Ransomware has evolved from a nuisance to a central cyber threat that disrupts businesses, government agencies, and critical infrastructure. Organizations worldwide are facing higher attack frequency and complex extortion tactics, leading to significant financial and operational damage. From hospitals delaying patient services to manufacturing lines halting production, the real-world impact is visible across sectors. Understanding the latest data on ransomware trends, costs, and growth is essential for defenders and decision-makers. Below, explore the key statistics shaping the ransomware landscape this year.
Editor’s Choice
- Ransomware attacks have surged, with victim postings averaging over 535 per month in 2025.
- Global ransomware damage costs could reach $57 billion annually in 2025.
- Median ransom demands dropped to $1.32 million in 2025.
- Median ransom payments in 2025 were about $1 million, down from $2 million last year.
- Average recovery cost, excluding ransom, is roughly $1.53 million in 2025.
- Ransomware incidents grew year over year, with postings rising from 420 to 535 victims per month.
- Over 3,000 ransomware incidents affected critical sectors in a single year.
Recent Developments
- Ransomware victim postings stabilized at 535 per month in late 2025, up from 420 year over year.
- New victims appeared at 520 to 540 per month by mid-2025, roughly double the early 2024 rates.
- Global ransomware payments dropped from about $1.1 billion in 2023 to $813 million in 2024.
- Median ransom demands in 2025 averaged $1.32 million, lower than 2024 levels.
- Median ransom payments fell to $1 million, about half of last year’s figure.
- Backup recovery rates declined, with only 54% of organizations restoring data via backups.
- Recovery speed improved, with 53% of victims recovering within one week, up from 35% in 2024.
- Only 16% of organizations recovered in one day, compared with 7% last year.
- Extortion-only ransomware attacks doubled to 6% of all incidents in 2025.
- About 40% of security teams reported higher stress and workload after ransomware incidents.
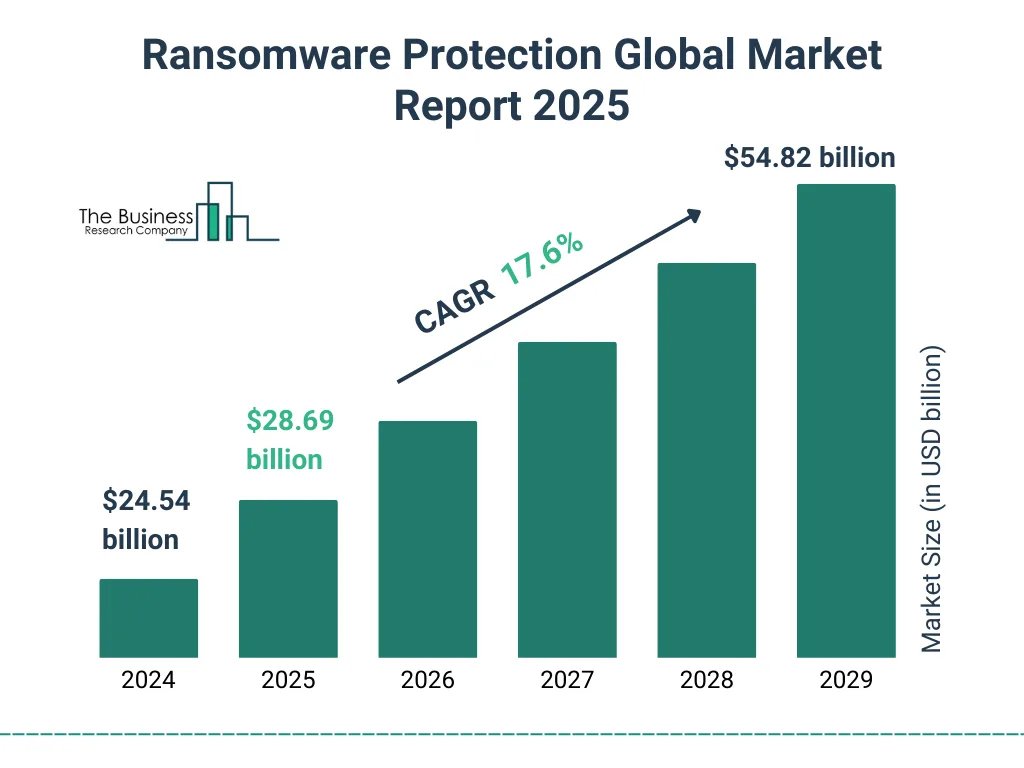
Global Forecast for Ransomware Protection Market Expansion
- The global ransomware protection market is projected to reach $28.69 billion in 2025, highlighting rapid growth driven by escalating cyber threats.
