Prompt engineering has become a cornerstone of modern AI workflows as generative models like GPT and Gemini move from niche tools to enterprise infrastructure. Businesses use prompt design to shape outcomes in customer support, code generation, and data analysis, directly impacting efficiency and decision‑making. For example, structured prompting can reduce AI errors by up to 76%, improving output quality for marketing teams and automating repetitive tasks in development workflows. This article unpacks the latest statistics and trends that define prompt engineering’s rapid rise and wide‑ranging influence in AI systems.
Editor’s Choice
- The global prompt engineering market is projected to exceed $6.7 billion by 2034, growing over 30% annually.
- 88% of organizations report regular AI use across business functions, a clear driver of prompt engineering demand.
- 80% of enterprises will use generative AI by 2026, with prompt engineering as a core skill.
- Weekly generative AI adoption at companies jumped from 37% to 72% year‑over‑year.
- Developers using AI tools daily reached 51% in 2025.
- Roles like prompt engineer grew by 135.8% in 2025.
- Structured prompting improves satisfaction with AI implementations by 34%.
Recent Developments
- AI adoption across businesses continues to gain momentum, with 88% of organizations using AI in at least one function in 2025.
- Weekly generative AI adoption rose from 37% to 72% year‑over‑year in corporate settings.
- 51% of developers report daily use of AI tools in workflows.
- Jobs tied to AI prompting and related skills surged: prompt engineer roles expanded by 135.8% in 2025.
- A surge in prompt engineering training programs and certifications reflects workforce demand.
- Structured prompt design increases satisfaction with AI implementations by 34%.
- Gartner predicts 75% of enterprises will adopt generative AI with prompt engineering at the core by 2026.
- Enterprise integration of GenAI APIs will reach 80% by 2026, expanding prompt engineering usage.
Global Prompt Engineering Market Expansion Overview
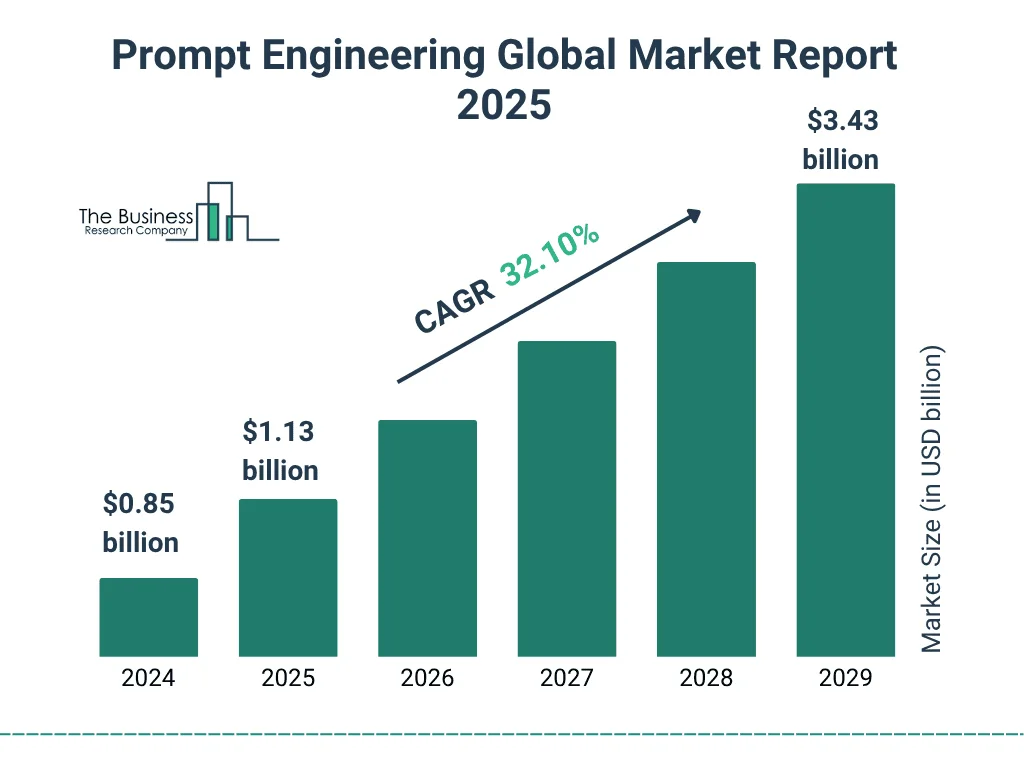
- The global prompt engineering market is valued at $0.85 billion in 2024, highlighting its early-stage yet rapidly scaling adoption phase across emerging AI-driven applications.
