forecasted to climb to $24.18 billion, maintaining its robust upward trajectory.
- The sector is projected to more than triple in size over five years, demonstrating strong industry confidence in AI’s transformative healthcare potential.
- Year-over-year expansion underscores steadily rising investment and integration of AI technologies in diagnostics, treatment, and patient management.
AI in Diagnostic Accuracy and Early Detection
- 71% of institutions reported using AI in medical imaging by 2025.
- AI algorithms detect tumours in scans with 94% accuracy, surpassing radiologists.
- AI in the diagnostics market is valued at $1.97 billion in 2025, projected to reach $5.44 billion by 2030.
- 42% of providers use AI tools for disease risk forecasting.
- AI systems achieve 94% accuracy in lung nodule detection, outperforming radiologists at 65%.
- AI-supported breast screening boosts cancer detection by 17.6% over radiologists alone.
- 90% of health systems have deployed AI in imaging and radiology.
- Generative AI reduces diagnostic errors by 45%, from 22% to 12%.
- AI detects 23.5% of interval breast cancers on prior mammograms at 96% specificity.
Predictive Analytics in Healthcare
- Predictive AI is used in 71% of acute care hospitals in 2024.
- Billing automation increased from 36% to 61% and scheduling automation from 51% to 67% between 2023 and 2024.
- Predictive analytics are used for forecasting trajectories, readmission risk, and outpatient deterioration.
- Organisations in 2025 report benefits: 81% increased revenue and 73% reduced operational costs after AI adoption.
- Predictive analytics streamlines administration, care coordination, and resource allocation.
- In 2025, 78% of organisations across sectors use AI in at least one business function.
- EHR-integrated predictive tools form the majority of hospital implementations.
- Predictive analytics support staffing, capacity planning, and patient flow management.
Generative AI in Healthcare
- In a 2025 survey, generative AI documentation tools reached 100% deployment activity, and 53% reported high success.
- Approximately 90% of organisations reported deploying AI-based imaging tools by 2025.
- The generative AI market for healthcare is estimated at $3.3 billion in 2025.
- Key generative AI applications include virtual nursing (≈ 50%), monitoring and prediction (≈ 43%), imaging (≈ 42%), and personalised treatment (≈ 33%).
- Clinical documentation is among the earliest and most adopted generative AI use cases.
- 46% of U.S. hospitals use AI in revenue cycle operations in 2025.
- Many organisations now view generative AI as foundational rather than experimental.
AI-Powered Devices Across Medical Specialities
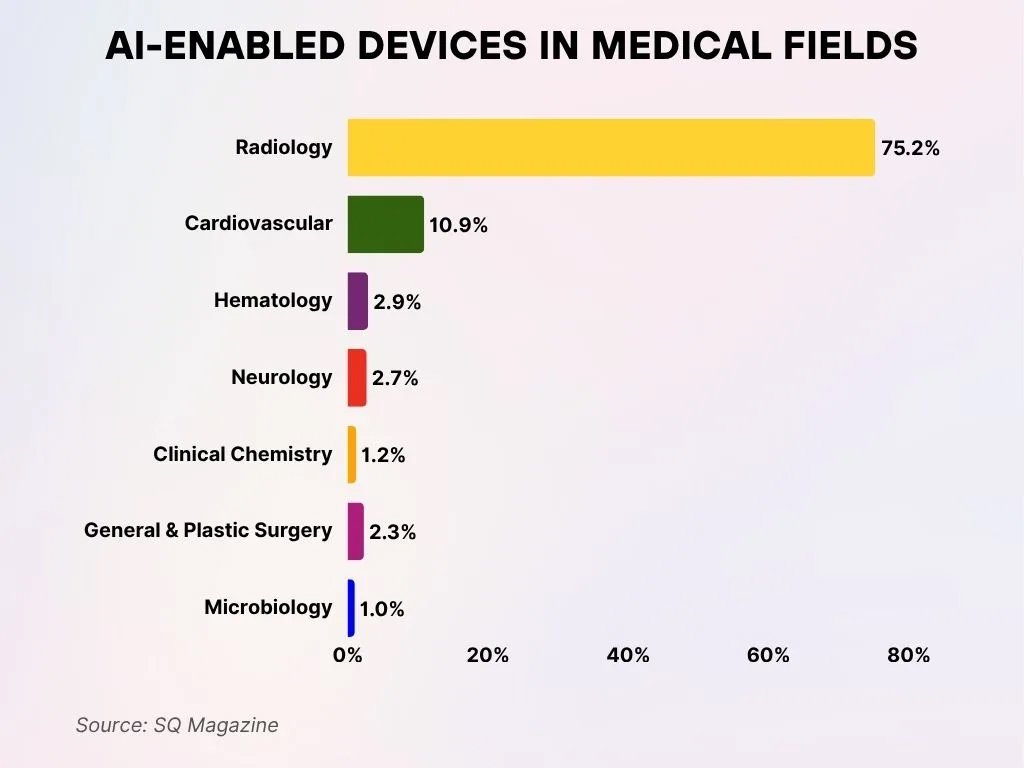
- Radiology overwhelmingly leads the adoption of AI-enabled medical devices, accounting for 75.2%, demonstrating the field’s early and dominant integration of artificial intelligence.