- By 2029, the market is forecast to hit $54.82 billion, more than doubling its size from 2024 as demand for advanced security solutions accelerates.
- This surge reflects the increasing urgency among businesses and governments to invest heavily in cybersecurity solutions to counter rising ransomware risks.
Global trends in ransomware incidence rates
- Ransomware attack frequency has increased by 13% over the past five years.
- Around 4,000 ransomware attacks occur globally every day in 2025.
- The United States accounted for 47% of global ransomware attacks.
- Monthly ransomware incidents averaged 535 victims throughout 2025.
- More than 3,200 ransomware episodes affected critical sectors in a single year.
- Reporting levels vary significantly by country and industry.
- Smaller organizations with fewer than 500 employees suffered over two-thirds of attacks.
- Manufacturing, healthcare, and energy experienced a disproportionate share of incidents.
Share of ransomware in the overall cyberattack landscape
- Ransomware accounted for 3,156 incidents reported to federal authorities in 2024.
- Total cybercrime losses exceeded $16.6 billion, with ransomware among the top threats.
- Ransomware remains one of the most disruptive categories of malware-driven breaches.
- Roughly 27% of malware-related breaches involved ransomware.
- Ransomware ranked among the leading causes of operational disruption complaints.
- In several critical industries, ransomware represented over 50% of reported cyberattacks.
- Attack volumes remain high despite declining overall ransom payments.
- Small and midsize businesses continue to represent a large share of ransomware victims.
Financial impact caused by ransomware attacks
- Global ransomware damage is projected at approximately $57 billion per year in 2025.
- Median ransom demands averaged $1.32 million in 2025.
- Median ransom payments were $1 million, roughly half of 2024 levels.
- Total ransomware payments declined to about $813 million in 2024, a 35% drop.
- Average recovery cost, excluding ransom, reached $1.53 million.
- Businesses lose roughly $53,000 per hour in downtime related to ransomware.
- Non-ransom costs account for about 68% of the total financial impact.
- Total reported cybercrime losses, including ransomware, surpassed $16 billion.
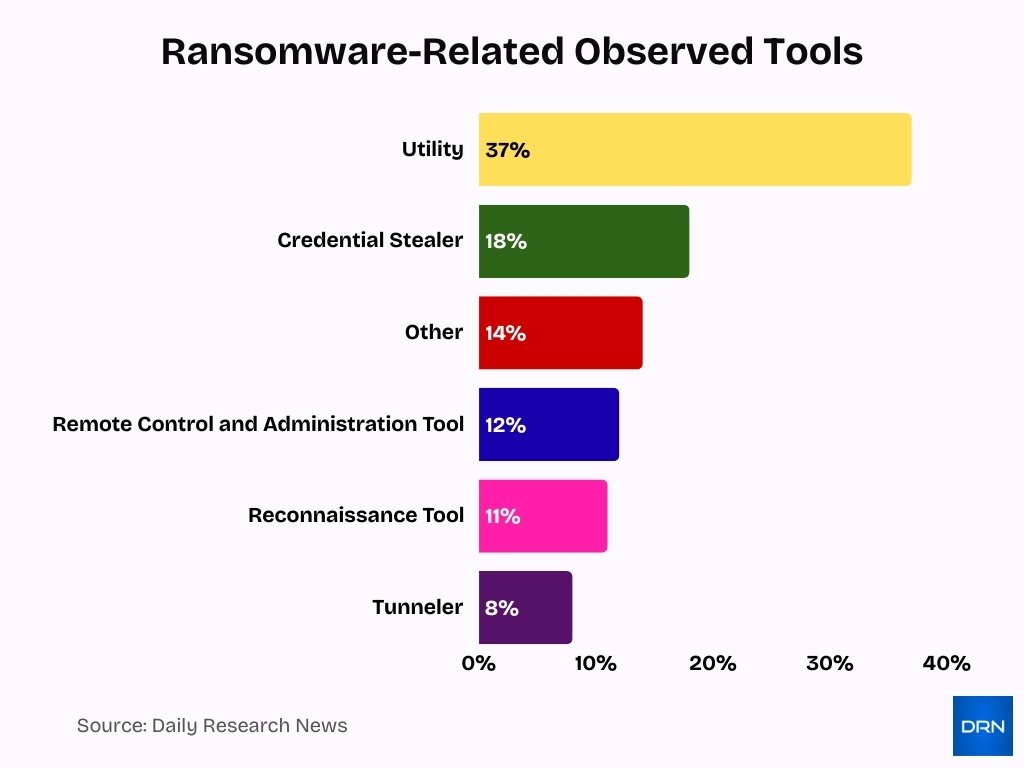
Ransomware-Related Tools Used in Cyberattacks
- Utility tools dominate ransomware operations, accounting for 37% of all observed tools, showing that attackers heavily rely on general-purpose system utilities to execute and manage attacks.