- The market size increases to $1.13 billion in 2025, clearly signaling strong and accelerating demand from enterprises and developers worldwide.
- Continued expansion is projected as the market reaches $1.52 billion in 2026, driven by deeper AI integration across multiple industries.
- By 2027, prompt engineering is expected to generate $2.01 billion, reflecting the broader commercialization of generative AI tools and platforms.
- Growth accelerates further to $2.66 billion in 2028, fueled by advanced prompt optimization techniques and workflow automation adoption.
- The market is forecast to reach $3.43 billion by 2029, underscoring its transition into a core and strategic AI capability for organizations.
- Overall market growth stands at a strong 32.10% CAGR, positioning prompt engineering as one of the fastest-growing segments within the AI ecosystem.
History and Evolution of Prompt Engineering
- Prompt engineering emerged alongside early large language models.
- Initial research cast NLP tasks as question‑answer problems.
- Techniques like chain‑of‑thought prompting appeared in 2022.
- Public prompt repositories grew significantly by 2024.
- Prompt methods diversified rapidly with research publications.
- Standardized prompt vocabularies now support research and practice.
- Academic surveys reflect increased methodological rigor in the field.
- Prompt engineering moved from trial‑and‑error to structured frameworks.
How Large Language Models Work
- GPT-4 features approximately 1.8 trillion parameters.
- LLMs trained on datasets exceeding 15 trillion tokens, like Llama-3.
- ChatGPT reaches 501 million monthly users with 74.2% market share.
- Gemini models support context windows up to 1 million tokens.
- Claude offers 200,000-token context windows for extended inputs.
- RAG boosts factual accuracy by 7.9% and reduces hallucinations.
- Prompt engineering lifts few-shot accuracy from 8% to 51%.
- LLM market valued at $10.57 billion in 2026, growing 34.44% CAGR.
Effective Prompt Engineering Best Practices
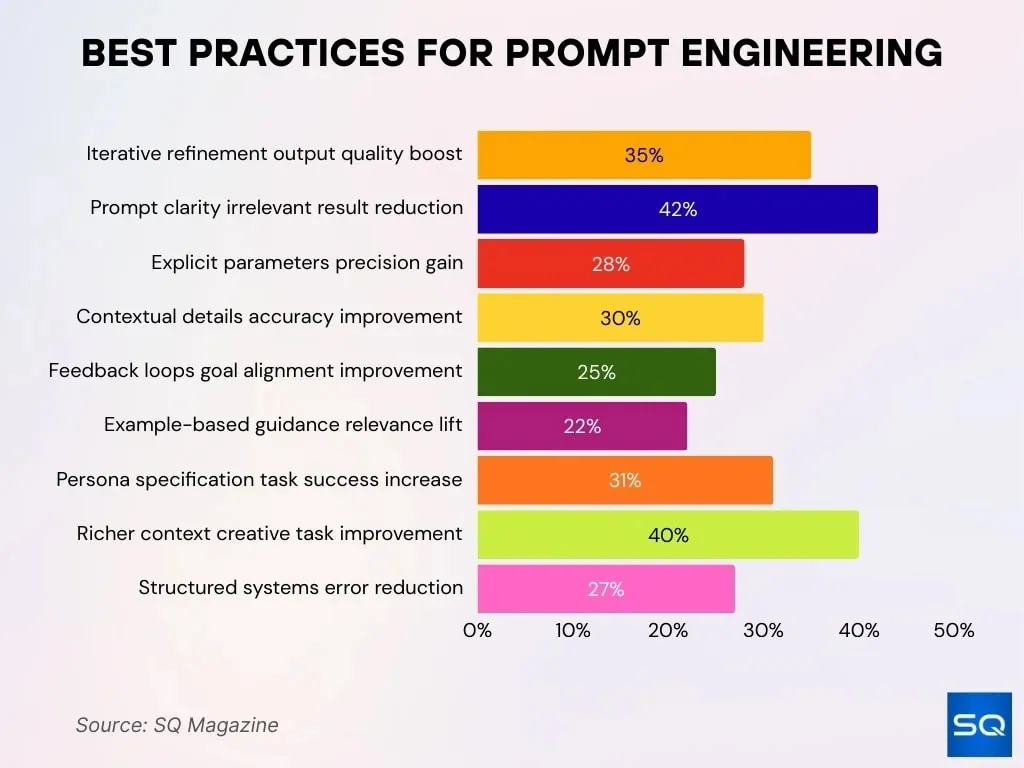
- Iterative refinement significantly improves overall output quality by 35%, enabling continuous optimization through repeated prompt adjustments.