- Cardiovascular applications follow next, representing 10.9% of AI-enabled medical devices, indicating strong momentum in heart-focused diagnostics and monitoring.
- Haematology maintains a modest share at 2.9%, reflecting the growing utilisation of AI in blood analysis and pathology.
- Neurology captures 2.7% of AI-based device applications, supporting advancements in brain imaging and neurological diagnostics.
- Clinical Chemistry contributes 1.2%, where AI enhances the evaluation of bodily fluids and chemical processes.
- General and Plastic Surgery represents 2.3%, possibly distinguishing AI tools designed for general surgical tasks from those used in aesthetic procedures.
- Microbiology accounts for 1.0%, aiding in infection detection and microorganism classification through AI technologies.
AI Automation in Clinical Workflows
- 66% of U.S. physicians used healthcare AI in 2024.
- Hospitals report shorter documentation cycles and fewer denied claims after automation adoption.
- 65% of hospitals use AI-driven predictive analytics or automation in operations in 2025.
- 74% of hospitals implemented revenue cycle automation using AI or RPA.
- 20% report improved efficiency in filing claims, and 18% report fewer data entry errors.
- 30% reported faster payments and collections after adopting AI in revenue cycle management.
- Approximately 79% rely on predictive models embedded within EHRs.
- 60% of workflow automations focus on staffing shortages and clinician burnout.
AI for Hospital Operations and Revenue Cycle
- 46% of U.S. hospitals and health systems use AI in revenue cycle operations.
- The global AI RCM market was $20.63 billion in 2024.
- It is projected to reach $70.12 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 24.16%.
- North America represented more than 55% of the RCM AI market in 2024.
- Integrated RCM solutions accounted for over 70.8% of the market.
- Web-based delivery represented more than 52% of RCM AI use.
- Physician back office use accounted for approximately 37% of adoption.
- AI-enabled automation in billing and claims may generate $9.8 billion in annual savings.
Impact on Healthcare Cost Reduction
- AI may help realise up to $150 billion annually by 2026 in savings.