- Credential stealers represent 18% of ransomware-related tools, highlighting a strong focus on password theft and identity compromise to gain deeper network access.
- Other ransomware tools make up 14%, reflecting the diverse and evolving toolkit used by threat actors beyond standard categories.
- Remote control and administration tools account for 12%, enabling attackers to maintain persistent access and manage infected systems remotely.
- Reconnaissance tools comprise 11%, underscoring the importance of network discovery and intelligence gathering before launching full-scale ransomware attacks.
- Tunnelers are used in 8% of cases, helping attackers bypass network defenses and exfiltrate data securely.
Average payment amounts in ransomware demands
- In 2025, the average ransom payment fell to about $1 million, nearly 50% lower than in 2024.
- Only 36% of ransomware victims paid the ransom in 2025.
- Median ransom demands remained high at approximately $1.324 million.
- Some sectors, such as finance, faced average demands approaching $2.3 million.
- Global ransom payments declined as more organizations refused to pay.
- Payment amounts vary significantly by industry, with critical infrastructure facing the highest pressure.
- Some individual ransom payments exceeded historical annual highs.
- Additional costs often include negotiation fees and cryptocurrency transfer expenses.
Downtime and recovery costs after ransomware events
- The average cost to fully recover from ransomware reached $1.53 million in 2025.
- Total ransomware costs can exceed $5 million when downtime and reputation damage are included.
- Organizations experienced an average of 24 or more days of downtime after attacks.
- Financial sector recovery costs averaged about $2.58 million.
- Indirect losses include lost revenue and reduced customer confidence.
- Companies without reliable backups faced significantly higher recovery costs.
- Regulatory reporting and compliance penalties increased total financial exposure.
- Smaller organizations faced disproportionately high economic impact relative to revenue.
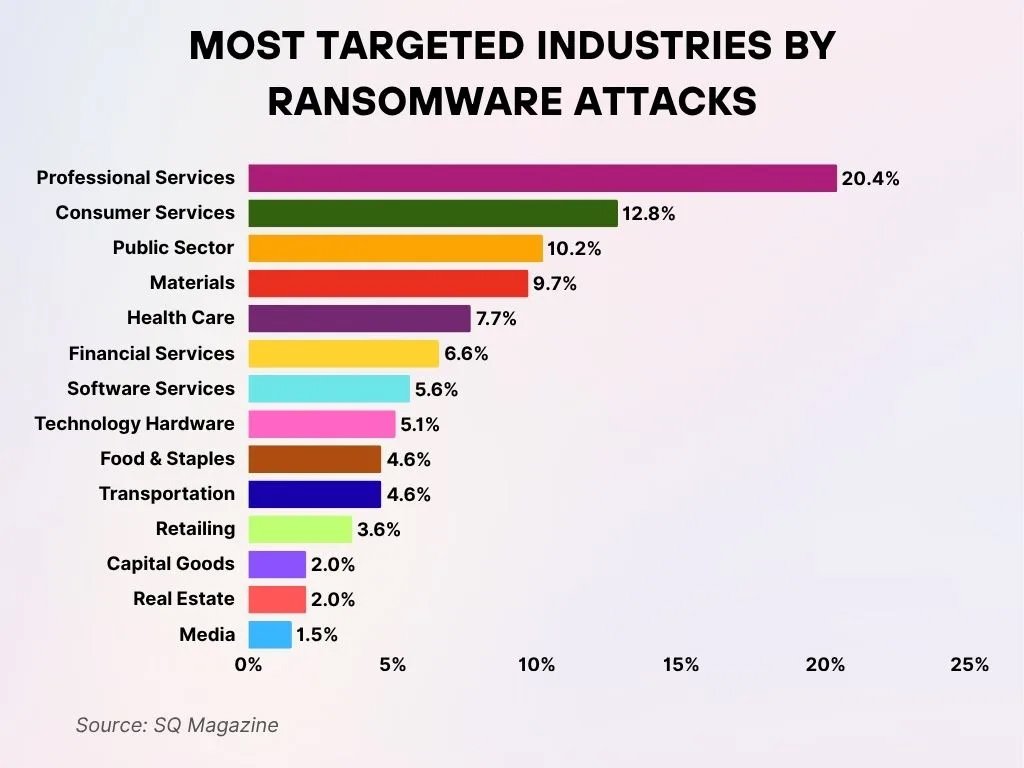
Most Targeted Industries by Ransomware Attacks
- Professional Services endure the largest proportion of ransomware activity, representing 20.4% of total recorded incidents across all sectors.