- Unambiguous prompts lower the occurrence of irrelevant or off-target results by 42%, improving response alignment.
- Explicit parameters and constraints raise response precision by 28%, ensuring more controlled and predictable outputs.
- Detailed contextual information enhances response accuracy by 30%, allowing models to better interpret intent.
- Feedback loops and iterative validation align model outputs 25% better with predefined goals and expectations.
- Example-based guidance and demonstrations increase content relevance by 22%, especially in complex task scenarios.
- Persona specification and role definition boost task completion success rates by 31%, improving contextual consistency.
- Richer contextual framing supports creative tasks 40% more effectively, enabling nuanced and imaginative outputs.
- Structured prompt systems and templates reduce overall error rates by 27%, improving reliability and consistency.
Key Components of an Effective Prompt
- Prompts that clearly define task, context, and output format improve model accuracy by up to 45%, according to controlled enterprise tests.
- Adding explicit constraints, such as word limits or tone, reduces irrelevant responses by 32%.
- Including examples inside prompts improves task completion rates by 38% compared to instruction‑only prompts.
- Prompts that specify the intended audience outperform generic prompts in business use cases by 29%.
- Step‑based instructions increase reasoning accuracy in analytical tasks by 41%.
- Explicit formatting requests, such as tables or bullet points, cut post‑processing time by 27% for teams.
- Ambiguous prompts increase hallucination risk by 2.3x, especially in factual queries.
- Enterprises that standardize prompt components report 34% faster onboarding for AI tools.
Types of Prompts Used in AI Systems
- Instruction‑based prompts account for over 60% of enterprise AI interactions in 2025.
- Context‑rich prompts improve relevance scores by up to 40% in customer support applications.
- Question‑answer prompts remain the most common format in search and RAG workflows.
- Role‑defined prompts reduce tone mismatches in marketing copy by 31%.
- Data‑driven prompts outperform free‑text prompts in analytics tasks by 46%.
- Constraint‑based prompts lower unsafe outputs by 22% in regulated industries.
- Multi‑input prompts, combining text and data, are now used by 44% of AI‑enabled enterprises.
- Hybrid prompts mixing instructions and examples deliver the highest consistency scores.
Zero‑Shot, One‑Shot, and Few‑Shot Prompting
- Zero‑shot prompting dominates simple classification tasks, used in over 70% of basic workflows.
- One‑shot prompting improves accuracy by 18% compared to zero‑shot in structured tasks.
- Few‑shot prompting boosts performance by up to 35% in complex reasoning problems.
- Few‑shot methods require larger context windows, increasing token usage by 20–40%.
- Developers favor few‑shot prompting for code generation in 52% of use cases.
- Zero‑shot prompting remains preferred for real‑time systems due to lower latency.
- Enterprises balance cost and accuracy by mixing zero‑shot and few‑shot strategies.
- Model performance gaps between zero‑shot and few‑shot narrowed by 12% in newer LLMs.
