Remote work reshaped the world of work, offering flexibility and broader talent access. Yet as millions of employees operate outside traditional office walls, cybersecurity risks have surged, demanding fresh data and strategic responses. From increased phishing campaigns to more exposed personal devices, organizations must adapt fast. For businesses, failing to secure remote environments can mean higher breach costs, lost data, and reputational damage.
In healthcare, law firms, and financial services, remote vulnerabilities have already triggered major incident responses. Let’s dive into the latest Remote Work Cybersecurity Statistics and explore what the numbers reveal about today’s threat landscape.
Editor’s Choice
- 78% of organizations reported at least one remote work-related security incident in 2025.
- The global average cost of a data breach in 2025 was $4.44M, and breaches involving remote work factors were about $0.17M more expensive than those without.
- Phishing attacks were the most cited threat by 60% of companies.
- Approximately 42% of employees worked remotely weekly in 2025.
- Phishing accounted for 43% of initial breach attempts in remote setups.
- Ransomware attempts numbered in the tens of thousands per day by late 2025.
- Phishing emails sent daily reached 3.4 billion globally.
Recent Developments
- As of early 2026, 25–30% of work remains remote, even as many companies tighten return-to-office mandates.
- Remote work expands the attack surface, increasing opportunities for cybercriminals to target unprotected endpoints.
- AI-assisted phishing and deepfake impersonation attacks have increased, exploiting remote communication habits.
- Credential theft surged 160% in 2025, now accounting for one in five data breaches.
- Cyber adversaries are accelerating automated scans, exceeding 36,000 per second globally.
- Nation-state actors are leveraging AI to intensify spear phishing and disinformation targeting US businesses.
- Remote work fraud schemes, such as sham remote job placements, continue as an ongoing cybercrime strategy.
Remote Work and Cybersecurity Statistics Overview
- Remote work adoption remains permanent, as 74% of organizations state that remote working is here to stay, signaling long-term shifts in workforce models.
- Cybersecurity threats are rising alongside remote work, with 65% of organizations reporting an increase in cybersecurity incidents due to expanded digital and remote access points.
- Existing security frameworks are falling behind, as 48% of organizations believe that cybersecurity needs to evolve to effectively address modern remote work risks.

Rise in Cybersecurity Threats
- 78% of firms encountered at least one remote work security incident in 2025.
- Remote work threats have increased by about 30% as work-from-home grows.
- 42% of workers access company systems remotely weekly, broadening exposure.
- Phishing is the top threat vector, cited by 60% of companies.
- Ransomware accounted for about 44% of breaches in broader cybersecurity contexts in 2025.
- Home network and personal device vulnerabilities persist without enterprise controls.
- Organisations report weakened cybersecurity postures due to remote infrastructure reliance.
Common Cybersecurity Incidents
- Phishing remains the most common incident type in remote settings.
- A typical organization faced ~1,000 attempted remote cyberattacks per month in 2025.
- Unsecured personal devices accounted for 22% of endpoint weaknesses exploited.
- Credential theft is now present in 20% of data breaches.
- Malware and infostealers continue to harvest large volumes of credentials and session data.
- Ransomware cases saw triple extortion tactics in most incidents.
- Remote-related breaches often result in legal and regulatory complications.
Ransomware and Malware Trends
- Global ransomware damage costs are projected to be $57B in 2025.
- Ransomware attempts may reach tens of thousands daily by late 2025.
- In 76% of ransomware incidents, attackers also stole data for leverage.
- Many ransomware attacks now refuse to pay the ransom (only ~23% pay).
- Infostealer malware harvested billions of credentials in 2025.
- North America accounted for 53% of known ransomware attacks in Q2 2025.
- Remote infrastructure remains a key entry point for malware deployment.