- Consumer Services hold the second-highest position, being targeted in 12.8% of all documented ransomware cases.
- The Public Sector remains heavily impacted, with 10.2% of ransomware attacks aimed at government and public institutions.
- Materials industries come next, accounting for 9.7% of overall ransomware threats and attack attempts.
- The Health Care sector, considered critical infrastructure, is targeted in 7.7% of reported ransomware incidents.
- Financial Services are affected by 6.6% of ransomware attacks, underscoring the rising risk within data-sensitive industries.
- Software Services comprise 5.6% of ransomware incidents, emphasizing ongoing security risks in the technology development ecosystem.
- Technology Hardware companies face ransomware exposure in 5.1% of all documented attack cases.
- Food & Staples and Transportation sectors are each targeted in 4.6% of ransomware attacks, highlighting weaknesses in essential supply chains and logistics.
- Retailing accounts for 3.6% of ransomware activity, signaling continued exposure across consumer-facing industries.
- Both Capital Goods and Real Estate sectors report 2.0% of total ransomware incidents, reflecting comparatively lower targeting levels.
- Media organizations are the least targeted, comprising only 1.5% of all reported ransomware attack cases.
Healthcare and public service exposure to ransomware
- Healthcare saw 458 ransomware events in 2024, with 293 attacks on providers in the first nine months of 2025.
- Ransomware attacks on U.S. healthcare surged 30% in 2025, targeting vendors and providers.
- State/local governments hit by ransomware dropped to 34% in 2024 from 69% in 2023.
- Healthcare breaches cost avg $7.42M per incident, the highest across industries.
- From 2009–2024, 6,759 healthcare breaches exposed 846M individuals’ data.
- In 2025, healthcare averaged 63.5 breaches monthly, affecting 500+ individuals.
- Healthcare cybersecurity investment to reach $125B from 2020–2025, up 15% yearly.
- Patient data breaches averaged $398–$408 per exposed record, triple the industry norm.
- U.S. saw 257 healthcare ransomware attacks in Q1-Q3 2025, mostly against providers.
- Government entities faced 525 ransomware attacksfrom 2018–2024, costing $1.09B downtime.
Education and government vulnerability to ransomware
- Educational institutions faced 180 ransomware attacks worldwide in Q1-Q3 2025, up 6% from 2024.
- Ransomware attacks in education jumped 23% year-over-year in H1 2025, totaling 130 incidents.
- University of Phoenix ransomware exposed the data of 3.49 million individuals in 2025.
- Government entities saw 276 ransomware attacks globally in Jan-Sep 2025, a 41% surge from 2024.
- Government ransomware incidents rose 65% year-over-year in H1 2025, hitting 208 attacks.
- Schools allocate just 2% of budgets to IT, with 1-2% of IT for cybersecurity.
- 69% of local government ransomware attacks encrypted data, the highest disruption rate.
- 67% of lower education ransomware attacks stopped pre-encryption in 2025.
- 63 confirmed education attacks in Q1-Q3 2025 breached 227,200 records total.