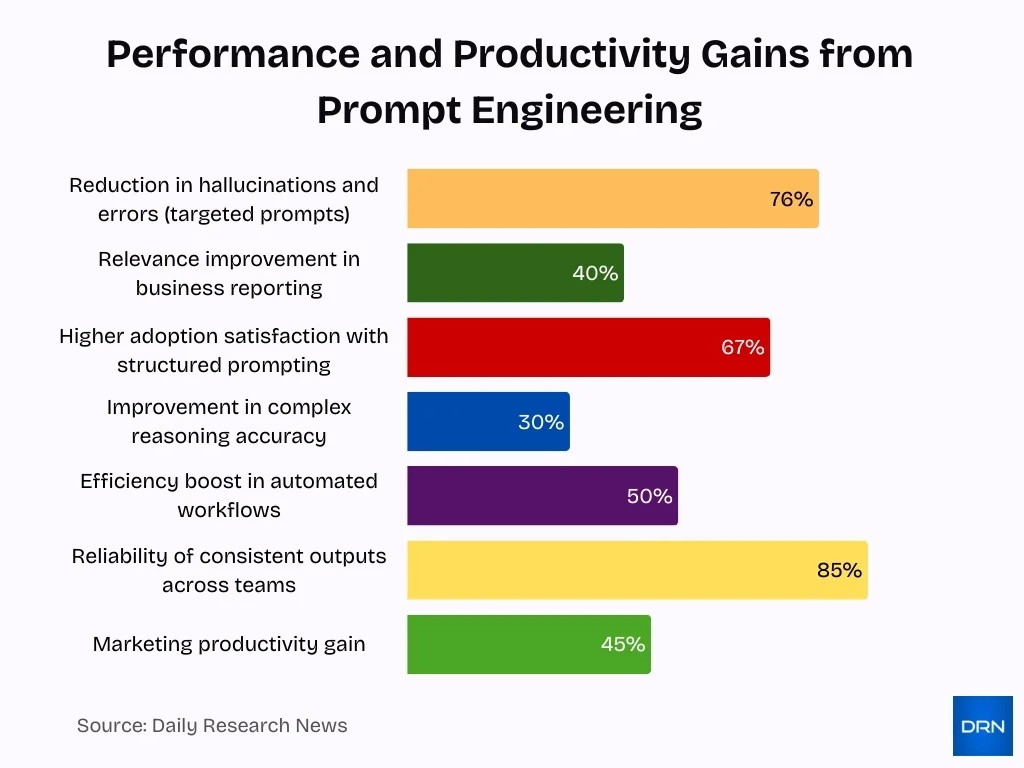
Why Prompt Engineering Matters for AI Performance
- Targeted prompts reduce AI hallucinations and errors by up to 76%.
- Clear prompts improve relevance in business reporting and analytics by 40%.
- Enterprises using structured prompting report 67% higher adoption satisfaction.
- Prompt design enhances complex reasoning accuracy by 30% in LLMs.
- Prompting boosts efficiency in automated workflows by 25-50%.
- Quality prompts ensure consistent outputs across teams with 85% reliability.
- Prompt engineers command $126K-$335K salaries due to surging demand.
- Impact spans marketing (45% productivity gain), coding, customer service, and data tasks.
Chain‑of‑Thought and Tree‑of‑Thought Prompting
- Chain‑of‑thought prompting improves reasoning accuracy by up to 58% in math and logic tasks.
- Tree‑of‑thought prompting outperforms linear reasoning in multi‑step decision problems by 41%.
- These techniques increase token usage by 2–4x, impacting inference cost.
- 63% of AI researchers now test reasoning prompts during model evaluation.
- Chain‑of‑thought prompts reduce logical errors in financial analysis workflows by 37%.
- Tree‑based approaches show higher success rates in planning and strategy simulations.
- Enterprises apply chain‑of‑thought prompting mainly in analytics and compliance use cases.
- Automated reasoning prompts are becoming standard in AI benchmarking.
Role and Persona‑Based Prompting
- Persona‑based prompts improve tone alignment by up to 33% in customer‑facing content.
- Marketing teams report 29% higher engagement when AI uses defined brand personas.
- Role prompts reduce revision cycles by 24% in content workflows.
- Developers use system‑role prompts in over 65% of production AI deployments.
- Persona prompts help reduce bias by enforcing neutral or professional roles.
- Customer support bots using persona prompts achieve higher CSAT scores.
- Role‑based prompts improve internal documentation clarity by 21%.
- Enterprises increasingly maintain persona libraries for AI consistency.
Prompt Chaining and Multi‑Step Prompts
- Prompt chaining improves task completion rates by up to 42% in complex workflows.
- Multi‑step prompts reduce manual intervention in automation pipelines by 36%.
- Chained prompts increase latency by 15–25%, requiring performance trade‑offs.
- 48% of AI teams now use prompt chains for data processing tasks.
- Prompt chaining enhances explainability in regulated environments.
- Multi‑step prompts improve consistency in long‑form content generation.
- Error propagation remains a key risk in poorly designed chains.
- Tools supporting prompt chaining saw adoption growth of over 40% year‑over‑year.
Structured Prompting With Templates and Formats
- Template‑based prompting improves output consistency by up to 50%.
- Enterprises using prompt templates report 31% faster deployment of AI workflows.
- Structured prompts reduce formatting errors by 44% in reporting tasks.
- JSON‑based prompts are now used in over 55% of API‑driven AI applications.
- Templates help non‑technical users adopt AI tools more quickly.
- Structured prompting improves integration with downstream systems.