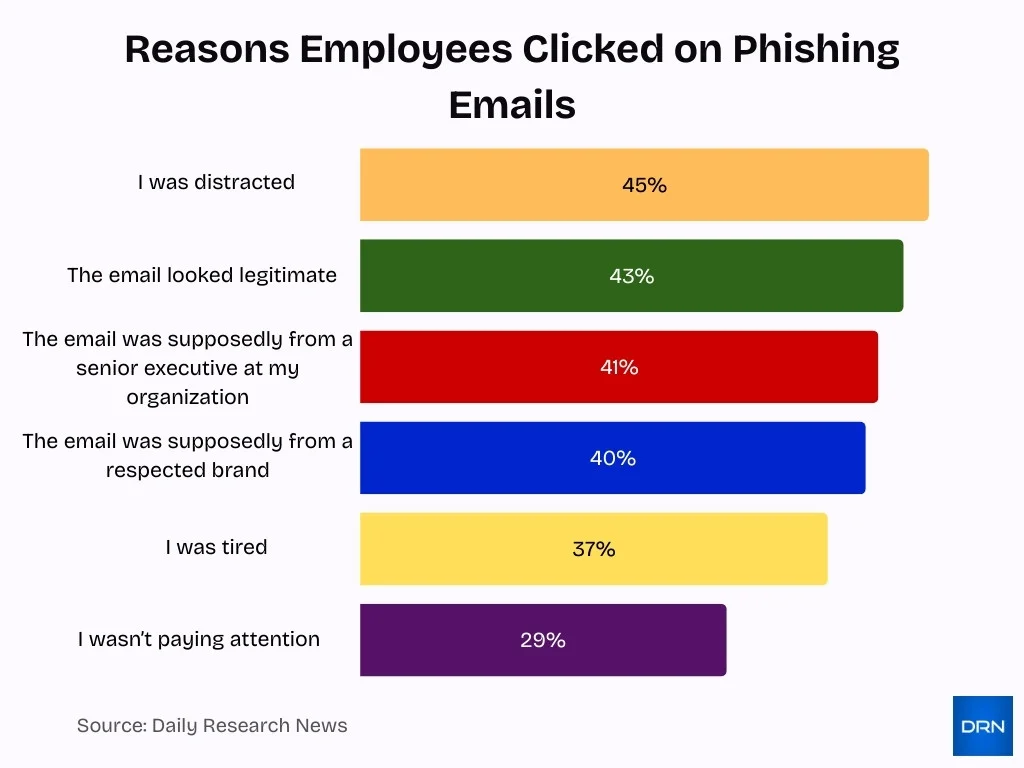
Why Employees Click on Phishing Emails
- Distraction is the leading cause, with 45% of employees admitting they clicked on phishing emails because they were distracted at the time.
- Email credibility strongly influences behavior, as 43% clicked because the phishing message looked legitimate.
- Executive impersonation remains highly effective, with 41% of employees fooled by emails claiming to be from a senior executive within their organization.
- Brand trust abuse is a major risk factor, as 40% clicked phishing emails that appeared to come from a respected brand.
- Employee fatigue contributes significantly, with 37% reporting they clicked phishing emails because they were tired.
- Lack of attention continues to be a concern, as 29% of employees clicked phishing emails simply because they weren’t paying attention.
Cloud Security Risks
- 69% of organizations report cloud security challenges stemming from tool sprawl and lack of visibility, worsening risk exposure.
- 66% of companies feel not confident in detecting or responding to cloud threats in real time.
- 88% use hybrid or multi-cloud environments, increasing complexity and security gaps.
- 77% identify identity and access issues within cloud configurations as a top risk factor.
- Misconfigurations account for a significant 70% of cloud security challenges in remote environments.
- 66% cite data exposure as a core vulnerability in cloud systems.
- Cloud misconfigurations contributed to 17% of remote work security incidents in 2025.
- Many cloud security postures remain in early stages, and about 59% of firms report immature controls.
- Organizations increasingly allocate ~34% of IT security budgets to cloud security, reflecting its critical priority.
VPN and Access Misconfigurations
- Misconfigured VPNs accounted for 14% of data leaks linked to remote work vulnerabilities in 2025.
- VPN exploitation is seen as a primary threat by 95% of organizations concerned about cloud and network risks.
- Study data shows that the rise of remote work triggered a significant increase in VPN targeted attacks post 2020.
- Poor access control and weak authentication practices remain common causes of unauthorized entry points.
- VPN misconfigurations often correlate with insecure credential management and inadequate MFA deployment.
- Remote workers frequently use personal networks that lack enterprise-grade security, further exposing VPN gateways.
- Legacy VPN setups without zero-trust policies are more prone to exploitation in remote environments.
- Combining VPN with multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly lowers compromise rates.