- 43% of local governments paid ransoms after ransomware incidents.
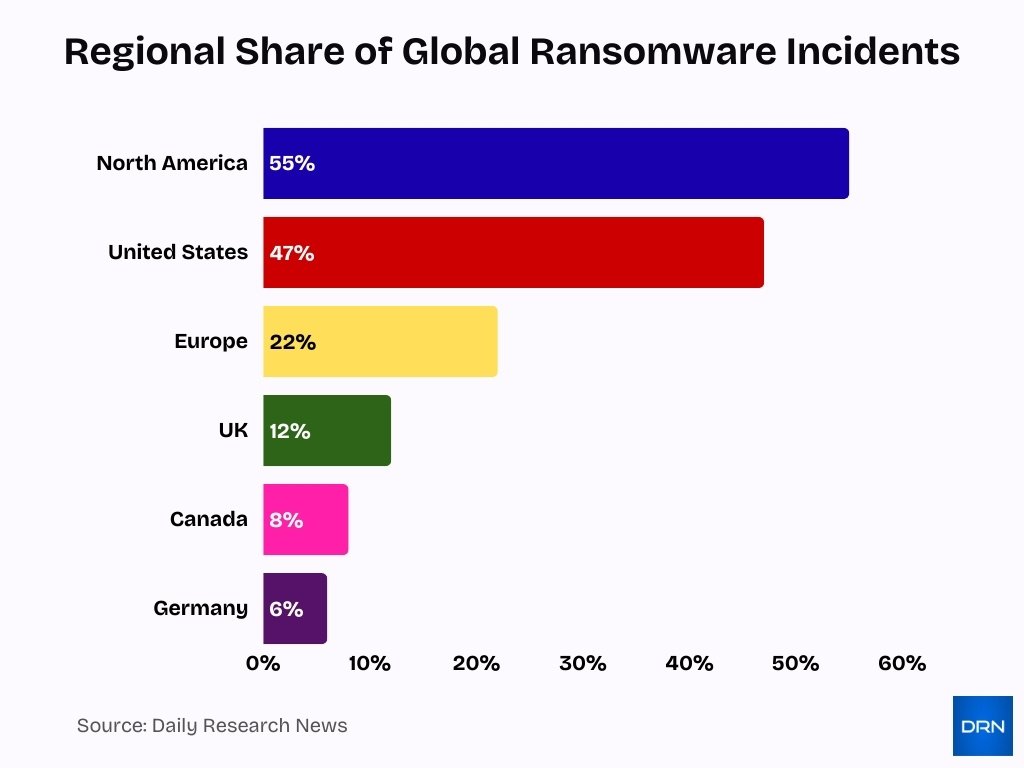
Regional and country-wise distribution of ransomware cases
- The United States dominated with 52% of global ransomware victims in November 2025.
- North America accounted for 55% of disclosed ransomware incidents worldwide.
- Europe represented 22% of global ransomware and extortion victims in 2025.
- Asia-Pacific saw 456 ransomware attacks across the region in 2025.
- The United States held 47% of global ransomware attacks with high recovery rates.
- The UK followed with 12% of attacks and 74% recovery success in 2025.
- Germany experienced 6% of global incidents alongside strong defenses.
- India emerged as APAC’s top target amid 1,586 regional data breaches.
- Canada recorded 8% of attacks with 72% recovery success rate.
Phishing and social engineering as ransomware vectors
- Phishing caused 24% of ransomware attacks in 2025.
- Infostealer malware via phishing drove ransomware growth, with 1 in 5 individuals infected.
- Phishing/social engineering accounted for 18-20% of ransomware initial access vectors.
- 50% of ransomware incidents used stolen credentials via RDP/VPN from phishing.
- Security awareness training reduced phishing susceptibility by 86% after 12 months.
- 90 days of awareness training cut phishing risk by over 40%.
- MFA countered phishing credential theft, blocking 90% of ransomware via stolen logins.
- Advanced email filtering blocked 81% of phishing emails in mid-2025.
- Phishing enabled double extortion in 25% of ransomware breaches.
RDP, VPN, and Exposed Services Exploited in Ransomware
- RDP abuse featured in 90% of ransomware breaches analyzed in 2023.
- VPN vulnerabilities accounted for 28.7% of all ransomware attacks in Q3 2024.