- Prompt libraries cut duplicate work by 28% across teams.
- Organizations standardizing prompts report higher governance compliance.
How Prompt Engineering Roles Are Expected to Evolve
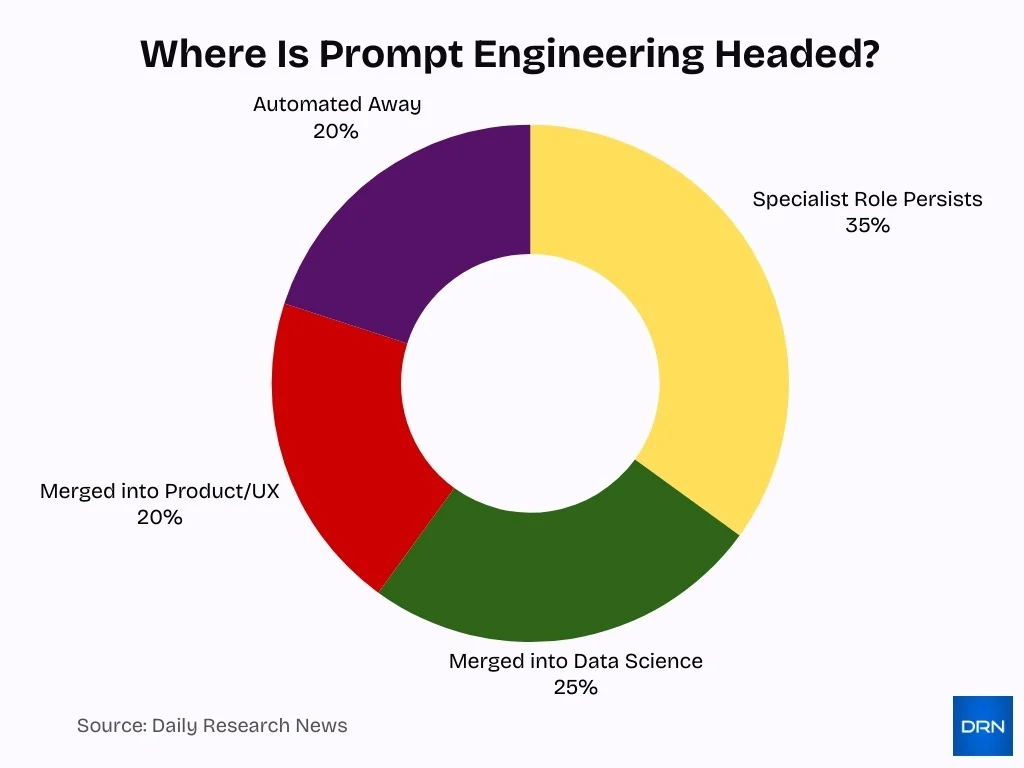
- 35% of industry respondents indicate that prompt engineering will continue as a specialized role, underscoring long-term demand for dedicated AI interaction expertise.
- 25% expect prompt engineering responsibilities to merge into data science, signaling tighter alignment with model optimization, analytics, and AI workflows.
- 20% believe the function will be absorbed into product and UX teams, highlighting the rising importance of AI-driven user experience and interface design.
- Another 20% anticipate prompt engineering being automated away, reflecting confidence in advanced tooling, self-optimizing models, and automated prompt systems.
Prompt Engineering for Text, Code, and Data Analysis
- Prompt engineering is used in >60% of AI‑assisted code generation workflows in 2025, helping automate unit tests, documentation, and debugging tasks.
- Teams using carefully engineered prompts report up to 42% fewer syntax errors in AI‑generated code.
- In data analytics, structured prompts improve insight relevance by ~38% compared with generic queries.
- Summarization and extraction tasks in legal and healthcare workflows see 50–65% faster turnaround with optimized prompts.
- Enterprise BI teams that embed prompt templates in dashboards report a 30% increase in actionable insights.
- Code generation models guided by examples (few‑shot prompting) outperform zero‑shot alternatives by 25–35% on complex tasks.
- Prompt engineers often act as liaisons between data teams and developers, reducing translation errors by 41%.
- Prompt frameworks paired with automated testing tools enhance reliability in ML workflows by up to 27%.
Prompt Engineering for Search and RAG Workflows
- Search and RAG (retrieval‑augmented generation) workflows now rely on engineered prompts in 55–70% of AI‑search deployments.
- Prompt design improves RAG precision by ~40% over simple keyword‑based templates.