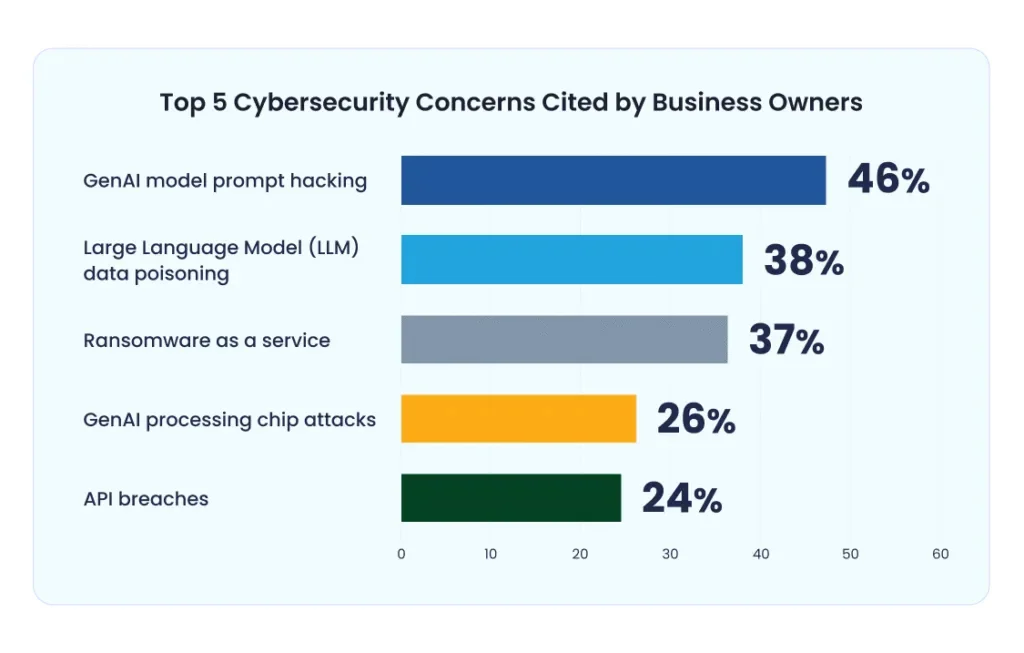
Key Cybersecurity Risks Facing Business Owners Today
- 46% of business owners express concern over GenAI model prompt hacking, positioning it as the leading cybersecurity threat in the current AI landscape.
- 38% identified Large Language Model (LLM) data poisoning as a significant risk to the reliability and integrity of AI-driven systems.
- 37% are worried about Ransomware as a Service, underscoring continued anxiety around evolving cybercrime business models.
- 26% fear GenAI processing chip attacks, drawing attention to hardware-level vulnerabilities within AI infrastructure.
- 24% view API breaches as a notable cybersecurity risk, emphasizing the critical need to secure integration points.
Home Network Vulnerabilities
- 86% of users never change their router default admin passwords, exposing networks to easy compromise.
- 52% of routers run unchanged factory settings, amplifying home network attack risks.
- 84% of organizations have high-risk vulnerabilities in network hosts, common in home setups too.
- 60% of companies host unpatched critical vulnerabilities in 2025, including remote home endpoints.
- 88% of remote workers skip VPNs on home networks, risking data interception.
- IoT devices face 820,000 hacking attempts daily in 2025, turning homes into intrusion points.
- 50% of home routers retain default credentials or outdated firmware, heightening breach risks.
- 33% of organizations fully implement network segmentation, correlating with fewer breaches in remote setups.
- 14% of breaches now stem from exploited vulnerabilities like poor home network defenses.
BYOD Device Risks
- Around 60–70% of employees use personal devices for work tasks, regardless of whether formal BYOD policies exist.
- 78% of employees use personal devices for work even when policies forbid it.
- Unmanaged BYOD devices contribute to over 90% of ransomware incident roots, per industry data.
- Personal laptops and hotspots are increasingly linked to access control failures.
- Lack of standardized security controls on BYOD devices complicates endpoint protection.
- BYOD usage without proper containerization or device management elevates data leak risks.
- Secure BYOD frameworks, including MDM and identity verification, reduce compromise likelihood.
- IT leaders rank unmanaged devices as one of the top challenges in remote work security.