- Remote access tools served as the initial entry in 80% of ransomware attacks in 2024.
- Compromised credentials drove 50% of ransomware incidents in Q3 2025.
- Brute-force attacks on RDP surged to 100,000 daily incidents by mid-2020.
- Unpatched RDP enabled lateral movement in 65% of remote service attacks.
- 98.6% of organizations had cloud misconfigurations risking ransomware deployment.
- Poor patch management made organizations 7x more likely to suffer ransomware.
- Zero-trust implementations reduced ransomware incidents by 62%.
Prevalence of Known Families and Strains in Ransomware
- Prominent ransomware families in 2025 included Clop, Akira, and RansomHub.
- Analysts observed more than 30 new ransomware groups emerging.
- Many families shifted toward data theft and extortion-centric models.
- Certain strains generated hundreds of millions in cryptocurrency extortion.
- Modular ransomware code complicated attribution and tracking.
- RaaS-linked families diversified tactics across regions.
- Leak sites tracked dozens of active ransomware groups weekly.
- Some regions experienced localized ransomware strains.
Top Ransomware Groups by Leak Site Activity
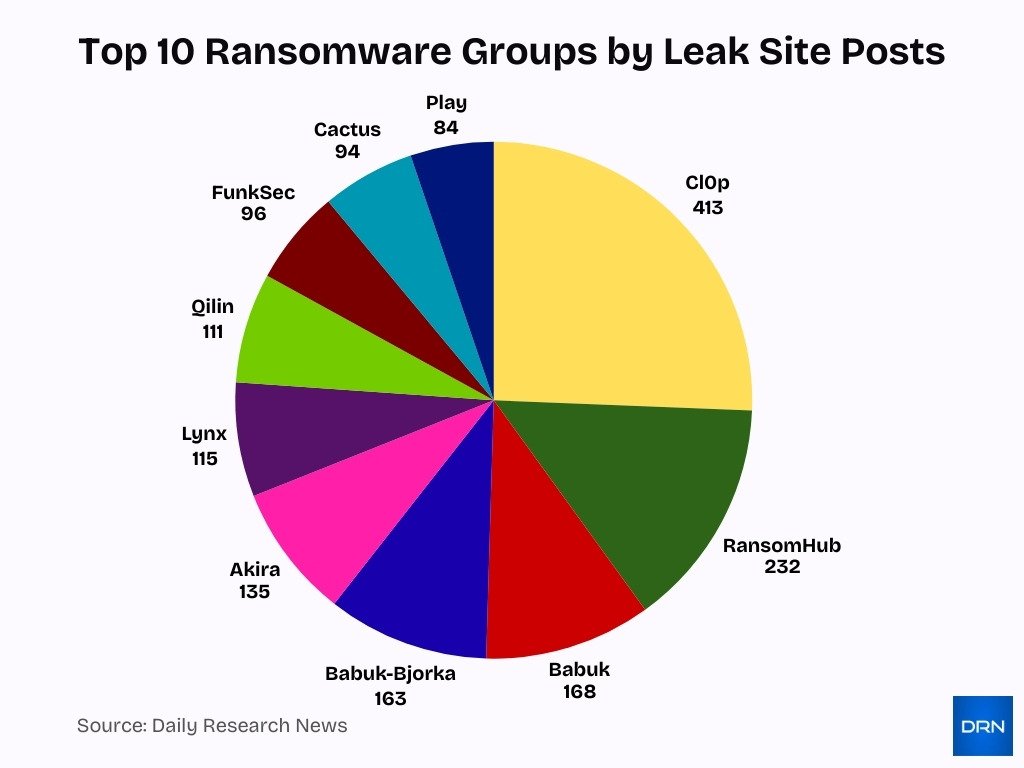
- Cl0p dominates ransomware leak activity with 413 leak site posts, making it the most active ransomware group between January 1 and March 31, 2025.
- RansomHub ranks second, recording 232 leak site posts, highlighting its strong and sustained operational presence during Q1 2025.
- Babuk remains a major threat actor with 168 posts, underscoring its continued influence in the ransomware ecosystem.
- Babuk-Bjorka closely follows with 163 leak disclosures, reflecting high posting frequency despite limited new leak activity.
