Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) face a sharp rise in cyber threats as they unfold. More organizations rely on digital tools, yet many still lack robust security measures. This imbalance leaves SMBs highly vulnerable. In real-world terms, a local retailer may lose critical customer data through a phishing attack, or a small SaaS startup may suffer major downtime due to ransomware, undermining trust and draining resources. The statistics below highlight how pervasive and costly these threats have become. Explore the sections that follow to understand the full scope and implications.
Editor’s Choice
- 46% of small and medium-sized businesses reported experiencing a cyberattack in 2025.
- 94% of SMBs faced at least one cyberattack in 2024, showing how nearly universal the risk has become.
- 75% of SMBs said they could not continue operating if hit by ransomware.
- Only 20% of small businesses (SMBs) have implemented multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- On average, small businesses now lose around $120,000 per cyber incident, with typical recovery costs ranging from $120,000 to about $1.24 million depending on breach severity and response quality.
- Among businesses hit by cyber-attacks, over half lost more than 5% of their total revenue, and 15% lost more than 10% from a single incident.
- Only 17% of small businesses carried cyber insurance in recent surveys.
Recent Developments
- A 2025 industry report identified a 12% year-over-year increase in ransomware-related breaches.
- Cyberattack incidents against SMBs nearly doubled during the first half of 2025 compared with the prior year.
- Global cybersecurity spending is projected to exceed 213 billion dollars in 2025, up from 193B in 2024, yet threats and breach costs continue rising.
- Adoption of cloud services and remote tools continues to grow, widening the attack surface for small firms.
- AI-enabled cyberattacks are rising. In 2025, many phishing and malware campaigns will use AI to scale and evade detection.
- Smaller businesses, particularly those with fewer than 25 employees, remain among the hardest hit by ransomware.
- Despite increased threat levels, many small businesses continue to underspend on security tools, citing cost as a persistent barrier.
- The digital skills gap and lack of dedicated cybersecurity staff continue to undermine small firms’ resilience.
Cyber Security as a Service: Global Market Outlook
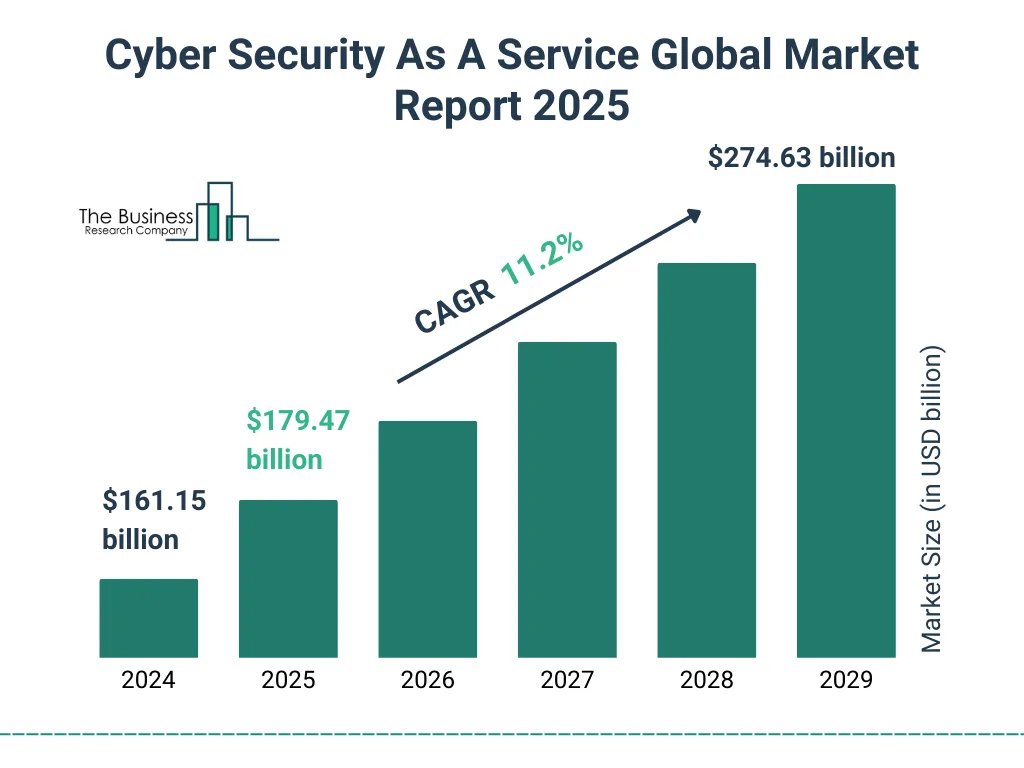
- The global market size for Cyber Security as a Service stood at $161.15 billion in 2024, highlighting its growing strategic importance across industries.