Jobs With the Highest Remote Work Adoption
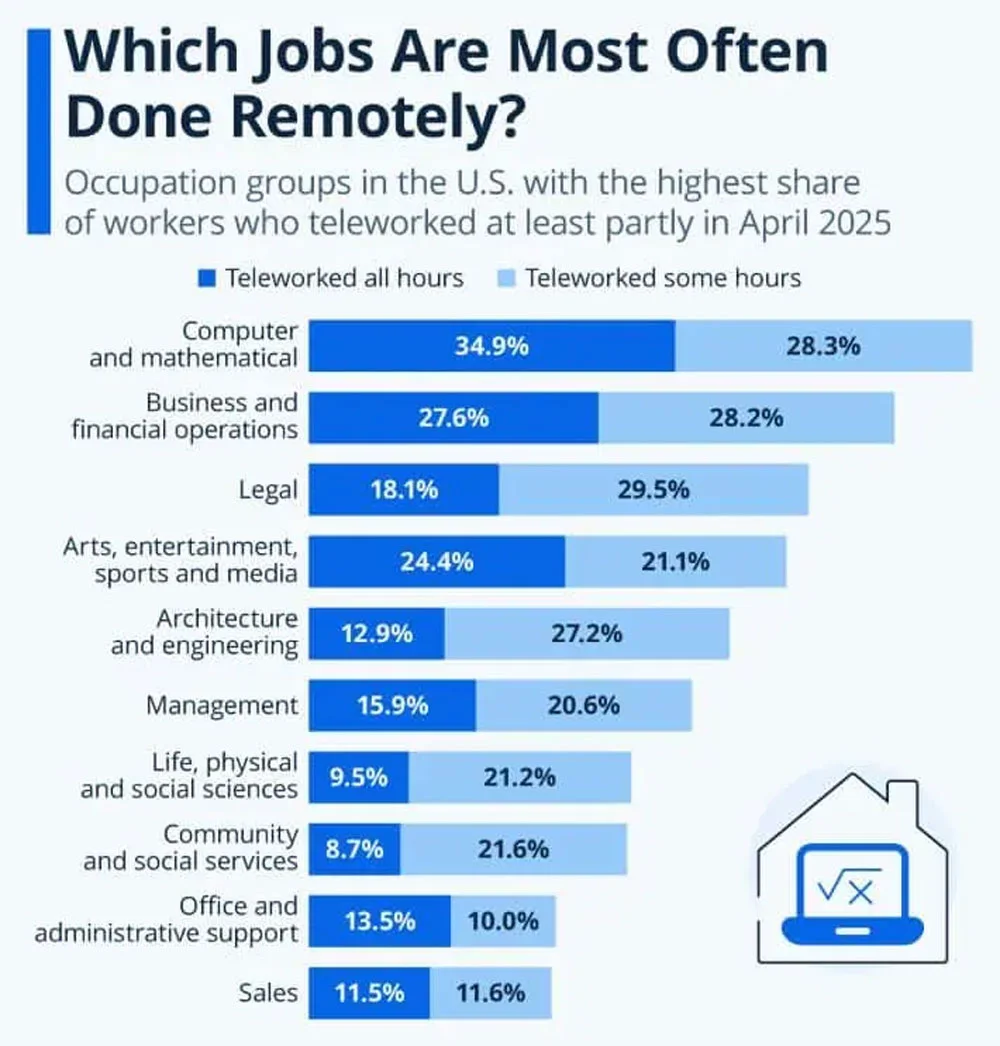
- Computer and mathematical occupations lead remote work adoption, with 34.9% of workers teleworking all hours and another 28.3% working some hours remotely.
- Business and financial operations roles show strong hybrid patterns, as 27.6% worked fully remotely while 28.2% teleworked part of their schedule.
- Legal professionals are more likely to work in hybrid models, with 29.5% teleworking some hours compared to 18.1% working entirely remotely.
- Arts, entertainment, sports, and media jobs maintain high flexibility, with 24.4% working all hours remotely and 21.1% combining on-site and remote work.
- Architecture and engineering roles favor partial remote work, as 27.2% teleworked some hours, while only 12.9% worked fully remotely.
- Management positions reflect moderate remote adoption, with 15.9% working all hours remotely and 20.6% following a hybrid approach.
- Life, physical, and social science occupations rely more on hybrid setups, with 21.2% teleworking some hours versus 9.5% working fully remotely.
- Community and social services roles remain largely on-site, though 21.6% teleworked some hours and 8.7% worked entirely remotely.
- Office and administrative support jobs show limited remote flexibility, with 13.5% teleworking all hours and 10.0% doing so part-time.