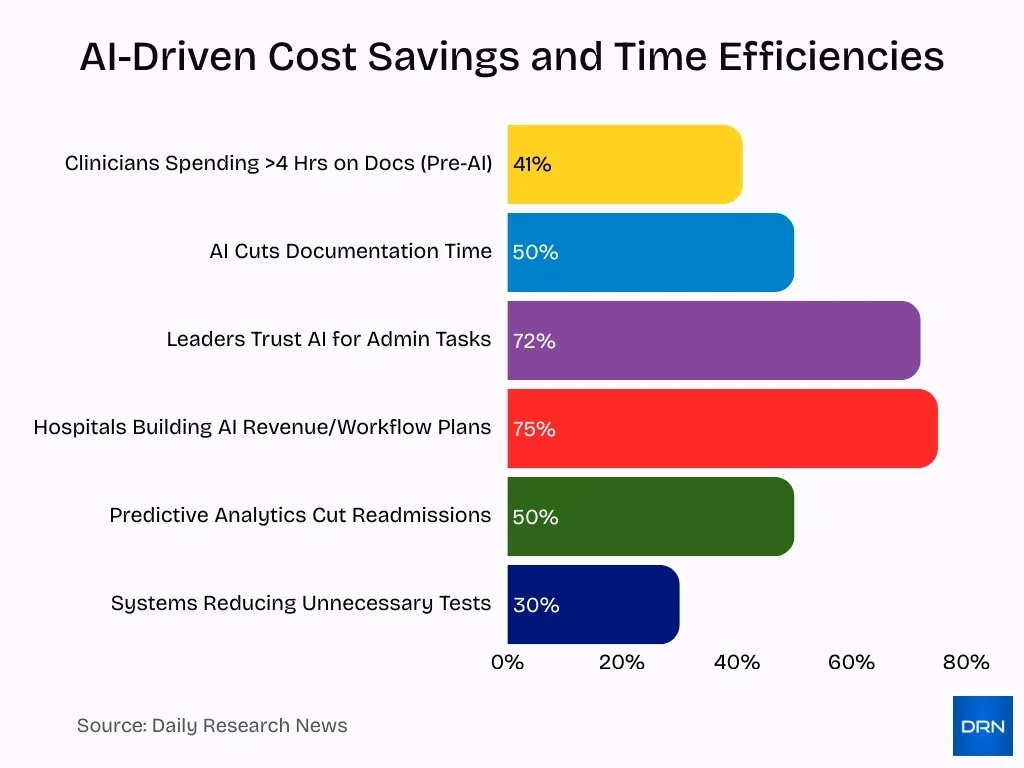
- Predictive analytics can reduce readmissions by up to 50%.
- Some systems using predictive models reduced unnecessary tests by ≈ 30%.
- 41% of clinicians spend more than 4 hours per day on documentation before AI tools.
- AI documentation tools may cut documentation time by up to 50% by 2027.
- 72% of healthcare leaders trust AI for non-clinical administrative tasks.
- 75% of hospitals are developing AI strategies for revenue and workflow optimisation.
- Automated billing and coding reduce errors and accelerate collections.
Impact on Patient Outcomes
- Predictive analytics in healthcare reduces overtreatment and adverse events by up to 30%, significantly improving patient safety.
- Readmission risk prediction tools can reduce hospital readmissions by 40-50% through targeted interventions.
- AI-based imaging achieves up to 94% accuracy in early disease detection, outperforming traditional methods.
- Generative AI documentation reduces clinician burnout by 20-35% and increases direct provider-patient interaction time.
- Automated workflows lead to a 50-80% reduction in data errors and decrease care delays.
- AI-driven faster billing processes improve claim payment speed by over 20%, reducing patient financial delays.
- AI workflow automation boosts staff efficiency by 36%, freeing time for more direct patient care.
- Over 70% of hospitals now view AI as a critical tool for long-term quality improvement.
- Predictive models improve personalised treatment adherence, leading to a 25% drop in complications.
- AI integration in clinical settings enhances overall patient throughput by up to 30% through optimised resource allocation.
AI in Chronic Disease Management
- AI predictive modelling improves early detection accuracy by over 20% in chronic disease control, according to a 2025 pilot study.
- Remote monitoring reduces hospitalisation risk by up to 14% for chronic disease patients.
- AI longitudinal data analysis flags complication risks with 85% prediction accuracy.
- AI support scales chronic care access, helping manage patient populations exceeding millions globally.
- Limited access to quality data restricts AI adoption in over 30% of low-resource regions.
- AI chronic care tools reduce rural healthcare inequities by improving access for nearly 2 billion underserved people.
- Long-term outcome improvements using AI in chronic disease management are tracked but remain limited, with less than 5 years of robust data available.
- Remote patient monitoring shows a 15% reduction in all-cause hospitalisations among chronic care populations.
- AI enhances clinical decision support, improving personalised treatments and reducing emergency visits by 12-18%.
- Generative AI systems demonstrate potential to cut diagnostic delays by up to 25% in chronic illness care.