- It is anticipated that the market will rise to $179.47 billion in 2025, driven by expanding adoption of cloud-enabled protection frameworks.
- The sector is predicted to advance at a CAGR of 11.2% through 2029, reflecting sustained investment in modern defense technologies.
- By 2029, the market is projected to achieve a valuation of $274.63 billion, signaling robust long-term momentum.
- This upward trajectory underscores the increasing demand for scalable, cloud-based security solutions across a wide range of industries.
Cyber Attack Prevalence
- Over 46% of small businesses faced a cyberattack in 2025, with incidents every 11 seconds.
- 94% of SMBs experienced at least one cyberattack in 2024.
- 61% of SMBs were targeted by cyberattacks in 2021.
- 37% of ransomware victims had fewer than 100 employees.
- 29% of SMBs with under 25 employees suffered ransomware attacks.
- Two-thirds of SMBs cite budget constraints preventing security upgrades.
- 75% of SMBs with 1-500 employees faced attacks in the past year.
- 51% of SMBs hit by ransomware end up paying the ransom.
Phishing Statistics
- Over 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent globally every day in 2025.
- Phishing remains the most common form of cyberattack on businesses, especially SMBs.
- Experts estimate that over 80% of cyberattacks and data breaches now involve phishing or email fraud.
- Many phishing emails now use AI-generated content, making them harder to detect than ever.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) and phishing remain the top complaint categories in cybercrime reports.
- The surge in remote work and cloud tool adoption during and after the pandemic increased SMB exposure to phishing risks.
- Less than 25% of SMBs feel “very confident” in their ability to identify potential phishing threats.
- Among SMB leaders, around 73% say getting employees to take cybersecurity seriously remains a major challenge.
Ransomware Trends
- In 2025, there was a 12% year-over-year increase in ransomware-related breaches.
- Around 55% of ransomware victims are small businesses with fewer than 100 employees.
- 75% of SMBs say they could not continue operations if hit by a ransomware attack.
- Average recovery cost for a ransomware incident dropped to about 1.53 million dollars in 2025, from 2.73 million dollars in 2024.
- In 2025, 53% of organizations recovered from ransomware within a week, up from 35% in 2024, showing improved response times.
- The share of ransomware attacks involving extortion doubled between 2024 and 2025.
- Ransomware remains a top concern for small businesses, with many considering it their greatest cybersecurity risk.
- Ransomware is often paired with other attack vectors such as phishing or credential theft, increasing danger for underprepared SMBs.
Malware Attacks
- 58% of malware victims are small businesses.
- 92% of malware infections occur via email for SMBs.
- Malware comprises 18% of all cyberattacks targeting small businesses.
- 358% increase in malware infections among SMBs from 2024.
- AI-powered malware attacks are 3x more successful against small businesses.
- Over 30% of SMB malware attacks exploit unpatched vulnerabilities.
- 40% of SMBs are affected by credential stuffing, leading to malware.
- 94% of SMBs faced at least one cyberattack, including malware, in 2024.