- Sales roles are evenly split between remote models, with 11.5% working fully remotely and 11.6% teleworking some hours.
Insider Threat Statistics
- 54% of IT leaders believe remote work increases insider threat risks, including negligent behavior.
- Insider threats span malicious actions and unintentional data loss from authorized users.
- Nearly half of security teams cite data leakage from insiders as a top concern.
- 61% reported experiencing insider-related breaches involving unauthorized data access.
- The average cost of insider incidents in reported studies reached $2.7M.
- Limited monitoring capabilities hamper early detection of insider activity.
- Only ~40% can detect file-based threats quickly, increasing dwell time for attackers.
- Organizational policies and awareness efforts remain uneven in addressing insider risks.
Top Security Concerns
- Nearly 2/3 of organizations experienced a cloud security incident in the past year, up 61% from previous reports.
- 77% of cloud security respondents cite identity and access management issues as a primary concern.
- Misconfigurations remain the #1 threat, causing 52% of unauthorized access incidents in cloud environments.
- 66% of security professionals worry about data exposure in distributed remote work settings.
- 92% of organizations fear ransomware via VPN vulnerabilities, with 93% concerned about third-party backdoors.
- Phishing attacks surged 61% in 2022, remaining the top threat to remote workforces with 16% of breaches.
- Insider threats rose 58% post-remote work, with negligent users causing 63% of incidents.
- Only 26% of organizations have full real-time threat detection, creating major security gaps.
- Unmanaged IoT/OT devices comprise 42% of assets but 64% of high risks, with 33% of breaches involving IoT.
Data Breach Impacts
- The global average cost of a data breach in 2025 was $4.44M, with the US average exceeding $10M.
- Remote work as a factor increased breach costs by roughly $173,000 per incident.
- Cybercrime is projected to cost the world $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
- Regulatory fines and legal expenses continue to climb with remote-related breaches.
- Data loss per breach often involves tens of thousands of records.
- Legal costs from remote work incidents can exceed $400,000 per case.
- Customer trust impact after a remote breach affected 74% of organizations.
- Secondary attacks frequently follow initial breaches due to inadequate response strategies.
Top Motivations for Choosing Remote Work Across Countries
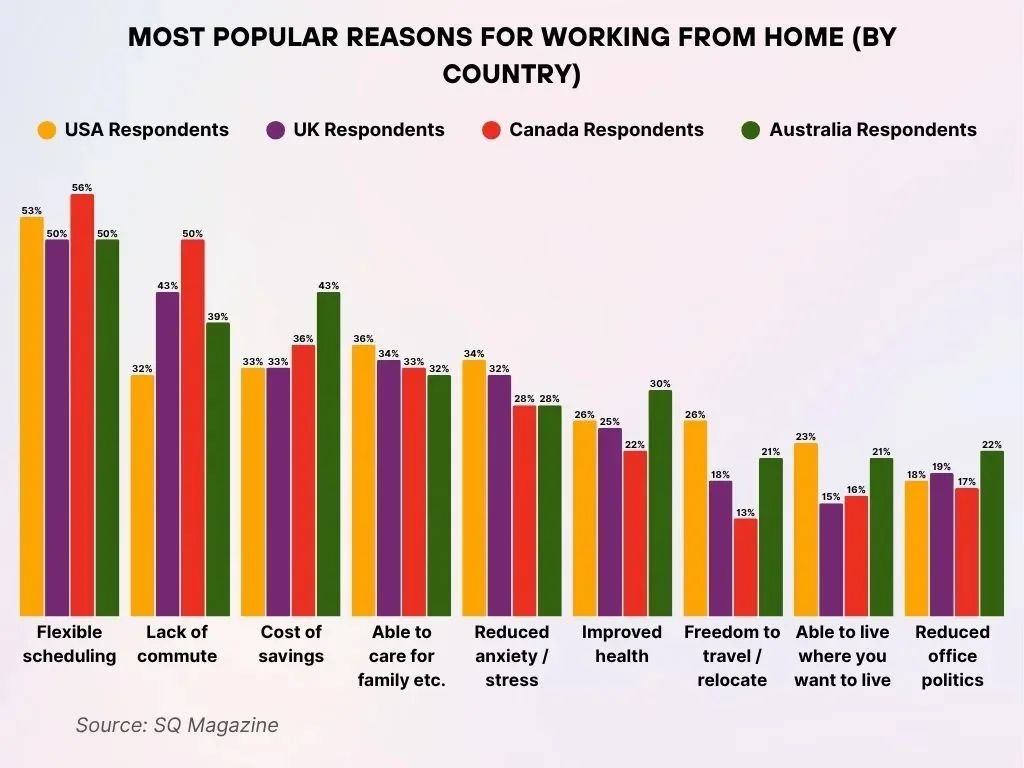
- Flexible scheduling stands out as the leading advantage across all surveyed countries, with particularly strong appeal in Canada (56%) and the USA (53%).