Benefits of AI for Healthcare Providers
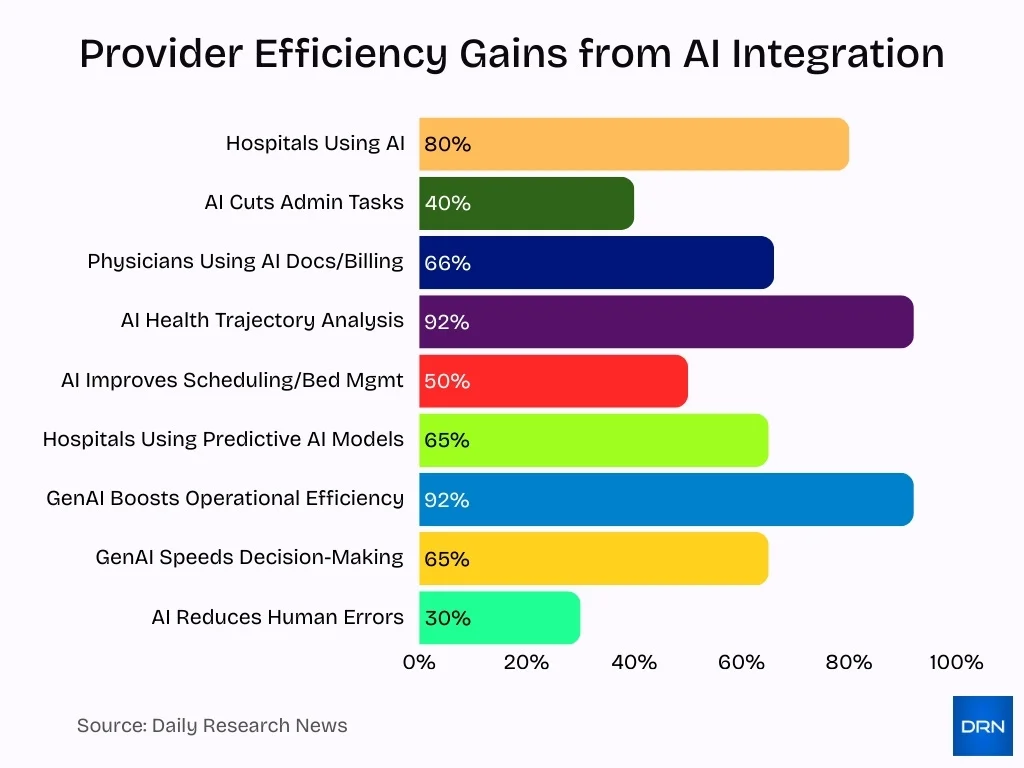
- Approximately 80% of hospitals use AI to improve care and operational efficiency.
- AI adoption in healthcare reduces administrative tasks by up to 40%.
- 66% of physicians use AI tools for billing codes and documentation accuracy.
- AI supports clinical decision-making by analysing 92% of inpatient health trajectories.
- Hospitals using AI report a 50% improvement in scheduling and bed management efficiency.
- AI automation helps reduce staffing shortages by handling routine and repetitive tasks efficiently.
- Smaller healthcare clinics adopting AI gain access to advanced diagnostic and operational tools without increasing staff size.
- AI implementation leads to a 30% reduction in human errors in clinical and administrative processes.
- Around 65% of U.S. hospitals use AI-assisted predictive models for patient care and workflow optimisation.
- Generative AI usage in healthcare improves operational efficiency by up to 92%, with 65% seeing faster decision-making.
Challenges and Barriers to AI Implementation
- 87.64% clinician override rate of AI decisions reduced to 33.29% with enhanced transparency and confidence calibration in healthcare AI.
- Only 12% of American adults have proficient health literacy, impacting AI adoption and understanding in healthcare.
- 52% of organisations cited data quality and availability as the top barriers to AI adoption.
- Healthcare AI infrastructure is lagging despite investments, with a projected AI healthcare market of $149 billion by 2030.
- About 95% of generative AI pilots in companies fail due to a lack of skilled talent and training.