Small Business Vulnerability to Cybersecurity Breaches
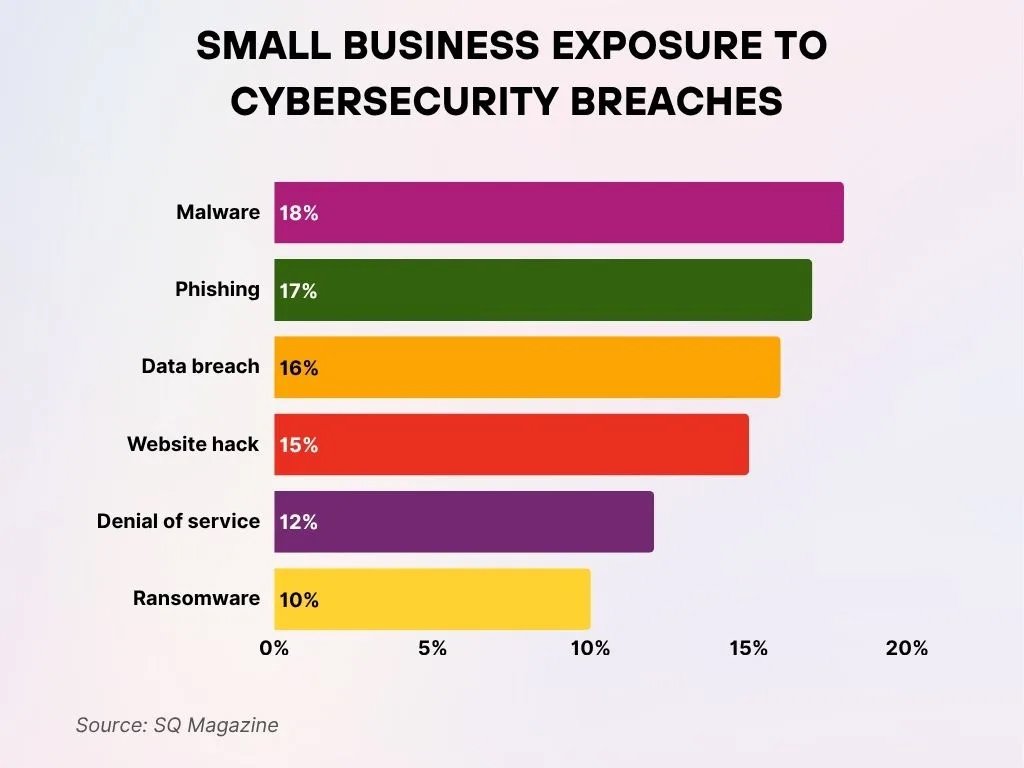
- Malware remains the leading cybersecurity threat, influencing 18% of small businesses while posing major operational risks.
- Phishing attacks follow closely, impacting 17% of small businesses and creating significant security challenges.
- Data breaches continue to trouble 16% of small businesses, emphasizing serious vulnerabilities in data handling practices.
- Website hacks affect 15% of small businesses, underscoring the importance of prioritizing site security.
- Denial of Service (DoS) attacks interrupt normal operations for 12% of small businesses, causing notable disruptions.
- Ransomware incidents strike 10% of small businesses, frequently resulting in costly consequences.
Credential Theft
- Stolen credentials contribute to around 31% of all data breaches in 2025.
- About 30% of small business data breaches stem from weak credential hygiene.
- Nearly 73% of breaches are driven by phishing and credential theft combined.
- Password reuse and credential stuffing remain common root causes for attacks.
- Nearly 83% of SMBs lack cyber liability insurance even after experiencing credential theft incidents.
- Credential theft often precedes secondary attacks such as data exfiltration or ransomware.
- Many small businesses do not conduct regular credential audits or password rotations.
- As attackers adopt automated, AI-powered credential cracking tools, overall risk increases.
Cloud Security Threats
- 80% of small businesses lack a formal cloud security policy.
- 45% of small firms have no endpoint protection on cloud-connected devices.
- 94% of SMBs faced at least one cyberattack in the past year.
- Credential theft incidents spiked by 300% in cloud environments.
- 55% of HTTP malware downloads originate from cloud apps.
- Nearly half of all AWS S3 buckets remain potentially misconfigured.
- 60% of cyber breaches stem from third-party vendors.
- 35% of small businesses fail to regularly back up cloud data.
- AI-assisted malicious emails doubled to 10% of phishing attacks.
Supply Chain Attacks
- Third-party vendor compromises account for 15% of small business breaches in 2025.
- 60% of cyber breaches in SMBs originate from a third-party vendor.
- The average cost of supply chain cyber attacks reaches $4.35 million per incident.
- Supply chain attacks surged to 41 incidents in October 2025, a record high.
