Cybersecurity threats continue to rise sharply, affecting organizations across sectors worldwide. Global companies face increasingly frequent ransomware, phishing, and malware attacks, often targeting critical infrastructure, consumer data, and corporate operations. In practice, a major hospital network might lose millions in downtime and reputational damage after a ransomware strike; similarly, a financial services firm may face identity theft and fraud via phishing campaigns targeting customer accounts. This article explores key statistics behind these trends and sets the stage for understanding evolving cyber risks.
Editor’s Choice
- The global average cost of a data breach dropped to $4.44 million in 2025, after an all-time high of $4.88 million in 2024.
- The average cost for a data breach in the United States soared to $10.22 million in 2025, the highest on record.
- There were 4,701 confirmed ransomware incidents globally between January and September 2025, a 34% increase compared to the same period in 2024.
- Infostealer and phishing-based credential theft rose sharply, with an increase of 84% year over year.
- Phishing remains the dominant vector, with 3.4 billion phishing emails sent daily worldwide.
- 45% of organizations rank ransomware as their top cyber risk.
- Global cybercrime is projected to cost $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
Recent Developments
- In 2025, attackers increasingly used credential-stealing malware delivered through phishing instead of traditional encryption ransomware.
- The rise of remote and hybrid work environments, along with accelerated cloud adoption, expanded the attack surface globally.
- Attackers shifted toward data exfiltration and extortion, stealing data instead of encrypting it.
- Malware-free attacks increased, making detection more challenging.
- Unpatched vulnerabilities and legacy software remained major breach factors.
- Organizations struggled to distinguish anomalies from real threats due to more subtle intrusion tactics.
- Cybersecurity budgets increased, although security talent shortages persisted.
Types of Cyberattacks
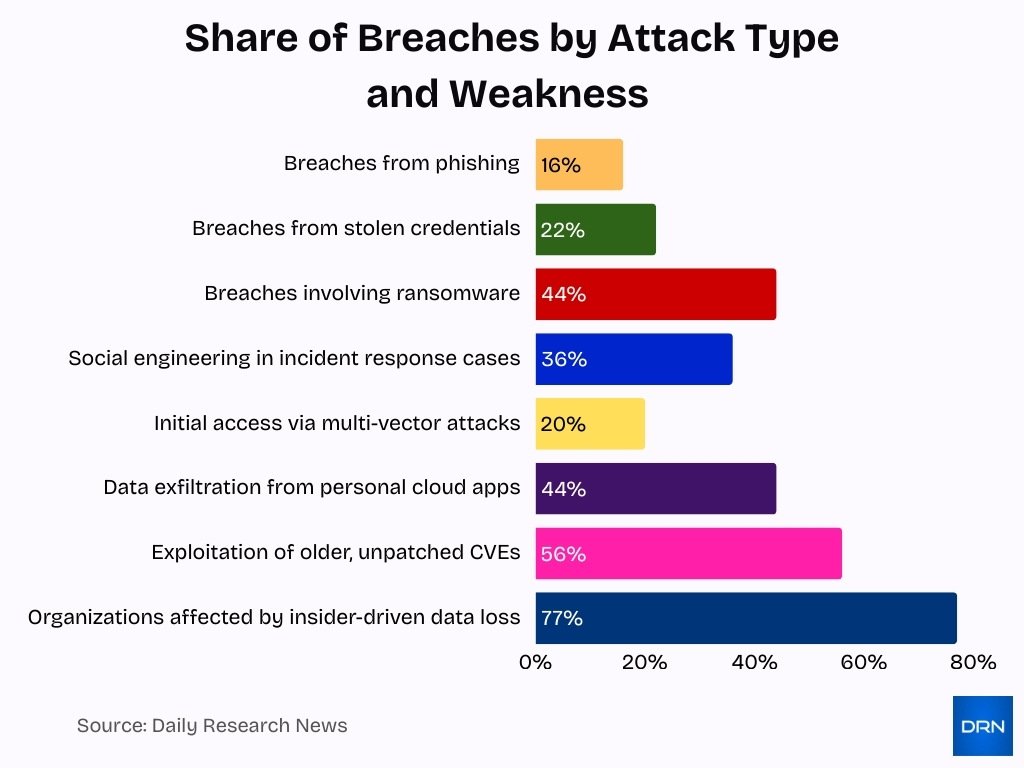
- Phishing attacks are involved in 16% of all breaches, with average costs of $4.8M.