- Only 43% of organisations surveyed have formal AI governance policies in place.
- High initial costs and uncertain ROI cause more than 80% of AI projects to fail.
- Regulatory and legal concerns affect 31% of organisations adopting AI.
- Bias in AI systems can exacerbate health disparities, with a significant focus on data quality to reduce such risks.
- Global digital infrastructure gaps restrict universal AI readiness, especially in smaller healthcare facilities.
AI and Staff Efficiency, Addressing Shortages
- Healthcare faces an estimated shortage of ≈11 million workers by 2030, increasing AI dependency.
- AI scribes reduce administrative work, lowering clinician burnout by ~40%.
- AI-driven coding speeds up medical billing, saving hospitals millions, including a $1 million+ case study in New York.
- Automation by AI improves staff utilisation by freeing up to 10–15% of nursing time.
- 75% of healthcare organisations report significant AI skills gaps, creating urgent upskilling needs.
- Excessive AI reliance may erode clinical skills, as shown by reduced tumour detection abilities in experienced doctors.
- Infrastructure challenges like unstable internet limit AI use in low-resource healthcare settings.
- AI workforce planning tools forecast clinician shortages to guide investment and training strategies.
- AI-enabled workflow automation is expected to mitigate staffing shortages by 60%.
- Hospitals report that AI reduces administrative burdens, saving healthcare professionals an average of 30 minutes per shift.
Public Comfort with AI in Healthcare Varies by Age
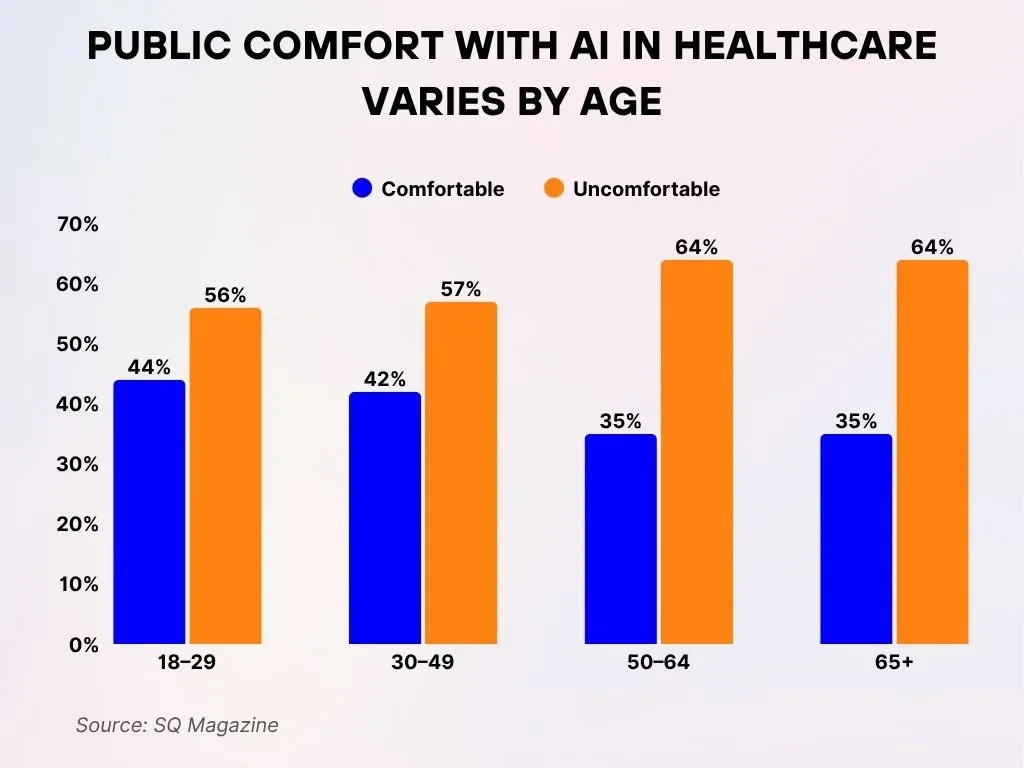
- Among adults aged 18–29, 56% report feeling uncomfortable with AI in healthcare, whereas 44% state they feel comfortable, maintaining the same division of sentiment.