- Teams applying refined query prompts cut irrelevant results by 30% in enterprise search applications.
- In RAG systems, curated prompt prefixes increase factual accuracy by 25–33%.
- Fine‑tuned prompts improve relevance ranking in hybrid RAG models by 28–36%.
- Prompt context windows extended with dynamic metadata improve topical coverage by 29%.
- Enterprises using guided RAG frameworks reduce hallucinations in retrieval tasks by 22%.
- Prompt tuning for search helps reduce latency in large corpora by 15–18%.
Prompt Engineering Skill Demand Breakdown
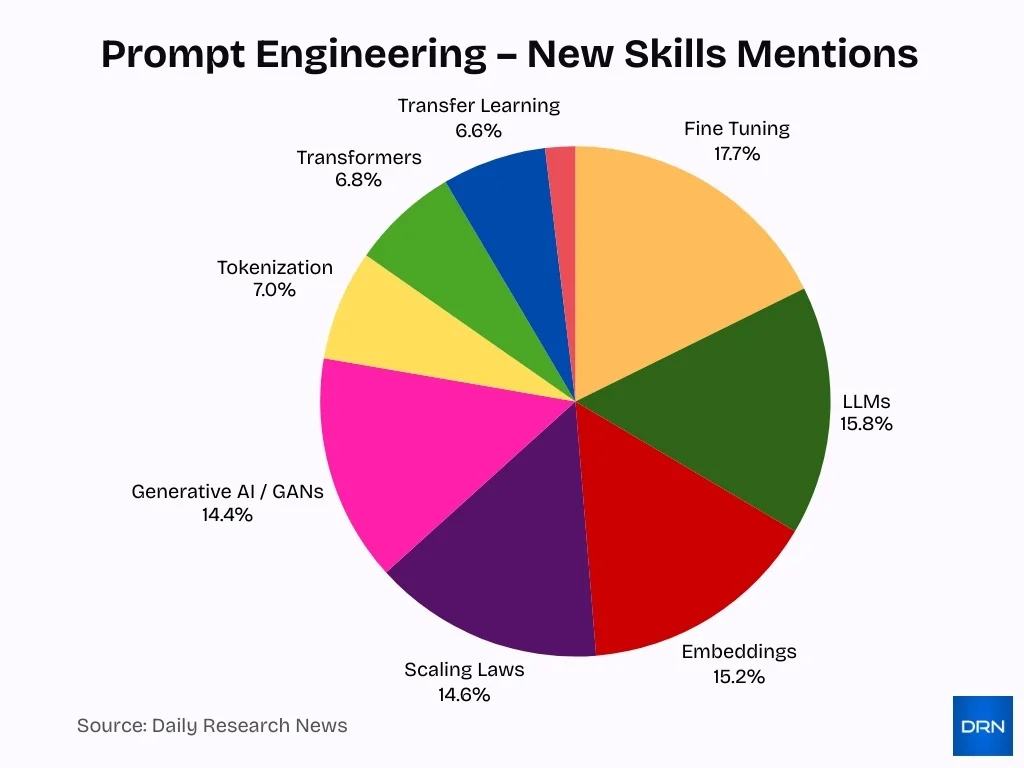
- Fine-tuning leads all new skill mentions at 17.7%, highlighting a strong industry focus on model customization and performance optimization.
- LLMs account for 15.8% of mentions, underscoring the growing importance of large-scale language model expertise across AI roles.
- Embeddings represent 15.2%, reflecting increased demand for semantic search, retrieval, and vector-based AI applications.
- Scaling Laws capture 14.6%, signaling heightened interest in model scaling strategies and performance predictability.
- Generative AI / GANs hold 14.4%, emphasizing continued momentum in content generation and creative AI systems.
- Tokenization contributes 7.0%, indicating its role as a foundational skill for efficient model training and inference.
- Transformers make up 6.8%, showing the sustained relevance of core neural architectures behind modern AI models.
- Transfer Learning stands at 6.6%, reinforcing its value in reducing training costs and accelerating deployment.
- Inference Efficiency, at 1.9%, remains a niche but emerging focus, suggesting future growth as production AI scales.
Prompt Engineering for Multimodal Models
- On multimodal reasoning benchmarks, top models now reach around 70–80% accuracy on complex image‑text tasks.
- Structured visual‑text prompts can improve task accuracy by roughly 5–25 percentage points compared with text‑only prompts on VQA‑style tests.