- Stolen credentials caused 22% of breaches globally in 2025.
- Ransomware appeared in 44% of breaches, up from 32% in 2024.
- Global ransomware attacks rose 34% the first nine months of 2025.
- Infostealer malware contributed to 16 billion credential dumps from trojans.
- Social engineering initiated 36% of incident response cases in 2025.
- Multi-vector attacks exploited vulnerabilities in 20% of initial accesses.
- Data exfiltration from personal cloud apps originated 44% of attempts.
- Unpatched vulnerabilities remained exploited in 56% of older CVEs.
- Insider threats caused data loss in 77% of organizations over 18 months.
Ransomware Attack Trends
- There were 4,701 confirmed ransomware incidents in the first nine months of 2025, a 34% increase year over year.
- 45% of organizations identified ransomware as their top risk in 2025.
- Ransomware attacks increased 13% between 2020 and 2025.
- The average ransom payment fell to $1.0 million from $2.0 million in 2024.
- 97% of organizations regained access to encrypted data via backups, decryption tools, or ransom payment.
- Ransomware shifted toward data theft and extortion rather than file encryption.
- Sectors most affected included finance, healthcare, and manufacturing.
- Ransomware added significant downtime, remediation, and legal exposure costs for companies.
Phishing and Social Engineering
- An estimated 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent daily.
- Phishing-delivered infostealers increased 84% year over year.
- Phishing now commonly precedes credential theft and identity-based attacks.
- 93% of businesses and 95% of charities experiencing cyber incidents reported phishing involvement.
- Remote work and cloud adoption expanded phishing exposure.
- Phishing often serves as the first step in multi-stage cyberattacks.
- Employee behavior remained a critical defense, leading to increased training investments.
- Phishing continues to be a low-cost, highly effective tactic for attackers.
Malware Statistics
- Malware incidents contributed to 40% of data breaches in 2023, rising 30% year-over-year.
- Malware-free attacks accounted for 79% of detected threats in 2024, up from 40% in 2019.
- Infostealers harvested 1.8 billion credentials from 5.8 million devices in 2025.
- Daily new malware samples averaged 450,000–560,000 in 2024.
- Median dwell time for cyberattacks dropped to 8 days in early 2025.
- Ransomware attacks hit 59% of organizations in 2024.
- Unpatched vulnerabilities drove 32% of malware attacks via poor patch management.
- Supply chain attacks initiated more data breaches than ever in H1 2025.
- MaaS ecosystems like Lumma and Vidar dominated dark web markets in 2025.
Top Cybersecurity Concerns Reported by Business Owners
- GenAI model prompt hacking stands as the primary concern, noted by 46% of business owners, and the sentence reflects increasing unease about malicious prompt injection targeting generative AI systems.
- Large Language Model (LLM) data poisoning is identified as a significant issue by 38% of respondents, underscoring the dangers associated with corrupted AI training datasets.
- Ransomware as a service troubles 37% of business owners, emphasizing the persistent threat posed by readily available ransomware kits for cybercriminals.
- GenAI processing chip attacks were reported by 26%, indicating rising concern over hardware-level vulnerabilities tied to AI-specific workloads.
- API breaches worry 24%, highlighting the ongoing need to secure digital integration points within modern infrastructure.

DDoS Attack Frequency
- DDoS attacks rose by 170% in 2025 compared with 2024.
- There were approximately 30–40 million DDoS attack incidents in 2025.
- At peak periods, 3,700–3,800 attacks per hour occurred, about one every second.
- The largest attacks reached ~29.7 terabits per second (Tbps) with 14.1 billion packets per second.
- 71% of HTTP layer and 89% of network layer attacks ended within 10 minutes.
- Sectors most affected included telecom, gaming, financial services, and ISPs.
- IoT botnets drove many of the largest DDoS attacks.