- 94% of SMBs experienced at least one cyber attack as of June 2024.
- 30% of breaches involved third-party vendors in the 2025 DBIR, doubled from the prior year.
- 20% of breaches began with unpatched third-party software vulnerabilities in 2025.
- 45% of organizations will face software supply chain attacks by 2025.
- 53% of small businesses do not require vendors to follow cybersecurity standards.
Vulnerability Exploits
- Vulnerability-based exploitation accounted for roughly 20% of all breaches in 2025, a 34% year-over-year increase.
- Many ransomware and data theft attacks originate from unpatched internet-facing systems.
- Only 20% of small businesses conduct regular vulnerability assessments.
- Around 45% lack comprehensive endpoint protection.
- Automated exploit kits have lowered the skill needed for threat actors to target SMBs.
- Many owners are unaware that outdated software significantly increases risk.
- Small firms often delay critical patches due to fear of operational downtime.
- Vulnerability exploitation combined with credential theft is projected to escalate in complexity.
Human Error Impact
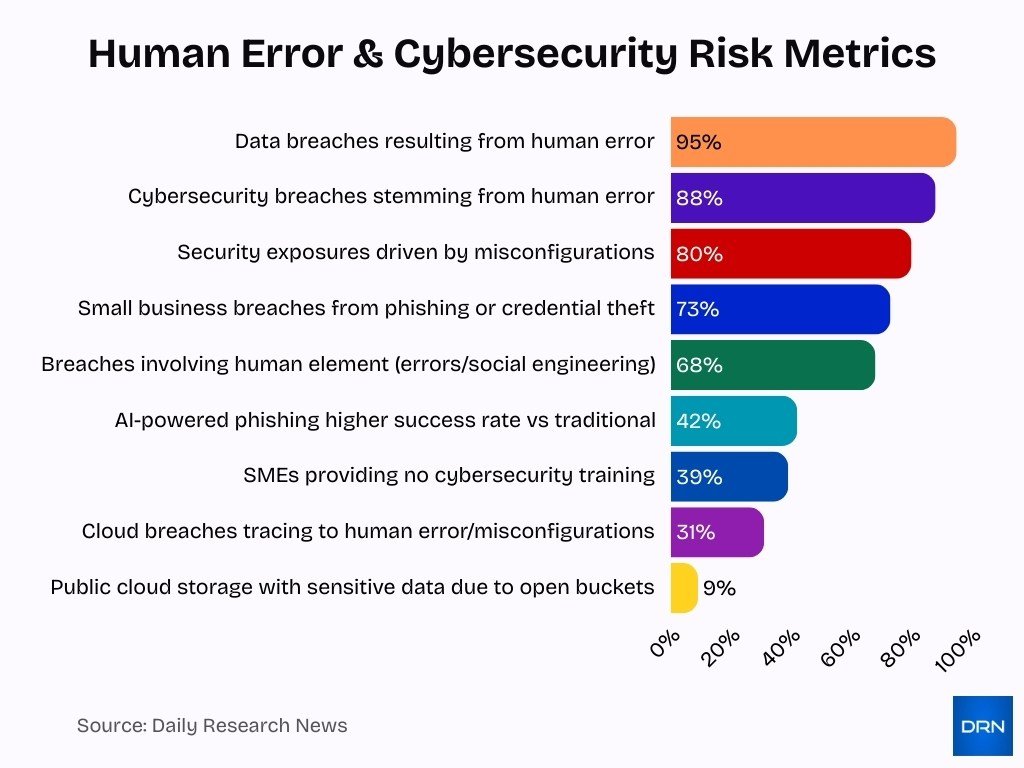
- 88% of cybersecurity breaches stem from human error.
- 95% of all data breaches result from human error.
- 68% of breaches involve the human element, like errors or social engineering.
- 73% of small business breaches come from phishing or credential theft. [ intro]
- 39% of SMEs provide no cybersecurity training to employees.
- 80% of security exposures arise from misconfigurations.
- 31% of cloud breaches trace to human error or misconfigurations.
- 9% of public cloud storage contains sensitive data due to open buckets.
- AI-powered phishing succeeds at a 42% higher rate than traditional scams.