- Akira reports 135 leak site posts, confirming its position among the top-tier ransomware operators in early 2025.
- Lynx accounts for 115 leak postings, signaling growing operational momentum in ransomware campaigns.
- Qilin records 111 posts, reinforcing its role as a consistent mid-tier ransomware threat.
- FunkSec contributes 96 leak site entries, showing moderate but persistent activity across the quarter.
- Cactus logs 94 posts, maintaining a steady presence among active ransomware groups.
- Play rounds out the top ten with 84 leak site posts, reflecting lower but notable attack visibility in Q1 2025.
Rise of Ransomware-as-a-Service Models
- RaaS enabled affiliates to claim up to 85% of ransom proceeds in groups like Qilin and GLOBAL GROUP.
- Q3 2025 recorded 14 new ransomware groups, totaling 45 newly observed actors in 2025.The
- The RaaS model expanded active threat actors to 85 distinct ransomware groups in Q3 2025.
- Extortion-only ransomware attacks doubled to 6% of incidents in 2025.
- Qilin executed 81 attacks in one month by June 2025, up 47.3% via RaaS affiliates.
- RaaS lowered barriers, boosting ransomware victims to 2,063 in Q1 2025, a record high.
- Double extortion tactics reached 70% usage, generating 340% higher payments.
- RaaS affiliates grew operations with profit splits like 80–90% for BlackCat partners.
- Akira ransomware hit 213 victims in Q1 2025, surging 261% year-over-year.
Double Extortion Tactics Linked to Ransomware Breaches
- Double extortion dominated ransomware with 70% usage rate in 2025.
- Data exfiltration preceded encryption in 89% of LockBit attacks.
- Attackers shifted to double extortion from 45% encryption-only in 2022 to 15% in 2024.
- Triple extortion tactics rose to 32% usage with 78% success rate.
- 85 active data leak sites drove double-extortion expansion in Q3 2025.
- 47 ransomware groups used fewer than 10 victims each in double-extortion campaigns.
- Double extortion generated 340% higher payments than encryption-only attacks.
- Backup compromise hit 66% in healthcare double-extortion incidents.
- Stolen data from 520-540 monthly victims provided ongoing leverage post-recovery.
Detection and Response Benchmarks for Ransomware Events
- Organizations with intact backups recovered operations within one week in 46% of ransomware incidents.
- 67% of victims with compromised backups paid ransoms, compared to 36% with secure backups.
- EDR tools blocked 98% of ransomware attacks before encryption began.
- XDR solutions reduced full threat correlation time to 20 minutes from EDR’s 1 hour.
- Tabletop exercises cut ransomware response times by 80% in client organizations.
- Automated playbooks shortened median containment time versus manual response.
- 57% of incidents were detected by external parties, highlighting internal monitoring gaps.
- Network segmentation limited lateral movement in ransomware attacks across segments.
- Patch management and segmentation reduced successful backup compromises to 30% in tech sectors.
Ransomware Impact Across Businesses by Employee Size
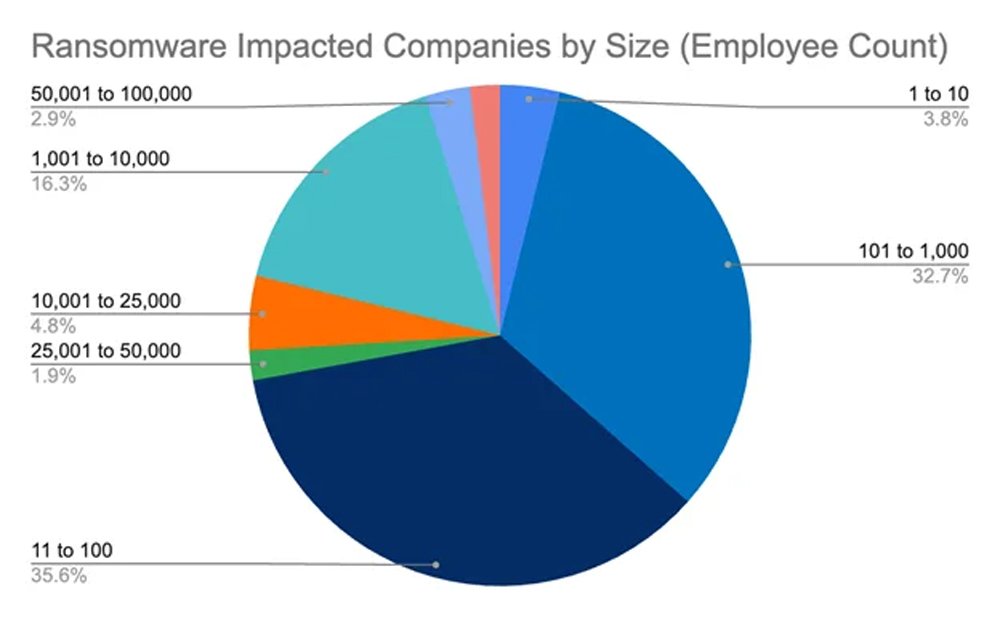
- Organizations with 11 to 100 employees account for the largest share, representing 35.6% of all ransomware incidents.