- Rising attack volume reflected attacker sophistication and insecure connected devices.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
- Vulnerabilities associated with legacy systems, cloud growth, IoT, and staffing shortages increased breach costs.
- A security skills shortage raised breach costs to $5.22 million, versus $3.65 million for well-staffed teams.
- Third-party breach rates rose to 35.5% in 2025.
- Hybrid work and cloud migration exposed new vulnerabilities.
- Poorly governed AI adoption created emerging security risks.
- Many breaches stemmed from unpatched known vulnerabilities.
- High system complexity correlated with higher breach costs.
- OT and IoT vulnerabilities increase risks in manufacturing and utilities.
Sources of Data Breaches
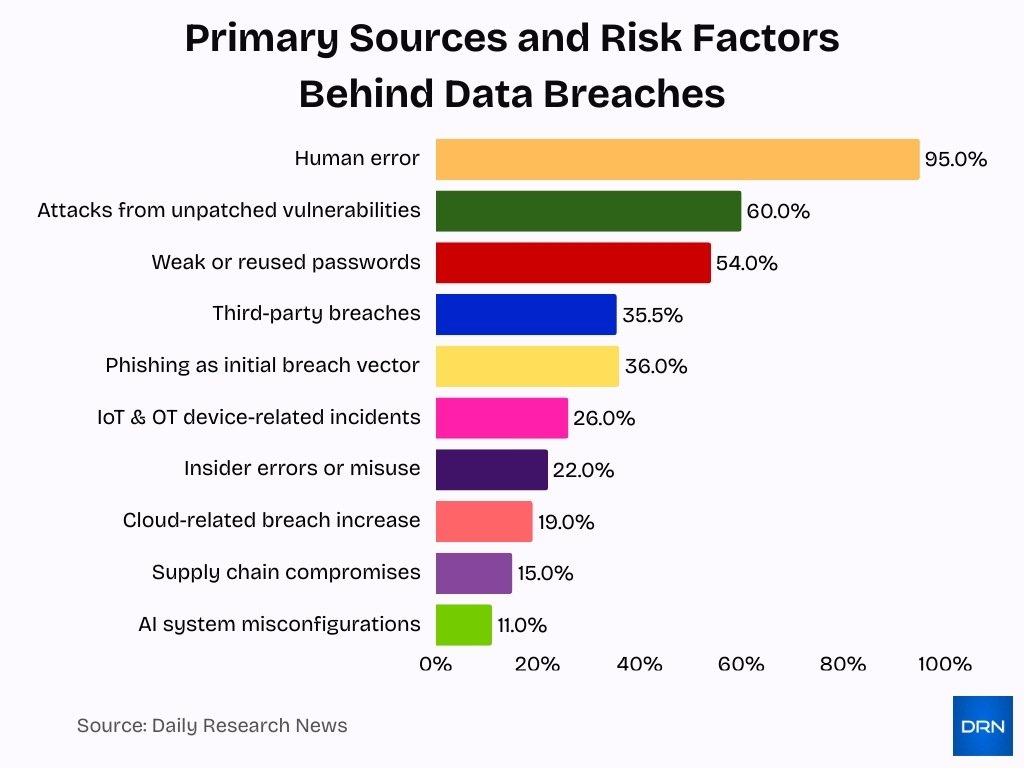
- Third-party breaches were responsible for 35.5% of all data breach incidents in 2024.
- Human error contributed to nearly 95% of cybersecurity breaches globally.
- Cloud-related breaches rose by 19% as hybrid work environments expanded.
- Unpatched vulnerabilities led to over 60% of successful attacks in organizations.
- Supply chain compromises accounted for approximately 15% of major data breaches.
- Weak or reused passwords caused 54% of credential-based attacks.
- IoT and OT devices were linked to 26% of security incidents in 2024.
- AI system misconfigurations were exploited in about 11% of new cyberattacks.
- Phishing emails were the initial vector in 36% of confirmed breaches.
- Insider errors or misuse contributed to around 22% of all breach cases.
Costs of Cybercrime
- Global cybercrime is projected to reach $10.5 trillion annually in 2025.
- Analysts expect further cost growth in the coming years.
- The global average breach cost fell slightly to $4.44 million in 2025.
- U.S. breaches averaged $10.22 million, the highest worldwide.