- Comprehensive multimodal surveys cover performance across over 80 benchmarks and more than 200 evaluation datasets for MLLMs.
- A leading image‑text benchmark (SEED‑Bench) includes about 24,000 multiple‑choice questions spanning 27 evaluation dimensions and 22 MLLMs.
- Dynamic subtitle systems that combine gaze, video, and text inputs achieve over 92% average accuracy, improving precision and recall by more than 8% versus static subtitles.
- Automatic captioning platforms for clear audio commonly report 90–98% accuracy, with typical systems averaging around 95% for English videos.
- Major ASR engines from Google, Microsoft, and Amazon show word‑error rates near 15–18%, corresponding to roughly 82–85% caption accuracy.
- Accessibility research notes that people with disabling hearing loss could exceed 900 million globally by 2050, underscoring demand for audio‑text prompting tools.
- Multimodal LLM benchmark suites now track over 20 distinct capability dimensions across perception, reasoning, and other modalities to evaluate prompt strategies.
Safety, Bias, and Ethical Issues in Prompting
- Approximately 40% of companies report AI‑related privacy or safety incidents, illustrating risks when prompts interact with sensitive data.
- Public trust in AI is low; ~70% of adults don’t trust companies to use AI responsibly.
- Prompt design can inadvertently propagate bias if not checked, especially in high‑stakes domains like hiring and lending.
- Surveys show that bias mitigation is a top ethical concern for >50% of AI teams.
- Safety benchmarks for multimodal AI indicate current systems misclassify unsafe content at meaningful rates, calling for better prompting controls.
- Ethical prompting often includes explicit fairness constraints and contextual framing to reduce stereotyping.
- Responsible prompt engineers now embed guardrails that avoid offensive or harmful outputs by default.
- Best practices emphasize transparent design, audit trails, and inclusive datasets to address ethical gaps.
Prompt Engineering Manager Average Salaries Across Industries
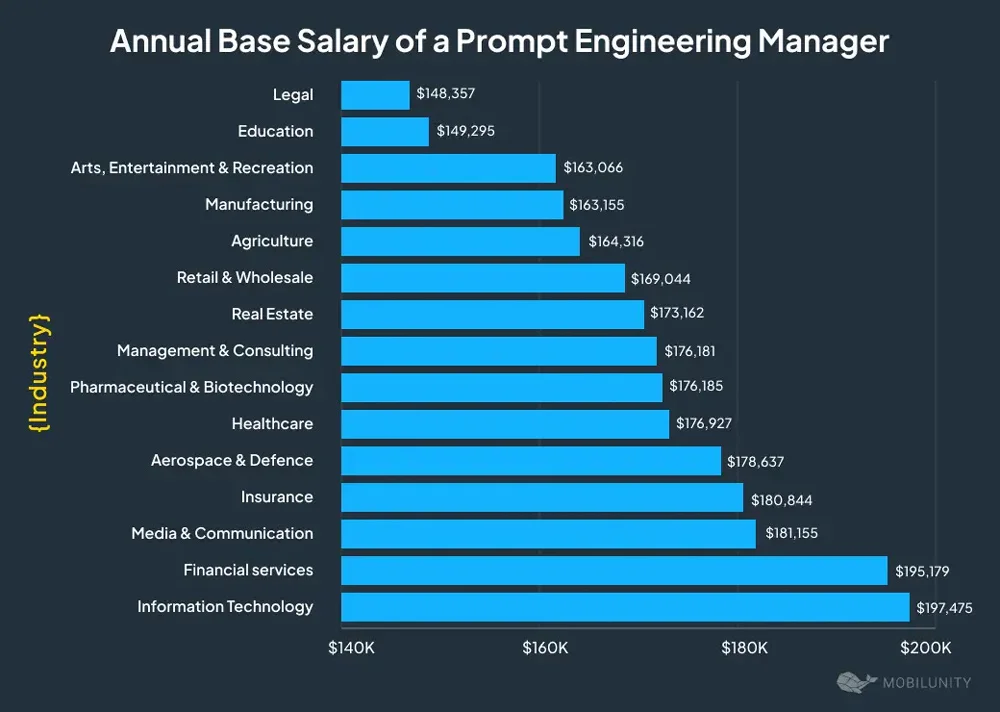
- Information Technology tops compensation benchmarks with an average base salary of $197,475, underscoring strong demand for advanced AI expertise within tech-driven organizations.