- Within the 30–49 age bracket, 57% indicate being uncomfortable, while 42% express comfort regarding the use of AI in medical settings.
- For individuals aged 50–64, scepticism rises as 64% feel uncomfortable, contrasted with 35% who report feeling comfortable with AI in healthcare.
- older people aged 65 and older reflect similar views, with 64% describing themselves as uncomfortable and only 35% stating they feel comfortable with healthcare-related AI use.
Ethical and Privacy Considerations in AI Healthcare
- 40% of healthcare AI systems show bias due to non-representative training data.
- Over 60% of patient data used in AI lacks explicit patient consent for aggregation.
- Diagnostic accuracy drops by up to 25% in minority populations due to biased datasets.
- 74% of clinicians express concerns about AI’s lack of transparency in healthcare decisions.
- No clear accountability exists for harm from AI recommendations in over 50% of hospitals.
- Regulatory frameworks lag by an average of 3-5 years behind AI innovation in healthcare.
- Weak governance correlates with 30% higher disparities in AI-driven healthcare access.
- 90% of trustworthy AI frameworks emphasise fairness, transparency, privacy, oversight, and accountability.
- Privacy breaches affect 15% of AI healthcare projects annually due to weak data protection.
- Lack of explainability in AI models reduces patient trust, with 65% of users reporting scepticism.
Regional and Institutional Adoption Variations
- North America commands 45% of the global AI healthcare market share, dwarfing other regions.
- 72% of hospital-employed physicians use AI tools, compared to 64% in private practice.
- Urban hospitals achieve 77–81% AI integration, while rural ones lag at 48–56%.
- Sub-Saharan Africa, with 25% global disease burden, holds just 3% of healthcare workers.
- Over 70% of AI research and patents in healthcare stem from high-income countries.
- Only 8% of rural hospitals deploy AI-driven analytics, versus 65% overall.
- LMICs face an 18 million healthcare worker shortage by 2030, spurring AI needs.
- Private institutions adopt AI twice as fast annually as public systems.
Future Outlook and Trends in AI Healthcare
- By 2030, AI is expected to help achieve universal health coverage for 4.5 billion people currently lacking essential services.
- Around 80% of hospitals use AI to improve patient care and operational efficiency in 2025.
- The AI telehealth market is projected to reach $27.14 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of around 23%.
- AI integration in EHR systems can reduce manual coding errors by up to 40% and speed up billing cycles by 25%.
- At least 29 US states have enacted legislation regulating AI in healthcare as regulation tightens globally.
- Clinician training for AI-enhanced workflows is becoming essential as 92% of healthcare leaders believe automation addresses staffing shortages.
- AI supports global health initiatives, especially in low-resource regions, through partnerships impacting millions of patients worldwide.
- The long-term impact of AI in healthcare relies on governance, infrastructure, equity, and human-centred design to ensure inclusivity.
- AI-driven monitoring tools for chronic diseases have reduced preventable hospitalisations by early intervention based on wearable data analysis.
- AI telemedicine platforms in the Asia Pacific grow fastest with a CAGR of 24.3%, expanding healthcare access in developing countries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The global AI in healthcare market is estimated at USD 46 billion in 2025.
One projection estimates the market could reach about $208.2 billion by 2030.
By 2024, 66% of U.S. physicians reported using AI tools in their practice.
As of 2025, 22% of healthcare organisations had implemented domain-specific AI tools.
Conclusion
AI has matured beyond early experimentation in healthcare. Many hospitals and providers, especially in well-resourced settings, leverage AI in chronic disease management, workflow automation, and operations. At the same time, significant challenges remain, including data quality, ethics, governance, infrastructure gaps, and uneven regional adoption. The next phase of AI in healthcare will depend on implementing trustworthy, equitable, and transparent systems, alongside training providers to work with AI tools effectively.
As AI technologies evolve and policymakers strengthen frameworks, the sector may finally see a scalable, global impact, improving care quality, accessibility, and efficiency worldwide.