- The average cost per compromised record was ~$160.
- Detection and escalation averaged $1.47 million per breach.
- Breaches taking over 200 days to contain averaged $5.01 million.
- 51% of breach costs occur in the first year.
- Self-reported cybercrime losses rose 219% among large firms.
Breach Costs by Sector
- Healthcare breach costs averaged $7.42 million in 2025.
- Healthcare breach costs fell from $9.77 million in the previous year.
- Financial services ranked second for the highest breach costs.
- Some public sector and small enterprise breaches had lower average costs.
- Security skills shortages raised breach costs across sectors.
- Internally detected breaches averaged $4.18 million, compared with $5.08 million for external discovery.
- Sectors handling large personal data volumes faced higher per-record costs.
- Organizations with stronger cybersecurity practices saw reduced breach costs.
Top Major Data Breaches in History
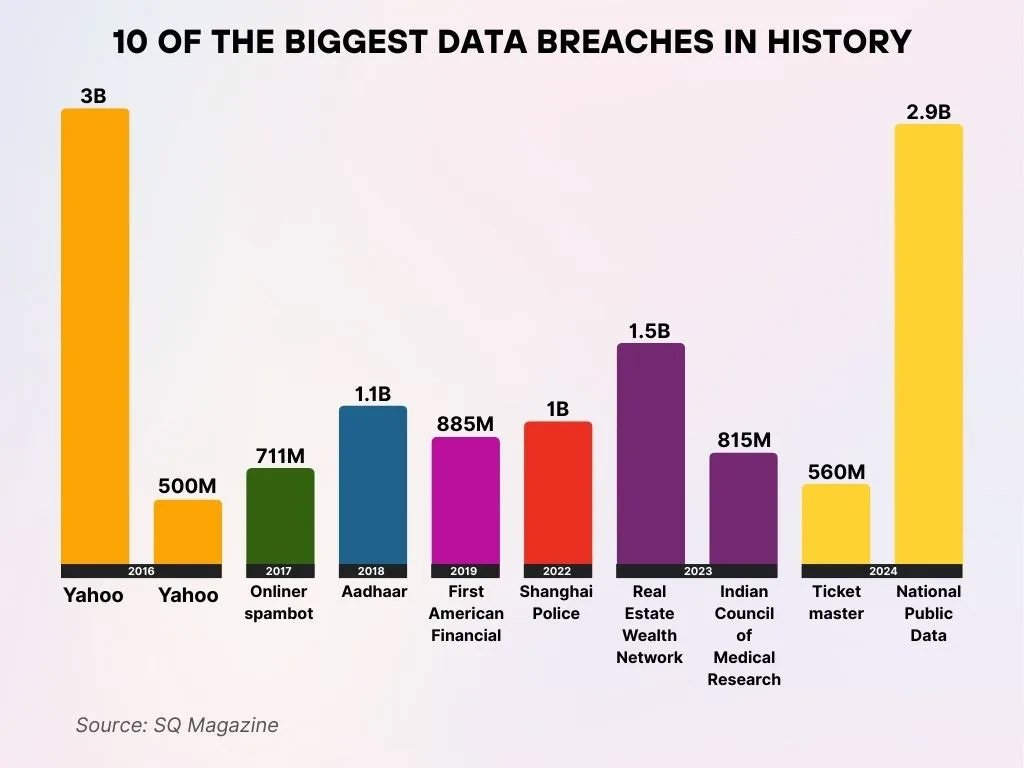
- Yahoo (2016) leads the list with 3 billion records compromised, marking the largest data breach ever recorded.
- A second Yahoo (2016) incident exposed an additional 500 million accounts in another major breach.
- The Onliner spambot (2017) breach impacted 711 million email addresses, which were used to run massive spam campaigns.
- India’s Aadhaar (2018) database breach compromised 1.1 billion citizen records, raising serious privacy concerns.
- First American Financial (2019) leaked 885 million sensitive real estate documents due to poor security controls.
- The Shanghai Police (2022) breach exposed 1 billion citizens’ records in one of the largest government data leaks.
- Real Estate Wealth Network (2023) saw 1.5 billion records compromised, highlighting significant risks in property tech platforms.