- Eliminating daily commutes is highly appreciated in Canada (50%), followed by the UK (43%) and Australia (39%), underscoring time and convenience benefits.
- Cost savings resonate most strongly with workers in Australia (43%), compared to Canada (36%), while both the USA and UK report 33% citing this as a key reason.
- Caring for family, pets, or relatives is most important to respondents in the USA (36%), closely followed by the UK (34%), highlighting personal responsibility factors.
- Lower anxiety and reduced stress levels are a significant motivator for 34% in the USA, with both Canada and Australia at 28% emphasizing mental well-being.
- Improved overall health, including mental, physical, or spiritual well-being, is more strongly emphasized in Australia (30%), ahead of the USA (26%).
- Freedom to travel or relocate is valued by 26% of Americans, while only 13% of Canadians consider it a major benefit of working from home.
- The ability to live where you prefer appeals more to Americans (23%) and Australians (21%), compared to 15% in the UK.
- Reduced office politics matters most to workers in Australia (22%), while it is a lower priority in Canada (17%) and the USA (18%).
Adoption of Security Tools
- 74% of US organizations increased spending on endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools to protect remote devices in 2025.
- 68% of companies now deploy multi-factor authentication across all remote access points, up from 59% in 2024.
- Zero-trust network access adoption reached 61% among mid to large US enterprises supporting remote work.
- 57% of IT teams report expanding cloud security posture management (CSPM) tools to address misconfigurations.
- Secure access service edge (SASE) usage grew 23% year over year as firms consolidated remote access security.
- 49% of organizations adopted mobile device management (MDM) specifically to reduce BYOD risk.
- Email security gateway investments increased 18% in response to phishing-driven remote breaches.
- Firms using integrated security platforms reported 30% faster incident response times than tool-fragmented peers.
Employee Training Metrics
- 56% of breaches in remote settings involved human error, highlighting training gaps.
- Organizations conducting quarterly security training saw 45% fewer phishing clicks than those training annually.
- 64% of US employees completed at least one cybersecurity awareness course in 2025, up from 52% in 2024.
- Simulated phishing programs reduced successful attacks by 37% within six months.
- Only 41% of remote workers feel confident identifying sophisticated phishing attempts.
- Companies tying training to real-world scenarios improved retention rates by 28%.
- 33% of organizations still rely on static, compliance-only training models.
- Security leaders rank employee education among the top three defenses for remote environments.
Compliance and Regulations
- 72% of US companies updated cybersecurity policies to align with remote work requirements under state and federal guidance.
- Compliance with frameworks like NIST and ISO 27001 increased 19% year over year.
- 48 states now enforce updated data breach notification laws affecting remote work incidents.
- GDPR related fines tied to remote access failures exceeded $1.6B globally in 2025.
- 61% of compliance leaders say remote work complicates audit readiness.
- Financial services firms face the highest remote-related compliance costs, averaging $2.1M annually.
- Automated compliance monitoring adoption grew 22% to offset distributed workforce risk.
- Regulators increasingly scrutinize identity management and access logs for remote users.