- Companies employing 101 to 1,000 staff members follow closely, making up 32.7% of total ransomware victims.
- Mid-sized enterprises with 1,001 to 10,000 employees comprise 16.3% of affected organizations.
- Larger firms employing 10,001 to 25,000 people are targeted far less often, accounting for just 4.8% of all attacks.
- Very small businesses with 1 to 10 employees still represent a notable 3.8% of recorded ransomware cases.
- Major organizations with 50,001 to 100,000 employees make up 2.9% of ransomware-impacted entities.
- Enterprises employing 25,001 to 50,000 people account for only 1.9% of the overall ransomware attack total.
Law Enforcement Responses to Ransomware Operations
- International operations led to 574 arrests in Operation Sentinel across 19 countries, targeting ransomware.
- Authorities decryptedsix ransomware variants and recovered 30 TB of encrypted data in Ghana.
- Law enforcement crackdowns reduced ransomware payments by 35% to $814 million in 2024.
- Operation Cronos seizedLockBit infrastructure, 28 servers, and froze 200 cryptocurrency accounts.
- Operation Serengeti 2.0 dismantled 11,432 malicious infrastructures linked to 87,858 victims.
- Cross-border collaboration recovered$3 million in cybercrime proceeds and took down 6,000 malicious links.
- Australia mandated ransomware payment reporting within 72 hours for businesses over $3 million.
- Benin authorities made106 arrests and shut down 4,318 scam-linked social media accounts.**
- Interpol’s Operation Red Card apprehended306 suspects and seized 1,842 devices.
Forecasts and Future Projections Involving Ransomware
- Ransomware victims are expected to surge to over 7,000 publicly named by the end of 2026, a 40% increase from 2024.
- AI-powered ransomware attacks will fuel campaigns through sophisticated vishing and social engineering in 2026.
- RaaS platforms now operate like corporate franchises, enabling low-skill attackers with AI-enhanced kits.
- SMBs remain prime targets in 2026 due to weaker defenses and high operational disruption potential.
- Supply chain attacks surged to a record 41 incidents in October 2025, amplifying ransomware spread.
- Ransom payment rates dropped to roughly one in four victims in 2025, pressured by law enforcement.
- Ransomware protection market projected to reach $15 billion by 2026, driven by security automation needs.
- Attack attempts forecasted at 11,000 per day globally by late 2025, escalating into 2026.
- Cyber resilience investments will grow as 54% see ransomware as the top threat for 2026.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Globally, confirmed ransomware incidents rose by 34% in the first three quarters of 2025 compared with the same period in 2024.
In 2025, only about 30% of ransomware victims paid the ransom, reflecting a sharp decline in payment rates.
The global impact of ransomware is projected to reach approximately $57 billion in 2025, which equates to roughly $156 million per day.
Ransomware attacks on U.S. targets surged 149% year‑over‑year in the first five weeks of 2025, rising from 152 to 378 attacks.
Conclusion
Ransomware reflects a mature and adaptive threat landscape where attackers refine extortion strategies while defenders improve resilience. Although overall ransom payments have declined and law enforcement actions have disrupted major groups, ransomware continues to affect organizations across all sectors. Remote access vulnerabilities, data theft, and multi-layered extortion tactics remain persistent challenges. Looking ahead, sustained investment in preparedness, detection, and international cooperation will be critical to limiting ransomware’s impact as the threat continues to evolve.