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (2023) breach affected 815 million health-related records, worsening data security concerns.
- Ticketmaster (2024) suffered a breach involving 560 million user records, severely impacting customer trust and security.
- The National Public Data (2024) breach exposed 2.9 billion records, ranking as the second-largest breach ever.
Impact of Cyberattacks
- Cybercrime costs reached $10.5 trillion annually.
- The average global breach cost, $4.44 million, excludes long-term impact.
- U.S. breaches averaged $10.22 million.
- Per record costs reached ~$160.
- Long detection times increased breach severity.
- Healthcare and financial firms faced higher consequences due to sensitive data.
- Cyberattacks damaged customer trust and brand reputation.
- Multi-vector attacks amplified overall business disruption.
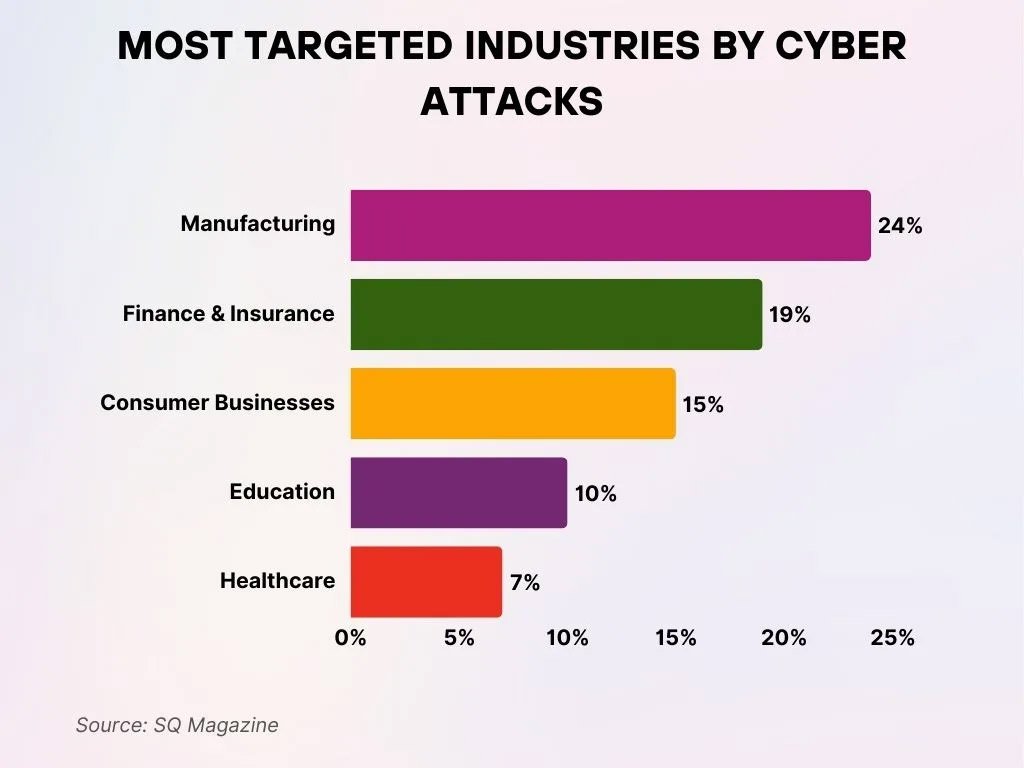
Most Frequently Targeted Industries by Cyber Attacks
- Manufacturing leads the ranking with 24% of all cyber attacks, emphasizing its heightened vulnerability caused by automation and supply-chain integration.
- Finance & Insurance comes next, representing 19% of attacks, as cybercriminals increasingly pursue sensitive financial data and high-value transactions.
- Consumer Businesses endure 15% of attacks, illustrating the risks linked to customer-facing platforms and expanding e-commerce operations.
- The Education sector encounters 10% of attacks, often because of outdated systems and the growing dependence on digital learning tools.
- Healthcare suffers 7% of attacks, with cyber threats directed at patient data, medical devices, and critical hospital infrastructure.
Healthcare Cyber Threats
- Healthcare breaches averaged $7.42 million per incident, the highest across industries.