Security Preparedness
- In 2025, 20% of SMBs report having no cybersecurity technology at all.
- About 32% of SMBs say they lack the budget to hire IT or security staff.
- 14% of SMBs do not require MFA for staff access.
- Around 18% do not enforce regular software updates.
- Nearly half of firms with fewer than 50 employees report no dedicated cybersecurity budget.
- Many SMB leaders remain unaware of the true risk facing their business.
- Some small firms rely solely on free or consumer-grade cybersecurity tools.
- Resource gaps leave SMBs unprepared for sophisticated attacks.
Cybersecurity Spending
- Global cybersecurity spending reaches $213 billion in 2025, up from $193 billion in 2024.
- 77% of organizations worldwide anticipate cybersecurity budget increases in 2025.
- Cyber insurance market valued at $15.3 billion in 2024, projected to hit $29 billion by 2027.
- 47% of businesses with under 50 employees have no cybersecurity budget.
- Gartner forecasts 15% growth in cybersecurity spending to $212 billion in 2025.
- Small firms spend 4-10% of IT budgets on cybersecurity, averaging $8,500-$78,000 annually.
- Cybersecurity market projected at $227.59 billion in 2025, growing to $351.92 billion by 2030.
- 93% of executives plan cybersecurity budget increases in the coming year.
- SMBs allocate 5-20% of total IT budgets to cybersecurity defenses.
Insurance Coverage
- Only 17% of small businesses had cyber insurance in 2025.
- Nearly 48% of insured SMBs purchased coverage only after an attack.
- Market penetration among SMEs remains below 10% globally.
- SMEs represent about 30% of total cyber insurance premiums worldwide.
- 78% of IT decision makers say they are “very familiar” with cyber insurance.
- Only 9% of insured firms report dissatisfaction with their coverage.
- Roughly 24% of cyber-insured companies have filed a claim.
- Many small businesses remain uninsured or underinsured, increasing closure risk.
Employee Training Gaps
- Less than25% of SMBs conduct regular cybersecurity training for employees.
- More than 60% of small businesses believe they are too small to be targeted by cybercriminals.
- 63% of small business employees reuse passwords across multiple platforms.
- 37.9% of untrained employees fail phishing tests on average.
- 95% of data breaches in 2024 were tied to human error.
- 90% of cyber incidents involve human error as the primary factor.
- AI-powered phishing attacks surged by 1,265% in the past year.
- Phishing susceptibility drops by over 90% after security awareness training.
- 42% of SMBs provide regular cybersecurity training to employees.
Multi-Factor Authentication Usage
- Only 34% of SMBs with 26–100 employees use MFA, dropping to 27% for those with up to 25 workers.
- 87% of companies with over 10,000 employees employ MFA, compared to 78% for 1,001–10,000 employee firms.
- MFA reduces account compromise risk by 99.9%, blocking nearly all attacks even with stolen passwords.
- 54% of SMBs implement no MFA at all, with just 28% mandating it across their operations.
- 83% of SMEs require MFA for all employee resource access, per 2024 IT professional surveys.
- 99% of organizations face account takeover attempts, with 62% suffering successful breaches despite safeguards.
- The global MFA market reached USD 20.9 billion in 2024, projected to hit USD 70 billion by 2033.
- 67% of companies implemented 2FA/MFA across systems by 2024, up from 56% in 2022.
- Microsoft Authenticator apps outperform SMS-based MFA, cutting compromise risk by over 99.22% overall.