Major Cybersecurity Obstacles in Remote Work Settings
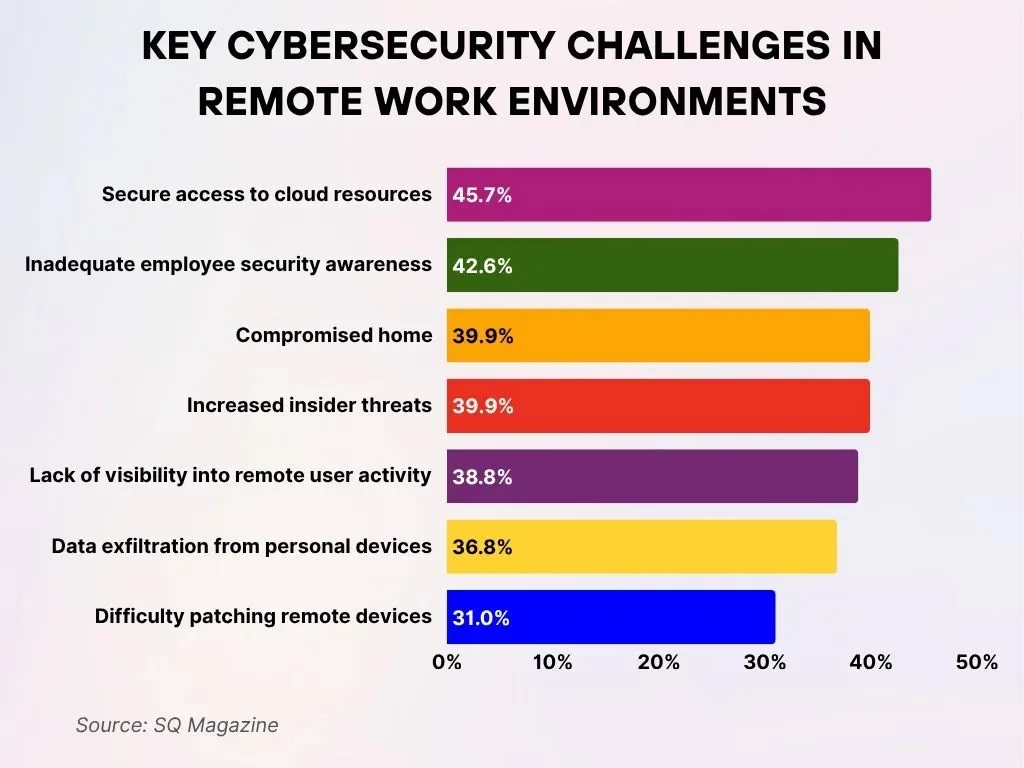
- 45.7% of organizations struggle with secure access to cloud resources, making it the most frequently cited challenge in remote work environments.
- 42.6% report issues due to insufficient employee security awareness, exposing organizations to vulnerabilities driven by human error.
- 39.9% face risks from compromised home networks, where security controls are weaker compared to traditional in-office environments.
- 39.9% also cite increased insider threats, highlighting ongoing trust, oversight, and monitoring concerns across distributed teams.
- 38.8% mention a lack of visibility into remote user activity, which directly limits effective threat detection and response.
- 36.8% are concerned about data exfiltration from personal devices, as employees increasingly blend work and personal technology.
- 31.0% struggle with patching remote devices, resulting in delays to critical security updates across remote endpoints.
Remote Work Security Posture & IT Leader Perspectives
- 67% of CISOs believe remote work permanently changed their organization’s threat model.
- 59% of IT leaders say visibility into remote endpoints remains their biggest challenge.
- Only 38% rate their current remote security posture as “highly mature.”
- 71% expect remote and hybrid work to remain core to operations through 2027.
- IT leaders report spending 20–25% more time managing access issues for remote users.
- 54% plan to replace legacy VPNs with zero trust solutions within two years.
- Security teams cite talent shortages as a barrier to improving remote defenses.
- Leadership alignment with security teams improves incident containment outcomes by 32%.
Workforce & Budget Trends Related to Remote Work Security
- Cybersecurity budgets grew 11% in 2025, with remote work cited as a key driver.
- 46% of security hires now focus on cloud and remote access expertise.
- Organizations allocate ~28% of security budgets to protecting distributed workforces.
- MSSP usage increased 21% as companies outsource remote security operations.
- 39% of SMBs report budget strain when securing remote teams.
- Wage premiums for remote security specialists rose 14% year over year.
- Budget reallocation away from perimeter security accelerated as offices downsized.
- Firms investing consistently in remote security show lower long-term breach costs.
Market Growth Statistics
- The global remote work security market reached $105.61B in 2025.
- North America holds ~43% of the market share in 2025.
- The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 22.44% through 2030.
- SASE solutions are expanding at a CAGR of 23.6% from 2025-2030.
- Endpoint security holds 33.4% market share in remote work security in 2025.
- The cloud security segment grows at a CAGR of 22% in remote work environments.
- SMB cybersecurity spending on remote tools rises at 15% CAGR to $109B by 2026.
- Identity security funding exceeded $300M in recent startup rounds amid AI growth.