- The global data breach average stood at $4.44 million, far below healthcare costs.
- U.S. healthcare breaches cost $10.22 million on average due to fines and detection.
- The first half of 2025 saw 29 million individuals affected by healthcare breaches.
- Healthcare organizations faced 1,426 attacks per week in recent years.
- Ransomware attacks on healthcare surged 30% in 2025.
- 88% of healthcare workers opened phishing emails in 2024.
- 90% of healthcare cyberattacks are phishing scams.
- Confirmed healthcare ransomware breaches exposed 7.4 million records in 2025 Q1-Q3.
Financial Sector Risks
- Financial services accounted for 34% of global DDoS attacks, the highest-targeted sector.
- 65% of financial organizations faced ransomware attacks in 2024, up from 64% in 2023.
- ENISA recorded 432 cyber attacks on finance from January 2023 to June 2024, with banks being hit the most at 46%.
- 42.5% of detected fraud attempts in financial services are now AI-driven.
- The average data breach cost in the financial sector reached $6.08 million per incident.
- 12.8% of global B2B finance firms suffered ransomware attacks in 2025.
- Financial services saw a 23% rise in application-layer DDoS attacks from 2023-2024.
- Phishing spearphishing caused 30% of finance sector breaches per the IBM 2025 Index.
Cybercrime for Small Businesses
- 46% of global data breaches in 2025 affected SMBs.
- 37% of ransomware victims had fewer than 100 employees.
- Common SMB attack types included malware (18%), phishing (17%), and data breaches (16%).
- Most SMBs lacked a robust cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Many small firms struggled to recover financially after cyberattacks.
- Ransomware as a service has increased attacks on SMBs.
- SMBs suffered from slow detection and response due to limited resources.
- Retail, hospitality, and service SMBs remained especially vulnerable.
Regions Most Affected
- The United States faced 86% of North American cyber incidents in 2025.
- Ukraine endured 2,052 cyberattacks in 2024, leading global frequency.
- Israel recorded 1,550 attacks in 2024 amid regional conflicts.
- Japan accounted for 66% of APAC incidents per IBM X-Force 2025.
- The United Kingdom saw over 100 million malicious attempts in one quarter.
- Saudi Arabia represented 63% of Middle East cyber incidents.
- Brazil comprised 53% of LATAM incidents, topping the region.
- India is hit with 12.4% of global endpoint malware attacks.
- Germany endured 18% of Europe’s cyber incidents in 2024.
- Poland faced 20-50 daily cyberattacks from Russian actors.
Future Cyber Trends
- AI-driven cybercrime expected to power fully automated attacks by 2026, transforming threat scale and speed.
- Credential theft incidents surged by 300% in 2025, outpacing traditional methods like ransomware.
- IoT malware attacks hit manufacturing and transportation at 20.2% each of total incidents in 2025.
- 820,000 daily hacking attempts target IoT devices in 2025, up 46% year-over-year.
- OT cybersecurity incidents rose in 2025, with 19% taking over a month to remediate.
- 60% of cyber breaches in SMBs stem from third-party vendors via supply chain flaws.
- 94% of SMBs faced cyberattacks in 2024, driving an urgent need for affordable defenses.
- The Zero Trust market in North America is expected to hit $3.5 billion by 2026 amid rising adoption.
- 78% of organizations deem cyber resilience insufficient, prioritizing business continuity plans.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The global average cost of a data breach in 2025 is $4.44 million.
Global cybercrime is projected to cost around $10.5 trillion in 2025.
Confirmed ransomware incidents increased by 34% year-over-year in the first three quarters of 2025 compared to the same period in 2024.
The average cost per compromised record in 2025 is about $160
Conclusion
Cybersecurity is no longer a niche concern; it has become a central business risk across industries, company sizes, and regions. The data shows that no sector is immune, from global manufacturing chains to small business storefronts, healthcare systems to financial institutions; the threat landscape is broad and evolving. As attackers shift toward credential theft, AI-driven phishing, and supply chain exploitation, organizations must adjust accordingly.
The years ahead will reward those who adopt proactive, identity-first security, invest in detection and response capabilities, and stay vigilant, because staying static is no longer an option.