Backup Practices
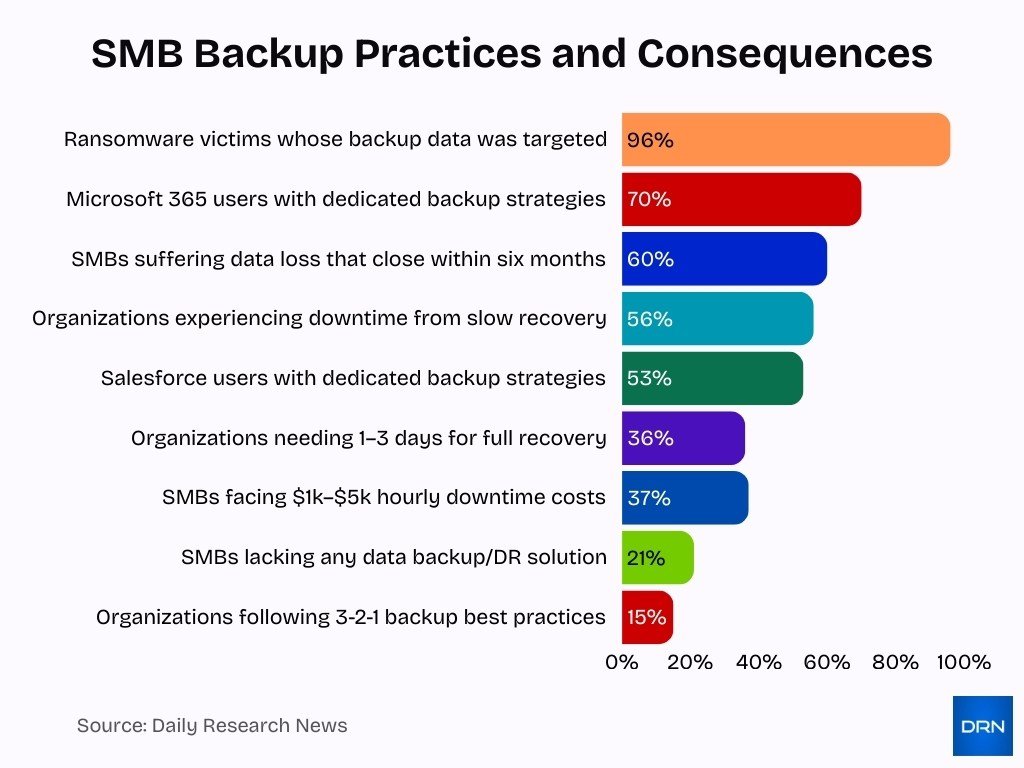
- 60% of SMBs suffering data loss close within six months due to neglected backup practices.
- Only 15% of organizations follow 3-2-1 backup best practices, leaving most SMBs unprotected.
- 96% of ransomware victims report that backup data was targeted, highlighting immutable backup.
- 70% of Microsoft 365 users, but only 53% of Salesforce users have dedicated backup strategies, showing cloud misconceptions.
- 36% of organizations require 1-3 days for full recovery without regular backups, increasing financial losses.
- 56% experience operational downtime from slow recovery, while strong backup habits enable faster restoration.
- 37% of SMBs face $1,000-$5,000 hourly downtime costs, often delaying backup implementation over perceived expense.
- 21% of SMBs lack any data backup or disaster recovery solution entirely.
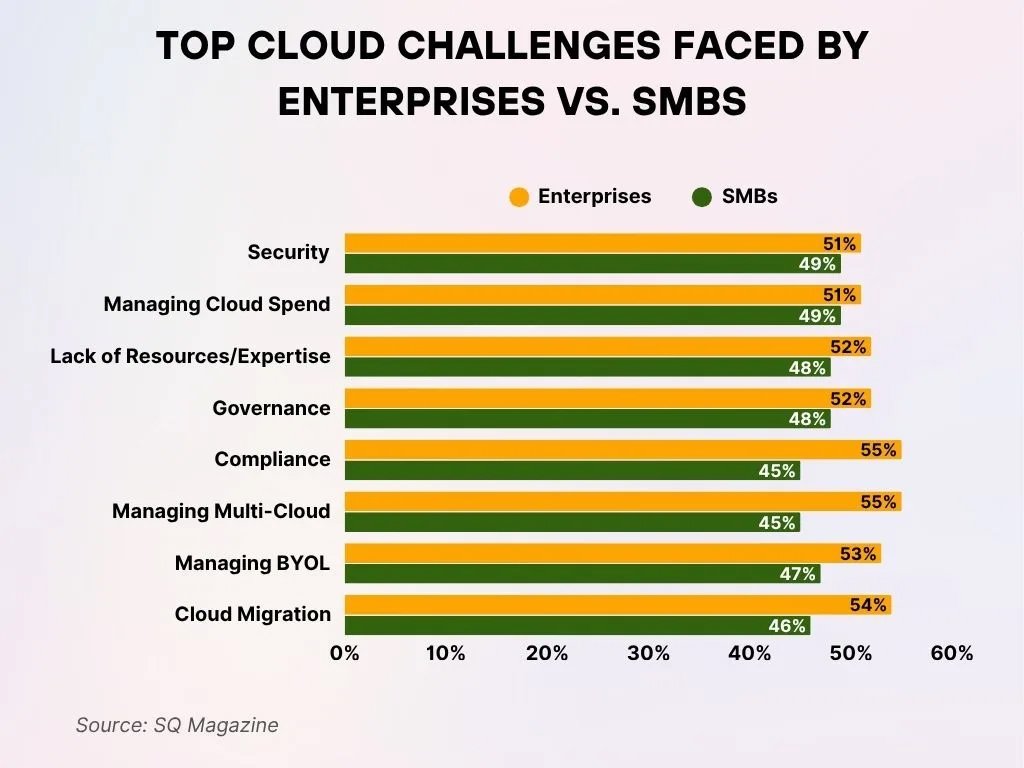
Major Cloud Challenges Encountered by Enterprises and SMBs
- Security stands out as the primary issue, with 51% of enterprises and 49% of SMBs marking it as their foremost cloud challenge.
- Difficulties in managing cloud spend affect both groups similarly, as 51% of enterprises and 49% of SMBs report being evenly divided on this challenge.
- A shortage of resources or expertise is a more significant concern for enterprises (52%) compared with SMBs (48%).
- Governance challenges are mentioned by 52% of enterprises in contrast to 48% of SMBs.
- Compliance demands create greater obstacles for 55% of enterprises, while 45% of SMBs face similar struggles.
- Handling multi-cloud environments poses challenges for 55% of enterprises and 45% of SMBs.
- BYOL (Bring Your Own License) appears to be a more notable concern for 53% of enterprises than for 47% of SMBs.
- Cloud migration continues to be a major hurdle, identified by 54% of enterprises and 46% of SMBs as a top concern.
Business Closure Risks
- 60% of small businesses suffering a major cyberattack close within six months.
- Nearly 1 in 5 SMBs (20%) would shut down after a successful cyberattack.
- Nearly a third of SMBs would close from a cyberattack costing under $10,000.