- Financial Services ranks closely behind, providing $195,179 in average pay, propelled by AI adoption across trading, risk modeling, and automation workflows.
- Media and Communication professionals earn approximately $181,155, emphasizing the strategic importance of prompt engineering in content intelligence and audience analytics.
- Insurance positions deliver an average salary of $180,844, supported by expanding AI applications in underwriting efficiency and claims optimization.
- Aerospace and Defence roles command about $178,637, where precision-driven, compliance-intensive AI systems are mission-critical.
- Healthcare compensation reaches $176,927, fueled by AI deployment across diagnostics, operational efficiency, and patient engagement initiatives.
- Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology roles pay nearly $176,185, reflecting AI’s growing influence in research acceleration and drug discovery.
- Management and Consulting averages $176,181, as firms increasingly monetize prompt engineering expertise across client AI transformation strategies.
- Real Estate offers around $173,162, driven by AI-powered valuation models, predictive forecasting, and customer engagement tools.
- Retail and Wholesale roles earn roughly $169,044, supported by AI-driven personalization and demand forecasting capabilities.
- Agriculture averages $164,316, as AI adoption expands into precision farming and supply chain optimization.
- Manufacturing reports mean salaries of $163,155, where AI enhances automation, efficiency, and quality control processes.
- Arts, Entertainment, and Recreation see compensation near $163,066, reflecting rising demand for creative AI and generative content applications.
- Education positions average $149,295, highlighting slower but steadily increasing institutional AI adoption.
- Legal remains the lowest-paying sector at $148,357, although AI usage continues to grow in compliance, analysis, and legal research.
Security and Prompt Injection Risks
- Prompt injection vulnerabilities allow attackers to insert malicious instructions into prompts, leading to data leakage or manipulation.
- Cybersecurity agencies classify prompt injection as a critical AI threat akin to traditional vulnerabilities.
- Real‑world examples show that prompt injection can compromise tools with a single malicious input.
- Some experts warn that prompt injection might never be fully mitigated due to foundational LLM architecture limits.
- Prompt injections have been used in practice to steer models into revealing sensitive information.
- Ongoing research highlights that even robust commercial models remain partially vulnerable to injection attacks.
- Prompt security is now a regular part of red‑team testing frameworks at major AI providers.
- Best defenses combine prompt sanitization with access controls, anomaly detection, and continuous monitoring.
Future Trends in Prompt Engineering and AI Prompting
- Prompt engineering job postings have surged by 250–400% YoY globally, making it one of the fastest‑growing AI careers in tech.
- AI‑related roles listing prompt engineering as a required skill have grown over 300% since 2023, especially in developer and product roles.
- Surveys show over 60% of AI‑focused job descriptions now mention prompt design, tuning, or optimization as core responsibilities.
- By 2026, demand for prompt engineers is projected to exceed 200,000 professionals worldwide as enterprises scale generative AI.
- Emerging prompt libraries and orchestration frameworks are shifting teams from ad‑hoc prompts to standardized, reusable prompt toolchains across projects.
- Multimodal prompt engineering is expanding rapidly, with models increasingly combining text, images, audio, and structured data in a single composite prompt.
- Enterprises are embedding governance into prompts, with ethics‑first multimodal AI roadmaps emphasizing fairness, transparency, and privacy as standard prompting requirements.
- AI‑native toolchains now automate large parts of prompt evaluation, A/B testing, and regression checks, integrating directly into QA workflows.
- Training providers report a spike in enrollments for prompt engineering courses, reflecting its emergence as a core AI literacy skill across non‑technical roles.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The global prompt engineering market is projected to reach roughly $6.7 billion by 2034, up from about $505 billion in 2025.
The global prompt engineering market is forecast to grow at a CAGR of ~33% between 2025 and 2034.
The prompt engineering market was valued at approximately $380 million in 2024 and is expected to be around $505 million in 2025.
By 2026, approximately 75% of enterprises are expected to utilize generative AI with prompt engineering as a core capability.
Conclusion
Prompt engineering remains central to how humans and machines interact. Across text, code, search, and multimodal tasks, the right prompt can dramatically shape the quality, relevance, and safety of AI results. While ethical challenges and prompt injection risks persist, industry focus on safeguards, fairness, and robust prompting methods is rising.
As AI evolves, prompt engineering will continue to expand, not just as a technical skill but as a foundational practice embedded across roles and industries, ensuring AI delivers value while minimizing harm in an increasingly automated world.