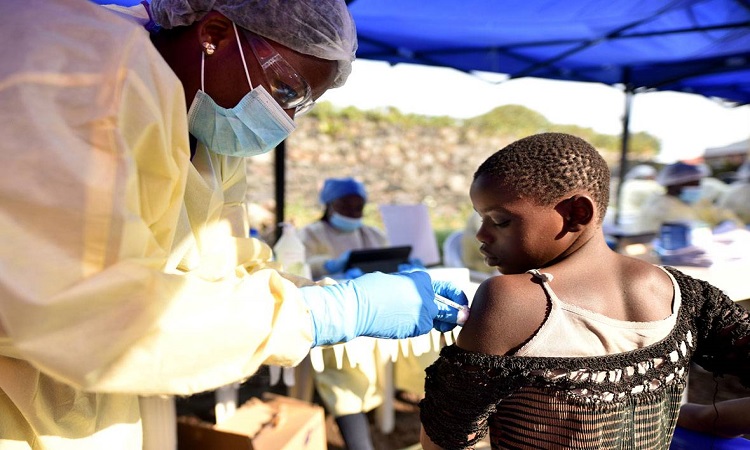
The World Health Organization (WHO) has announced the Public Health Emergency in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) affected by the Ebola risk. According to the WHO, international support is needed to deal with this disease. Since the outbreak of Ebola, about 1600 people have lost their lives so far.
This week the first case of Ebola has been found in a city of Goma, where millions of people living there are in millions. According to the WH report, four years ago, the Emergency has been implemented due to the death of Ebola. This includes West African Emergency, in which about 11,000 people died.
According to the report, this is the second-largest outbreak of Ebola. Most people have been affected since 2018 in the two major provinces of the Democratic Republic of Congo, North Kivu, and Ituri. More than 2,500 cases of Ebola-related cases have been reported, two-thirds of whom have lost their lives. That is, more than 1600 people have died.
Around 1,000 cases of Ebola were reported in 224 days of the beginning, but in the following 71 days, the number of these cases increased to 2000. About 12 new cases of Ebola are being seen in these areas daily.
What is Ebola-
According to WHO, Ebola is a type of viral disease. The symptoms are sudden fever, weakness, muscular pain, and sore throat. These symptoms are the beginning of the disease. The next step is vomiting, diarrhea, and in some cases, internal and external bleeding. In humans, its infection occurs due to direct contact with infected animals, such as chimpanzees, bats, and deer.