- 58% of ransomware victims were forced to shut down recovery operations.
- Only 17% of the smallest businesses carry cybersecurity insurance for breach costs.
- 43% of micro-businesses (1-10 employees) suffer successful breach attempts.
- 51% of SMBs hit by ransomware end up paying the ransom.
- Average cyberattack losses for SMBs reach $120,000 per incident.
- 46% of cyber breaches target businesses with under 1,000 employees.
Financial Costs
- The average total cost of a cyberattack on an SMB in 2025 is 254,445 dollars, with some reaching 7 million dollars.
- Smaller firms typically incur recovery costs between 120,000 and 1.24 million dollars.
- Among insured firms, 24% filed a cyber insurance claim.
- About 50% of SMBs report needing at least 24 hours to recover from downtime.
- 55% of U.S. consumers say they’d avoid a company that suffered a breach.
- Downtime, compliance fines, and recovery expenses add to the financial burden.
- A single breach can eliminate years of profit for a small business.
- Limited insurance and weak defenses magnify financial exposure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Approximately 46% of small businesses reported a cyberattack in 2025.
Only about 17% of small businesses have cyber insurance as of 2025.
Roughly 73% of breaches experienced by small businesses in recent data were driven by phishing and credential theft combined.
Around 51% of small businesses have no cybersecurity measures in place at all.
Conclusion
The data paints a clear but alarming picture: small businesses remain especially vulnerable to cyberattacks. Many operate without basic safeguards, such as multi-factor authentication, regular backups, or trained staff, while underinvesting in cybersecurity and often lacking cyber insurance. The financial stakes are high; for many SMBs, a single breach represents more than just a short-term hit, it can threaten long-term viability.
Yet the same statistics point to a path forward. By investing in MFA, regular backups, employee training, and comprehensive cyber insurance, small businesses can dramatically reduce risk and improve resilience. The time to act is now.