- Asia-Pacific remote security market grows fastest at 25.4% CAGR through 2032.
- Over 80% of Fortune 500 firms adopted hybrid models with enhanced endpoint security.
Future Trends Shaping Remote Work Security
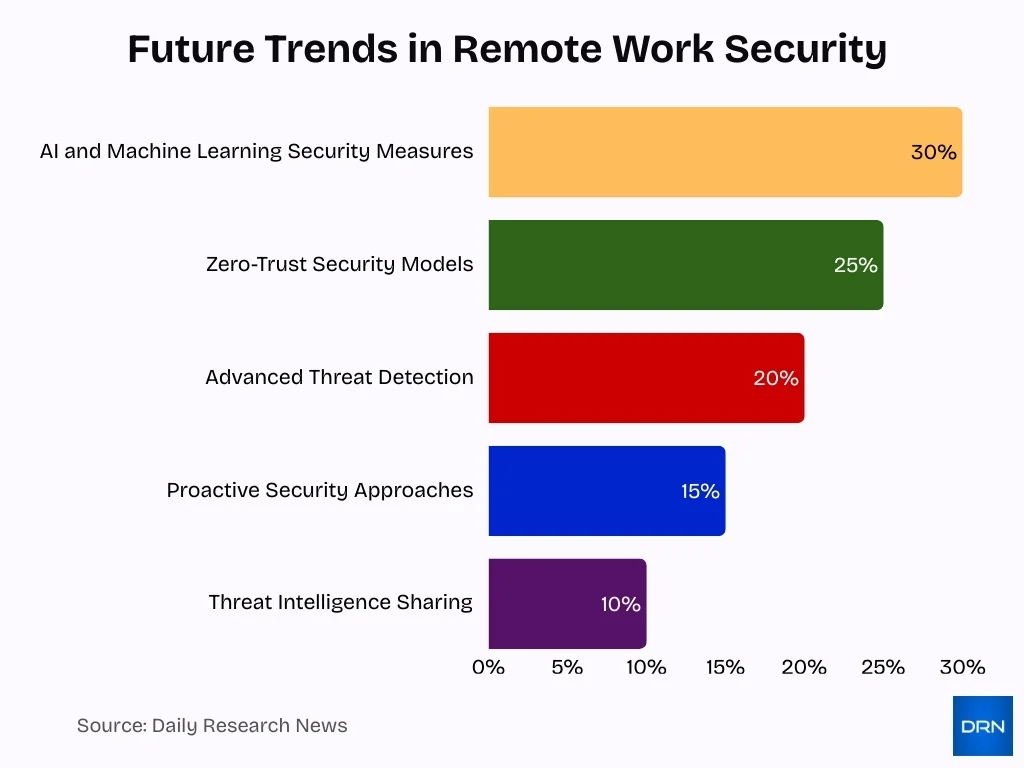
- AI and Machine Learning Security Measures lead the future of remote work protection, accounting for 30%, as organizations increasingly rely on automation to detect and respond to cyber threats in real time.
- Zero-Trust Security Models represent 25%, highlighting widespread adoption of strict identity verification and access controls for distributed and remote workforces.
- Advanced Threat Detection makes up 20%, underscoring the growing importance of behavioral analytics and continuous monitoring to identify sophisticated cyberattacks.
- Proactive Security Approaches account for 15%, reflecting a strategic shift toward prevention-focused cybersecurity frameworks rather than reactive incident response.
- Threat Intelligence Sharing contributes 10%, emphasizing collaborative efforts among organizations to exchange threat data and strengthen collective cyber resilience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
78% of organizations reported experiencing at least one remote work‑related cybersecurity incident in 2025.
The average cost of a remote work‑related breach in 2025 was approximately $4.56 million.
Phishing accounted for 43% of initial breach attempts in remote work environments in 2025.
About 42% of workers logged in remotely at least once per week in 2025, expanding the attack surface.
Conclusion
Remote work is no longer a temporary shift; it’s a permanent operating model that reshapes cybersecurity priorities. The data shows clear progress in tool adoption, training, and compliance, but also highlights persistent gaps in visibility, identity control, and workforce readiness. Organizations that invest consistently in people, process, and technology reduce both breach frequency and long-term costs.
As threats evolve alongside remote work itself, leaders who act on these statistics will be better positioned to protect data, maintain trust, and scale securely into the future.